Now Reading: Systema: A Framework to Assess Genetic Response Predictions Beyond Variations
-
01
Systema: A Framework to Assess Genetic Response Predictions Beyond Variations
Systema: A Framework to Assess Genetic Response Predictions Beyond Variations
Swift Summary
- Advancements in predicting single-cell genetic perturbations are crucial for applications such as understanding gene functions, regulatory networks, and therapeutic discovery.
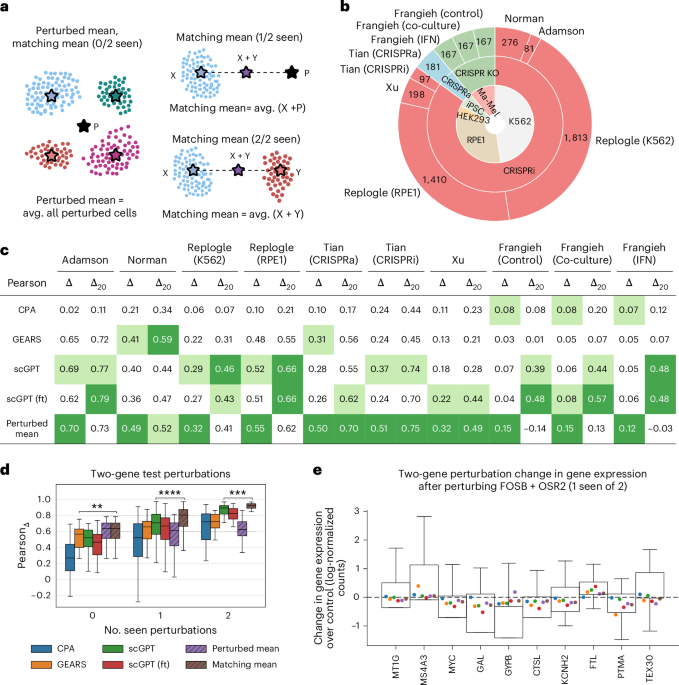
- Recent studies benchmark computational methods aimed at predicting transcriptional outcomes of unseen genetic perturbations using advanced models like CPA (Compositional Perturbation autoencoder), GEARS, and scGPT.
- Simple baselines (like perturbed mean averages) performed comparably to state-of-the-art methods across ten datasets collected from six different sources. These simple approaches capture broad patterns without requiring sophisticated computation.
- Systematic biases caused by inherent biological factors were observed to influence prediction accuracy in existing datasets.
- Systema is introduced as a new evaluation framework that mitigates biases and measures the ability to infer meaningful perturbation-specific effects, offering more interpretable insights into predictive models.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The exploration of simpler baseline methods performing comparably to advanced tools in predicting genetic perturbation effects highlights the need for reevaluating priorities within computational genomics research.For India’s burgeoning biotech sector-focusing on precision medicine and genomic solutions-this evolution suggests cost-effective approaches could provide robust solutions without the dependency on complex infrastructure or expensive AI frameworks. the introduction of Systema offers global researchers an accessible tool with tangible interpretability advantages, perhaps bolstering India’s academic collaborations globally while encouraging local adoption within practical laboratory setups.
Read More: sourceQuick Summary
- Research explores predictive methods for transcriptional changes in single-cell gene perturbation studies using metrics such as Pearson correlation, RMSE, and differential expression analysis.
- Findings suggest that simple baselines often outperform advanced models in predicting one-gene and two-gene perturbation responses across datasets.
- Systematic differences between control cells and perturbed cells heavily influence results, potentially skewing generalization capabilities for novel perturbations.
- Commonly used datasets (e.g., Adamson, Norman, Replogle) show structured biological variation due to experimental design choices or biological effects like chromosomal instabilities influencing cell cycle behavior.
- Tools like Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) reveal enriched pathways tied to stress response or replication processes among perturbed cells versus controls.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study highlights critical methodological challenges in large-scale gene perturbation research related to systematic variation between control and treated samples.These findings emphasize the need for models that can better isolate true biological effects from experimental biases. For India’s burgeoning genomics sector-where CRISPR screening technology is gaining traction-the insights may guide better data designs for precision medicine research or translational applications like cancer treatment optimization and drug discovery pipelines. As India continues its investments in bioinformatics infrastructure,refining predictive modeling frameworks could ensure higher quality outputs free of systematic errors,adding credibility on international platforms.
Read more: Nature Article LinkQuick Summary
- In single-cell perturbation datasets, transcriptional changes often align similarly across different experimental conditions, indicating shared shifts that may be nonspecific.
- Datasets such as Adamson, Norman, and Replogle RPE1 showed higher systematic variation compared to others like Frangieh’s, which exhibited more heterogeneous responses.
- Predictive models trained on datasets with high systematic variation may face selection bias due to consistent expression shifts across experiments.
- A newly developed framework called “Systema” proposes using perturbed centroids as references instead of control cells to isolate perturbation-specific biological effects and mitigate the influence of systematic variation.
