Now Reading: Can Mining for Renewable Tech Be Made Sustainable?
1
-
01
Can Mining for Renewable Tech Be Made Sustainable?
Can Mining for Renewable Tech Be Made Sustainable?

Speedy Summary
- The global shift to renewable energy, while beneficial for the climate, necessitates vast quantities of critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, copper, and rare earths.
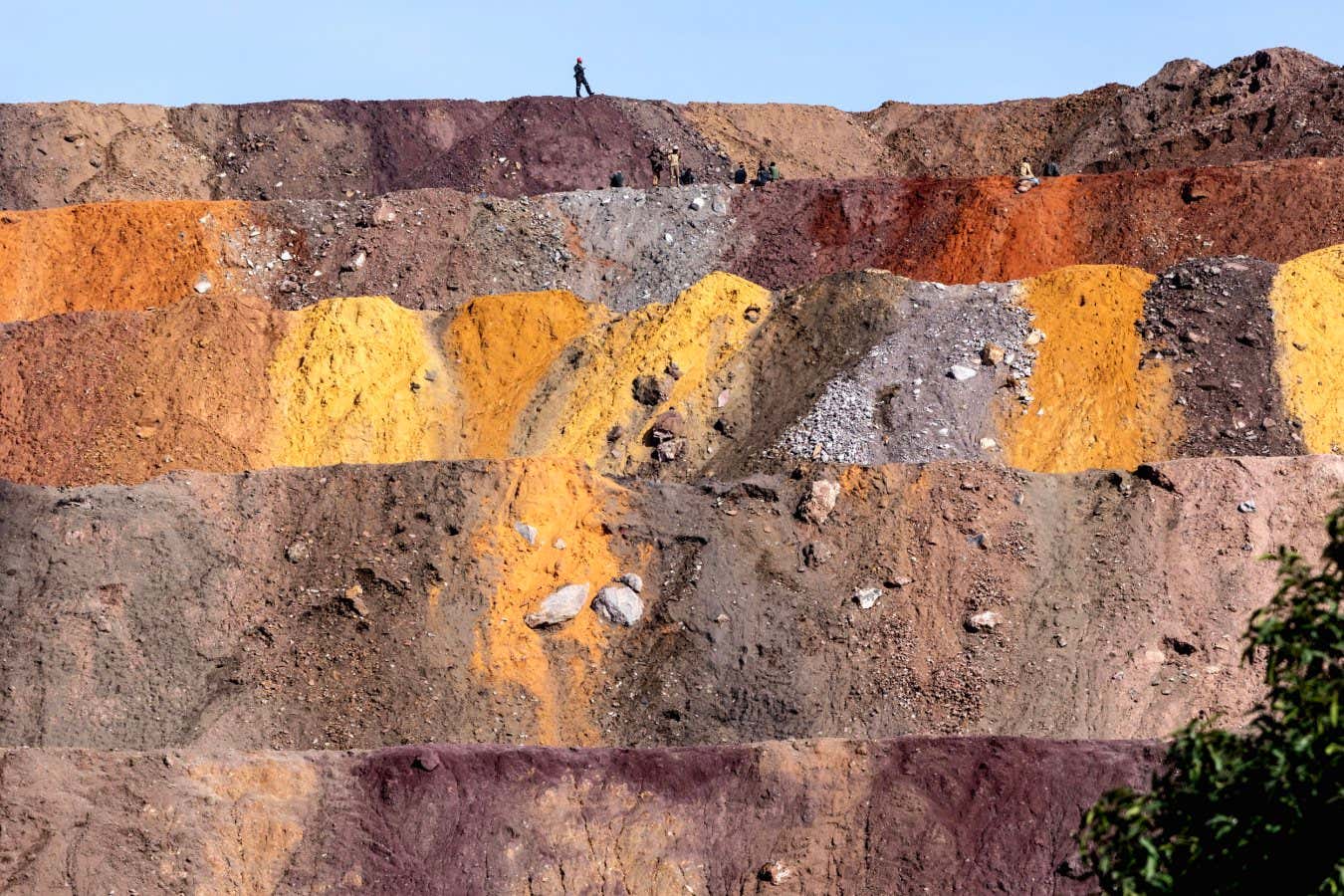
- Mining these materials is causing important environmental damage and societal issues including deforestation, water scarcity, pollution, forced labor, and child exploitation.
- Major producers of these minerals include Chile (copper & lithium), Indonesia (nickel), the Democratic Republic of Congo (cobalt), and China (rare earths).
- China dominates processing capacity for critical minerals globally-exerting considerable political leverage in international trade and economic policy.
- Innovative technologies like phytomining and electrokinetic mining aim to reduce mining’s ecological impact by extracting metals from waste or polluted soil. Recycling e-waste offers untapped potential due to its rich metal content but remains underutilized due to technical challenges.
- Efforts to explore option sources include deep-sea mining robots trialed in the Pacific Ocean despite environmental opposition; asteroid mining ventures remain speculative but promising with recent improvements in space technologies.
Images:
- Waste tailings containing cobalt & copper from a mine in the Democratic Republic of Congo (
Pascal Maitre/Panos Pictures). - Lithium evaporation pond extraction at Chile’s Atacama desert (
PHILIPPE PSAILA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY). - Rainforest destruction caused by nickel mines in Sulawesi (
Ulet Ifansasti/Getty Images). - EV battery production line requiring critical minerals such as lithium & cobalt (
Hu Xiaofei/VCG via Getty Images).
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...