Now Reading: 2024 Breaks Record for Extreme Heat and Humidity Days
1
-
01
2024 Breaks Record for Extreme Heat and Humidity Days
2024 Breaks Record for Extreme Heat and Humidity Days

Rapid Summary
- The planet experienced a record number of dangerously hot and humid days in 2024 due to climate change.
- Global average high humid heat days over land exceeded the 1991-2020 average by 35.6 days, surpassing the previous record set in 2023 by 9.5 days.
- Climate change is leading to higher global humidity levels, making conditions hazardous for human health by impeding the body’s ability to cool itself through sweating.
- Regions including the Middle East, South-East Asia, and eastern China recorded “wet bulb temperatures” exceeding dangerous thresholds (29°C or higher). These conditions are deadly when prolonged exposure occurs.
- Wet bulb temperature is used as a metric to assess combined heat and humidity effects on human health – with survivability limits traditionally considered at 35°C but recent research suggesting fatal risks even at around 31°C or slightly lower.
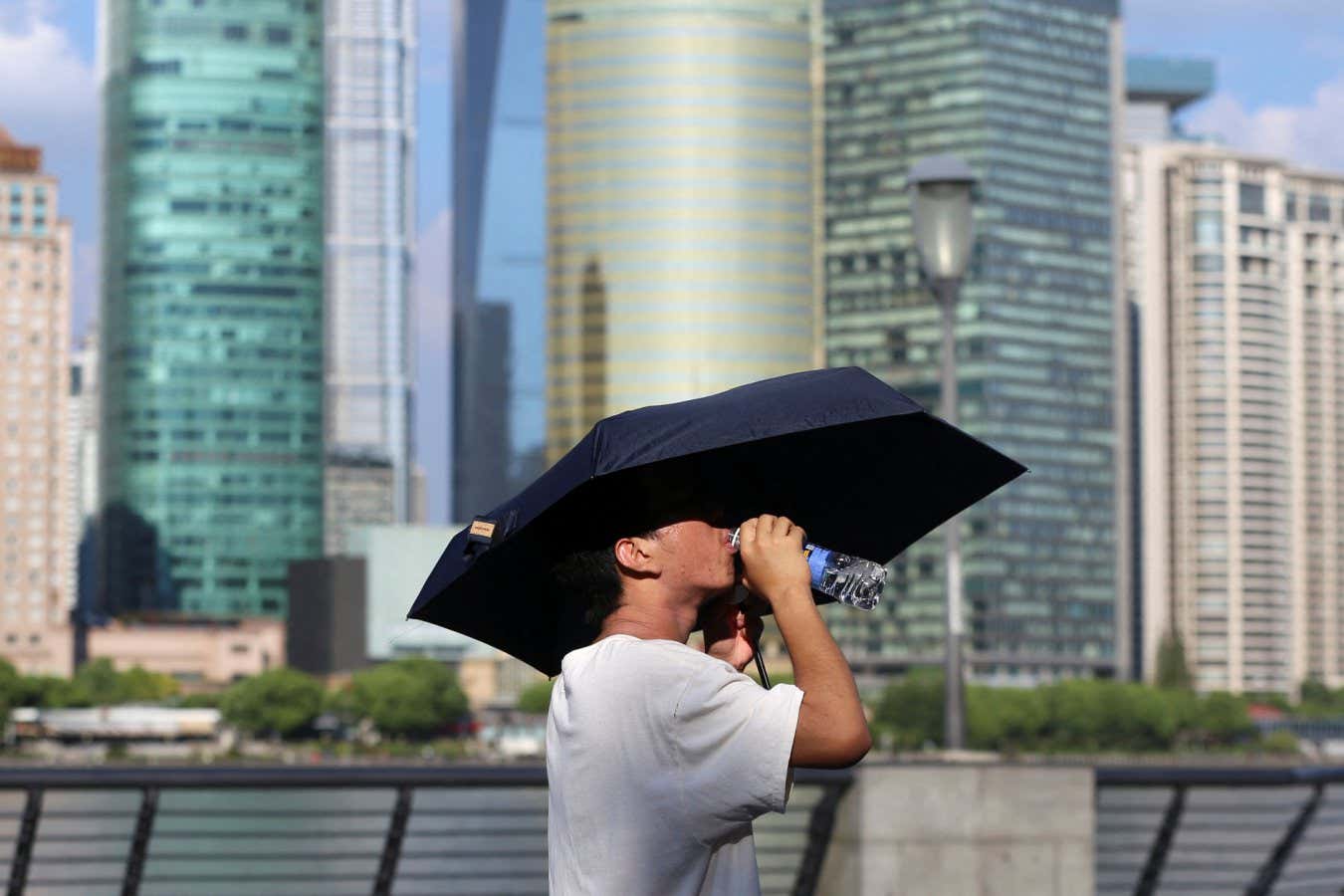
Image Caption: Shanghai experienced many extreme heat and humidity days in 2024 (Credit: REUTERS/Nicoco Chan).
campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utmsource=NSNS&utmmedium=RSS&utmcontent=home”>Read More
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...