- Systema highlights challenges in generating accurate predictions for unseen genetic perturbations while allowing refined evaluation metrics like centroid accuracy to assess biologically informative outcomes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India stands at a critical juncture in advancing biomedical research driven by single-cell technologies-a field increasingly influencing personalized medicine and genomic studies worldwide. The analysis of systemic variations outlined by the study brings opportunities for Indian researchers investing in predictive modeling techniques for disease mechanisms or drug discovery programs. By utilizing frameworks such as Systema that reduce confounding biases, India could set benchmarks in global precision medicine initiatives while addressing prevalent challenges like diverse genetic backgrounds affecting predictive capabilities uniquely suited to its population dynamics.
Read more: Nature Article LinkQuick Summary:
- Researchers introduced “Systema,” a framework to improve the evaluation of perturbation response prediction methods for genetic studies.
- Systema uses centroid accuracy as a novel metric, focusing on biologically meaningful predictions over systematic biases.
- The fine-tuned scGPT model was the most effective in predicting coarse-grained cellular responses, such as chromosomal instability (CIN), achieving notable Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Area Under Curve (AUC) scores of 0.73.
- scGPT also excelled in identifying gene groups involved in core cellular processes like DNA replication and translation over datasets like Replogle K562 and RPE1.
- Limitations remain, such as reference dependency and reduced performance on weak perturbations; larger datasets are essential for further advances.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Systema represents an incremental improvement toward decoding genetic phenomena using AI-backed frameworks like scGPT.For India’s scientific community, this approach offers potential utility in genomics research critical for biomedical advancements, drug discovery, and personalized medicine development. As India pushes forward with aspiring genomic projects under programs like GenomeIndia or precision healthcare initiatives backed by increased biotech funding, tools that enhance robustness in analyzing genetic perturbations align directly with national goals to refine healthcare outcomes through technology-driven insights.
Read more: Nature Article
Quick Summary:
- The research article focuses on evaluating metrics for analyzing genetic perturbation effects in single-cell RNA sequencing data.
- Reference-sensitive metrics like cosine similarity and Pearson correlation have limitations, such as sensitivity to weak perturbations and inability to measure the strength of perturbation effects accurately.
- “Centroid accuracy” is introduced as a novel metric to determine whether predicted post-perturbation profiles align closer to their ground-truth centroids compared to other perturbations.
- gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and AUCell were employed for identifying enriched pathways and quantifying pathway activity in perturbed vs. control cells.
- Data processing techniques normalized gene expression values, selected highly variable genes, and prepared datasets based on experimental conditions (control, co-culture, interferon-gamma treatments).
- Chromosomal instability was quantified using a z-score classification method from prior studies.
Read more: Article Link
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The study’s focus on defining improved evaluation metrics-such as centroid accuracy-for genetic perturbation analysis advances precision in understanding molecular responses at the single-cell level. For India’s burgeoning biotech sector, notably its efforts in personalized medicine powered by genomics research, such detailed methods may significantly enhance targeted drug development strategies. By providing systematic comparisons among various analytical tools like GSEA or AUCell under controlled genomic experiments, this framework can bolster reproducibility standards that Indian labs might adopt. Moreover, the integration of AI models with datasets highlights the convergence between computational expertise and biological science-a growing field with wide implications for India’s healthcare innovation ecosystem.Quick Summary
- A extensive list of references related to advancements in genetic perturbation research and cellular response modeling is featured.
- The studies involve CRISPR-based screening, single-cell RNA sequencing, and multimodal genetic analysis platforms.
- Published works range from 2005 to 2025, highlighting international contributions in genomics and biotechnology.
- The research provides insights into transcriptome kinetics, reprogramming heterogeneity, immune evasion mechanisms in cancer cells, and human cell morphology through scalable technologies.
Read more: pubmed Central, PubMed Central, Direct LinkQuick summary
- The article discusses the development and evaluation of “Systema,” a framework designed for predicting genetic perturbation responses even under systematic variation.
- It is authored by Viñas Torné, R., Wiatrak, M., Piran, Z. and others, and published in Nature Biotechnology in August 2025.
- Key dates highlighted include: Received on November 22, 2024; Accepted on July 14, 2025; Published on August 25, 2025.
- Systema aims to enhance the understanding of genetic response mechanisms across diverse conditions as part of advancing biotech research.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This study has potential implications for India’s biotech sector. genetic response prediction frameworks like Systema may provide useful tools in agriculture biotechnology or medical genomics-fields crucial to India’s economic growth and health innovations. As a notable example, leveraging such technologies could help address pressing challenges like improving crop yield resilience or tailoring precision medicine for India’s genetically-diverse population. As India continues its push toward becoming a global hub of biotechnology innovation through policy initiatives like Startup India and Make In India programs supporting biotechs-as well intercultural scientific collaborative ecosystems resources-frameworks thus align with envisioned goals aimed trajectory expansion end outcomes both public/ private stakeholders significant engagement uptakes likely impactful wherever scaled sustainably Read more→ Read More

























