Now Reading: Plug-and-Play System Boosts Scalable Production of Secondary Metabolites in Streptomyces
-
01
Plug-and-Play System Boosts Scalable Production of Secondary Metabolites in Streptomyces
Plug-and-Play System Boosts Scalable Production of Secondary Metabolites in Streptomyces
Swift Summary
- The article discusses findings related to the bacterial genus Streptomyces, renowned for producing antibiotics and pharmaceuticals.
- Research highlights how actinomycetes, including Streptomyces, are being studied for sustainable antibiotic advancement and enhanced pharmaceutical production.
- Numerous genomics-based and microbial engineering strategies are outlined, aiming for efficient biosynthesis of products like polyketides.
- Researchers explore mechanisms such as genome shuffling and precursor coordination to optimize yield while addressing challenges like physiological limitations.
- emerging biotechnological approaches focus on modifying cellular behaviors or reprogramming genetic switches within Streptomyces.
Indian opinion Analysis
The research underscores India’s opportunities in biotechnology, given its strong pharmaceutical industry. Actinomycete-based advancements can push innovation in drug manufacturing, aiding global markets while ensuring access domestically. With R&D investment,India could leverage these findings to align with sustainability goals-essential as antibiotic resistance grows globally. Collaboration between educational institutions, public sectors, and biotech firms will be critical to adopting such bioengineering methodologies effectively.
Read more: Nature Articlequick Summary
- This article provides references to critically important research in the field of microbiology, specifically focusing on quorum sensing and antibiotic production in the Streptomyces genus.
- Studies referenced cover developments like bacterial hormone-regulated antibiotic production, signaling systems influencing biosynthesis, and mechanisms involving quorum-sensing circuits.
- Research spans over two decades, showcasing advances from genome mining techniques in 2008 (Corre et al.) to studies on synchronized bacterial lysis for drug delivery in 2016 (Din et al.).
- Key publications include contributions from renowned journals such as Nature, Nat. Commun., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci., among others, highlighting interdisciplinary methods combining synthetic biology and molecular engineering.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India has substantial potential to leverage research like this due to its growing pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry. The detailed studies cited emphasize pathways for enhancing antibiotic production and broader microbial engineering possibilities-areas where India could invest further for innovation leadership globally.With a rich biodiversity of microbes native to India’s habitat, there is an opportunity to expand national contributions toward developing new antibiotic classes or sustainable bioengineering applications based on insights from global research trends mentioned here.Such advancements would align with India’s mission for Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance), especially by reducing dependency on imported antibiotics or creating novel treatments addressing resistant strains prevalent domestically.
For more details: PubMed referenceQuick Summary:
- The news article discusses various advancements in microbiology research, focusing on regulatory elements and gene expression systems related to streptomyces, a genus of bacteria.
- Key studies referenced include the engineering of strong promoters,novel inducible expression systems,ultrasensitive transcription factors,genetic circuits,and biosynthesis regulatory genes.
- Model studies explored genes like aveR for avermectin biosynthesis in Streptomyces avermitilis, as well as overexpression impacts on ABC transporter proteins boosting microbial natural products.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The highlighted microbiological research reflects India’s potential role in leveraging such global advancements for industries such as pharmaceuticals and agriculture. With Streptomyces being pivotal for antibiotic production (e.g.,avermectin),innovations in genetic regulation could enrich India’s bioeconomy while addressing challenges like drug resistance or crop protection through tailored microbial solutions. Embracing precision biology tools shared globally might position Indian researchers favorably within biotech collaborations while enhancing sustainable development goals aligned with domestic industry priorities.Read more: PubMed Central Reference | CAS Reference | Google ScholarQuick Summary:
- A team of researchers,primarily from several Chinese institutions,conducted a study focusing on advanced synthetic biology techniques for improving molecular production in Streptomyces bacteria.
- The research leveraged genetic modifications and novel gene circuits to enhance the biosynthesis of non-ribosomal peptides (NRPs) and other compounds.
- Key techniques included CRISPR applications, metabolic engineering, allosteric transcription factors for sensing molecules, and tailored promoters for bacterial systems.
