Now Reading: Restoring a Rembrandt: The Art and Science Behind the Masterpiece
-
01
Restoring a Rembrandt: The Art and Science Behind the Masterpiece
Restoring a Rembrandt: The Art and Science Behind the Masterpiece

Quick Summary
- Art conservation combines archaeology,chemistry,material sciences,imaging technologies,and history to restore timeless works affected by aging.
- Scientific approaches include material analysis for understanding art deterioration and construction. Destructive methods (e.g., paint sample removal) are declining as non-invasive techniques improve.
- Technologies adapted from other fields, like CT scanning and hyperspectral imaging, help analyze artwork at microscopic levels without damage.
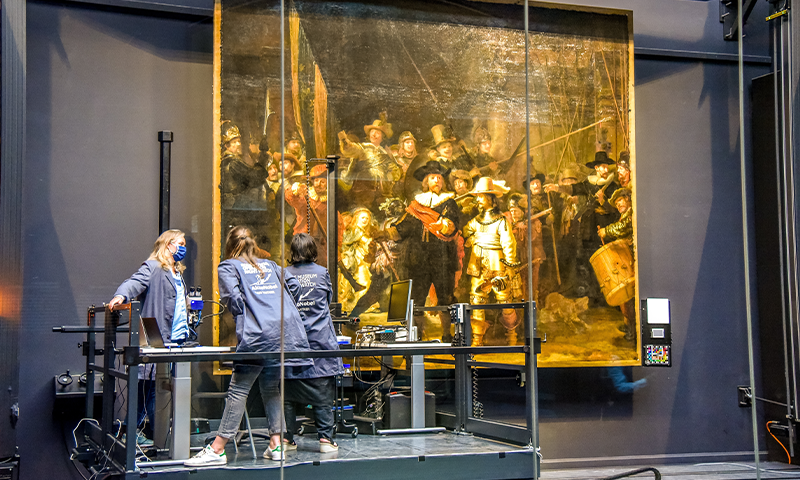
- A notable project is “Operation Night Watch” at Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam to restore Rembrandt’s iconic painting using advanced techniques such as hyperspectral imaging, XRF (X-ray fluorescence), and XRD mapping. Methods include removing brittle varnish and applying new layers to rejuvenate colors.
- AI has potential in identifying past restoration patterns and suggesting suitable methods by sorting vast amounts of data across global systems.
- The field increasingly emphasizes collaborative efforts with scientists, Indigenous experts, affected communities, museum professionals, aligning preservation processes with cultural values rather than a purely scientific framework.
- Customary practices like using neem leaves for textile conservation-originating from India-are being reintroduced into contemporary restoration strategies.
Indian Opinion Analysis
art conservation represents an evolving intersection of science and cultural heritage preservation. While highly technological advancements promise precision in restoring notable artworks globally-including notable influences like India’s neem-tree-based traditional methods-the underlying shifts toward inclusivity have broader implications. India’s abundant cultural artifacts stand to benefit through such modern collaborations that integrate local knowledge systems into global practices.
The story highlights how accessible technologies can democratize art preservation beyond traditionally wealthy institutions or Western-centric frameworks. for India’s museums or heritage sites often limited by financial constraints or expertise shortages, adopting interdisciplinary approaches could ensure protection of its rich artistic legacy while embedding community-centric perspectives.
Investments into training personnel in the use of non-invasive techniques or AI-enhanced protocols could also foster international partnerships-expanding Indian innovations like pest-resistant measures rooted in neem usage across diverse regions facing similar challenges.
Beyond technical aspects lies a deeper philosophical question: should aging signs be conserved as integral elements representing time’s passage? Such discourse aligns well with India’s age-old traditions valuing natural decay while balancing aesthetic integrity-a dimension crucial to bridging art science with cultural essence globally.