Now Reading: Hyderabad Traffic Grinds to Halt Amid Heavy Rains
-
01
Hyderabad Traffic Grinds to Halt Amid Heavy Rains
Hyderabad Traffic Grinds to Halt Amid Heavy Rains

Fast Summary:
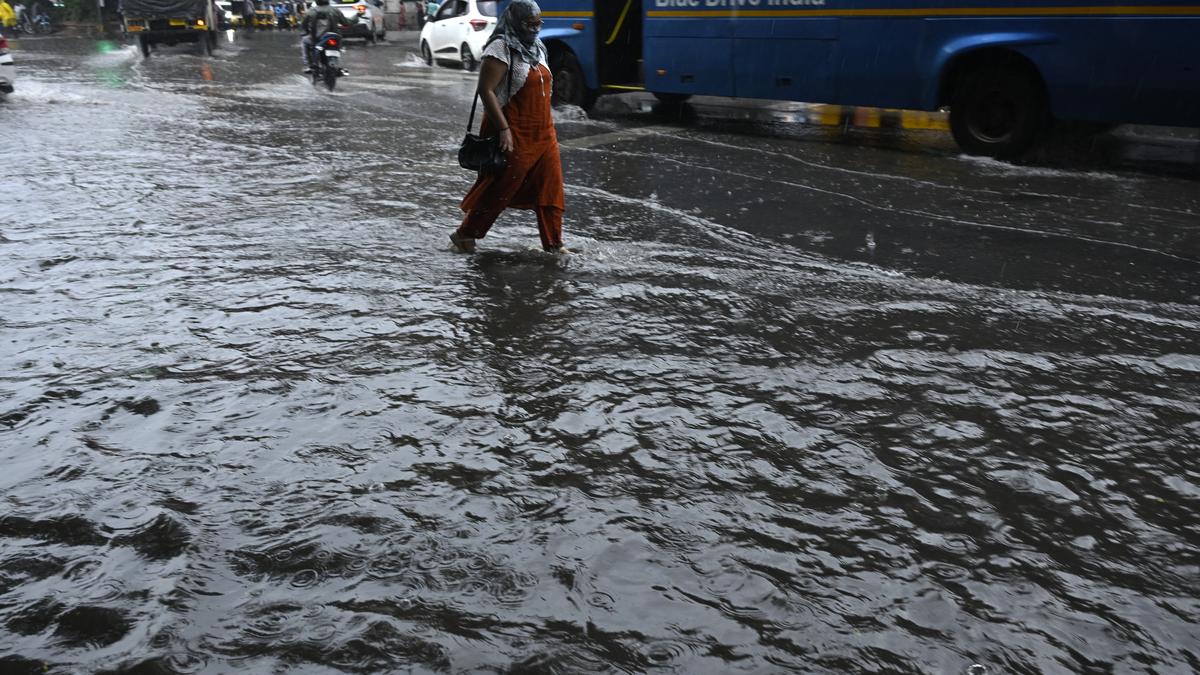
- Heavy rains in Hyderabad on Monday evening caused severe traffic disruptions due to waterlogged roads, particularly in the city’s West and Central zones.
- Key stretches like Raidurg metro station to Cyber towers, Ikea junction to Yashoda hospital, and JNTU to kukatpally Y-junction experienced major gridlocks.
- Inundation near underpasses and flyovers compounded the chaos, with notable trouble spots including Himayatsagar on the Outer ring Road (ORR), Bachupally U-turns, Rajiv Gruhakalpa underpass, Erragadda FCI Road, Jeedimetla pipeline road, and others.
- traffic crawled along critical link roads in IT corridors; some commuters reported taking over 45 minutes for less than 4 km of travel.
- Central areas such as Ameerpet-Panjagutta stretch, Jubilee Hills checkpost-Road No. 36 corridor, Shaikpet nala flyover among others were severely impacted by flooding.
- Social media posts highlighted frustration from commuters stuck in prolonged traffic jams due to standing water; live updates were shared by authorities for assistance.
- The Hyderabad Disaster Response Agency (HYDRAA) partnered with GHMC and deployed teams for flood clearance while police regulated traffic flow at chokepoints.
Indian Opinion analysis:
The heavy rainfall underscored ongoing urban challenges that Indian cities like Hyderabad face as they expand rapidly without proportionate infrastructure improvements. While advisories from Cyberabad Police facilitated staggered employee movements during peak hours, evident bottlenecks across low-lying areas indicated drainage inadequacies common to metropolitan regions during monsoons. real-time coordination between civic bodies (GHMC) and disaster response agencies was responsive but reactive in nature – reflective of larger urban planning imperatives needed nationwide around stormwater management systems.
For India’s IT hubs where productivity depends heavily on mobility within tech corridors like those affected here (Raidurg-Cyber Towers stretch), resilient solutions could include enhanced drainage projects alongside adaptive technologies capable of monitoring rainfall impacts dynamically while preemptively redirecting routes similar future scenarios.
Read more: https://www.thehindu.com/theme/images/th-online/1x1_spacer.png