Now Reading: Hurricane Katrina: Key Impacts and Essential Facts
-
01
Hurricane Katrina: Key Impacts and Essential Facts
Hurricane Katrina: Key Impacts and Essential Facts

Rapid Summary:
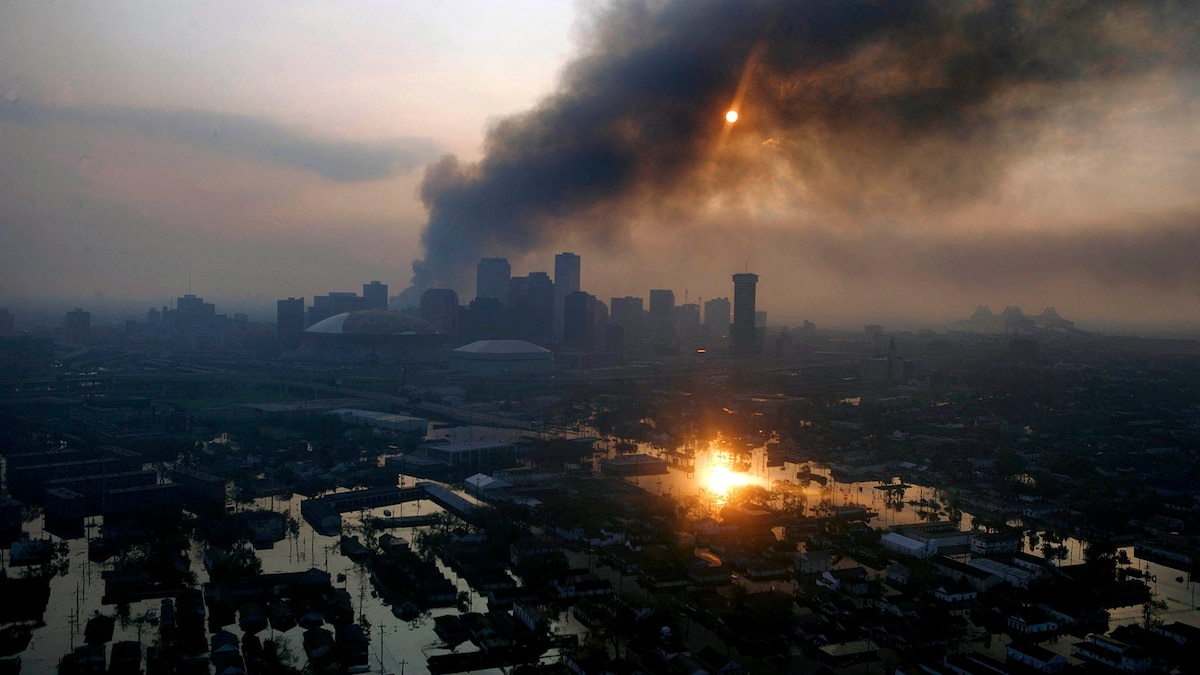
- Hurricane Katrina Details: A Category 3 storm that made landfall near louisiana on August 29, 2005, with wind speeds of up to 120 miles per hour.
- Fatalities and Costs: resulted in approximately 1,200 fatalities and caused $108 billion in damage, making it the costliest hurricane in U.S. history.
- levee Failures: Over fifty levees failed during the storm, flooding about 80% of New Orleans. The Lower Ninth Ward faced disproportionate impacts on low-income and African American communities.
- Government Response Issues: Criticism over federal and local preparedness failures; President Barack Obama referred to Katrina as a “man-made disaster.”
- Human Toll: An estimated 100,000 residents were trapped during evacuation failures; around 25,000 took refuge in the Superdome under dire conditions.
- Population Displacement: Nearly half the city’s population left after Katrina-a third became permanently displaced-shifting demographics toward more racial diversity but fewer African Americans returning.
- Economic Impact: severe effects on oil operations, tourism industries along coastal areas, logistical infrastructure damage; ongoing debates linger regarding fraudulent use of relief funds by FEMA (~$1.4 billion) amid initial Congressional oversight post-relief compliance failures.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The aftermath of Hurricane Katrina serves as a stark reminder for countries like india to evaluate urban disaster preparedness rigorously-especially for coastal cities vulnerable to similar risks such as Mumbai or Chennai. While hurricanes are rare in India compared to cyclones (Indian Ocean storms), lessons from America’s levee system highlight how aging or poorly maintained critical flood defenses can amplify disasters disproportionately for marginalised communities.
policy foresight could mitigate human suffering through proactive urban protections coupled with equitable recovery mechanisms targeting low-income groups often trapped socioeconomically under climate vulnerabilities post-events long-term displacement across Southern southern metros Urbanising densities shifts high seas erosion.require addressing Data precedent from National USA reflect Rebuild Learn Discern Contingency Water Basin dynamics.cross.Read More https://www.nationalgeographic.com/habitat/article/hurricane-katrina