- Financial support for this study came from multiple chinese programs including the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Agricultural Science Promotion efforts.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research exemplifies significant advancements in synthetic biology with implications not onyl globally but also potentially beneficial to India’s biotechnology sector, particularly pharmaceutical R&D. Enhanced Streptomyces-based molecule production could lead to streamlined antibiotic synthesis or development of innovative therapeutics-an area where India is actively involved.Given India’s strong focus on bio-manufacturing and healthcare innovation, similar approaches might be leveraged locally by Indian academia or industry players working towards self-reliance in drug discovery or agricultural bioproduction technologies. While this work comes under China’s purview today, collaboration could foster mutual growth given shared long-term goals in life sciences advancement.
Read More: [External Source Link]
Quick Summary:
- W.W., B.Y., and Z.L. have filed provisional patents related to quorum sensing-based regulatory systems with the China National Intellectual Property management.
- The peer review for this work involved contributions from researchers like Shuguang Zhang and anonymous reviewers.
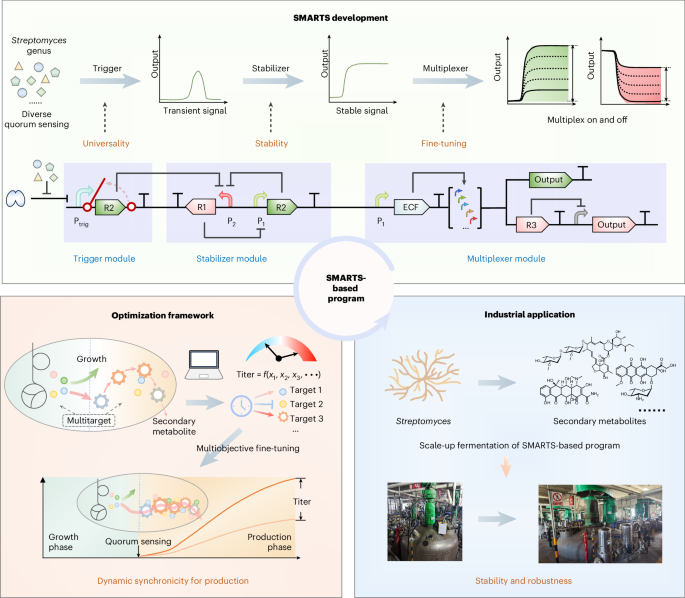
- A system called SMARTS (Synthetic Modular Artificial Regulatory Systems) has been developed, integrating modules for trigger, stabilizer, and multiplexer functions. It converts transient quorum sensing signals to stable outputs in Streptomyces strains.
- Advanced genetic engineering methods were used for optimizing secondary metabolite production like epidoxorubicin and baiweimectin through modular artificial control mechanisms.
- Tests on baiweimectin demonstrated efficacy against soil parasitic nematodes, showing competitive performance compared to commercial alternatives.
Indian Opinion analysis:
This development represents a significant breakthrough in microbial biotechnology by leveraging quorum sensing mechanisms to enhance secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces species. India being a key player in the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector could benefit from adopting such advanced techniques to streamline drug synthesis processes. Innovations like SMARTS have the potential to accelerate drug discovery while ensuring scalability and efficiency in production, which can substantially strengthen India’s position as a global pharmaceutical hub. Furthermore, optimization of compounds like epidoxorubicin aligns well with India’s focus on combating parasitic diseases endemic to tropical regions.
For details: Read MoreQuick Summary:
- The article discusses scalable methods for secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces, leveraging a plug-and-play system.
- This system, based on modular synthetic biology approaches, offers potential advancements in pharmaceutical and industrial applications by streamlining the production of bioactive compounds.
- The research emphasizes the adaptability and efficiency of this platform in enhancing microbial biosynthesis with broader impacts on biotechnology.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The innovation outlined offers significant implications for India’s biotechnology sector, particularly as the country seeks to strengthen its pharmaceutical manufacturing capacity and R&D capabilities. Microbial biosynthesis is crucial for producing cost-effective drugs and industrial materials, which aligns well with India’s focus on affordable healthcare solutions. Further adoption of such technologies could bolster India’s ability to scale up sustainable drug production while also supporting its push towards green technology development.Collaboration between Indian biotech firms and global innovators may foster fruitful results from advancements like these.