Now Reading: Choosing the Best Sugar Substitute: A Comparative Guide
-
01
Choosing the Best Sugar Substitute: A Comparative Guide
Choosing the Best Sugar Substitute: A Comparative Guide

Rapid Summary
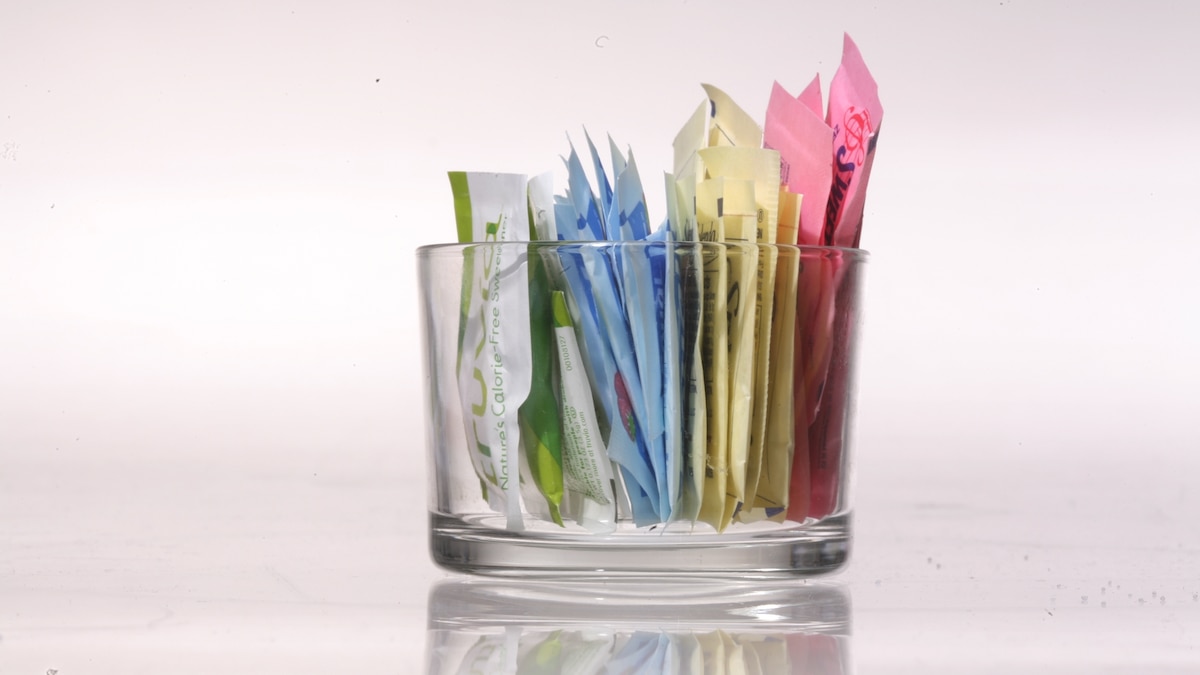
- Artificial and plant-derived sugar substitutes are widely marketed as healthier alternatives to sugar but have complex effects on the body beyond reducing calories.
- Aspartame: Approved by FDA since 1981, it is 200 times sweeter than sugar.It produces smaller blood-sugar spikes compared to regular sugar but has been linked to hunger and weight gain in some studies. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classified it as “possibly carcinogenic,” though regulatory intake limits remain unchanged.
- Sucralose: Made from chemically modified sucrose; 600 times sweeter than sugar and largely excreted undigested. Effects vary based on health status, with some obese individuals showing impaired glucose management after sucralose consumption in trials. Evidence of calorie reduction and slight weight loss exists alongside concerns about appetite signals in the brain.
- Stevia: Derived from a South American plant, stevia provides sweetness through compounds that reach the colon intact, potentially benefiting gut microbiota under specific conditions. Studies suggest reduced calorie intake and improvements in blood glucose regulation versus other sweeteners or regular sugar but no impact on appetite overall. Certain forms of stevia remain unapproved globally due to safety data gaps.
- Monk Fruit: A newer “natural” option containing mogroside V for sweetness (200x sweeter than sugar).Limited human studies show negligible differences between monk fruit and other sweeteners or ordinary sugars regarding energy intake or metabolic response but promising anti-inflammatory effects observed in animal research.
- Scientists advocate for reducing overall dietary sweetness (from any source) rather than solely replacing customary sugars with substitutes.
Indian opinion Analysis
India’s growing interest in artificial sweeteners amid rising cases of diabetes presents both opportunities and challenges for public health policy makers,food manufacturers,and consumers alike. As alternatives like sucralose, stevia, aspartame, and monk fruit gain traction globally-including limited penetration into Indian markets-this report underscores critical uncertainties about their long-term effects across diverse populations.
For India specifically-where diet significantly varies across regions-addressing chronic conditions such as obesity may benefit from targeted messaging around moderation rather than outright substitution of traditional foods like jaggery or natural cane sugar with artificial options whose impacts remain ambiguous scientifically.Initiatives focused more broadly on lowering overall “sweetness dependence” can harmonize well with India’s cultural emphasis on balanced diets rooted in locally sourced nutrition patterns while mitigating chronic disease risk burgeoning amongst urbanized segments increasingly adopting processed lifestyle tastes conflicting w/global-indigenous space intersects ops ahead educational outreach required