Now Reading: Could Disappearing Y Chromosomes Hold the Key to Men’s Health Issues?
1
-
01
Could Disappearing Y Chromosomes Hold the Key to Men’s Health Issues?
Could Disappearing Y Chromosomes Hold the Key to Men’s Health Issues?
Fast Summary
- Women globally, on average, live longer than men. This has been consistent across historical records and all countries.
- Previous explanations for the lifespan gap include behavioral factors (e.g., risk-taking) and biological differences, but none fully explain it.
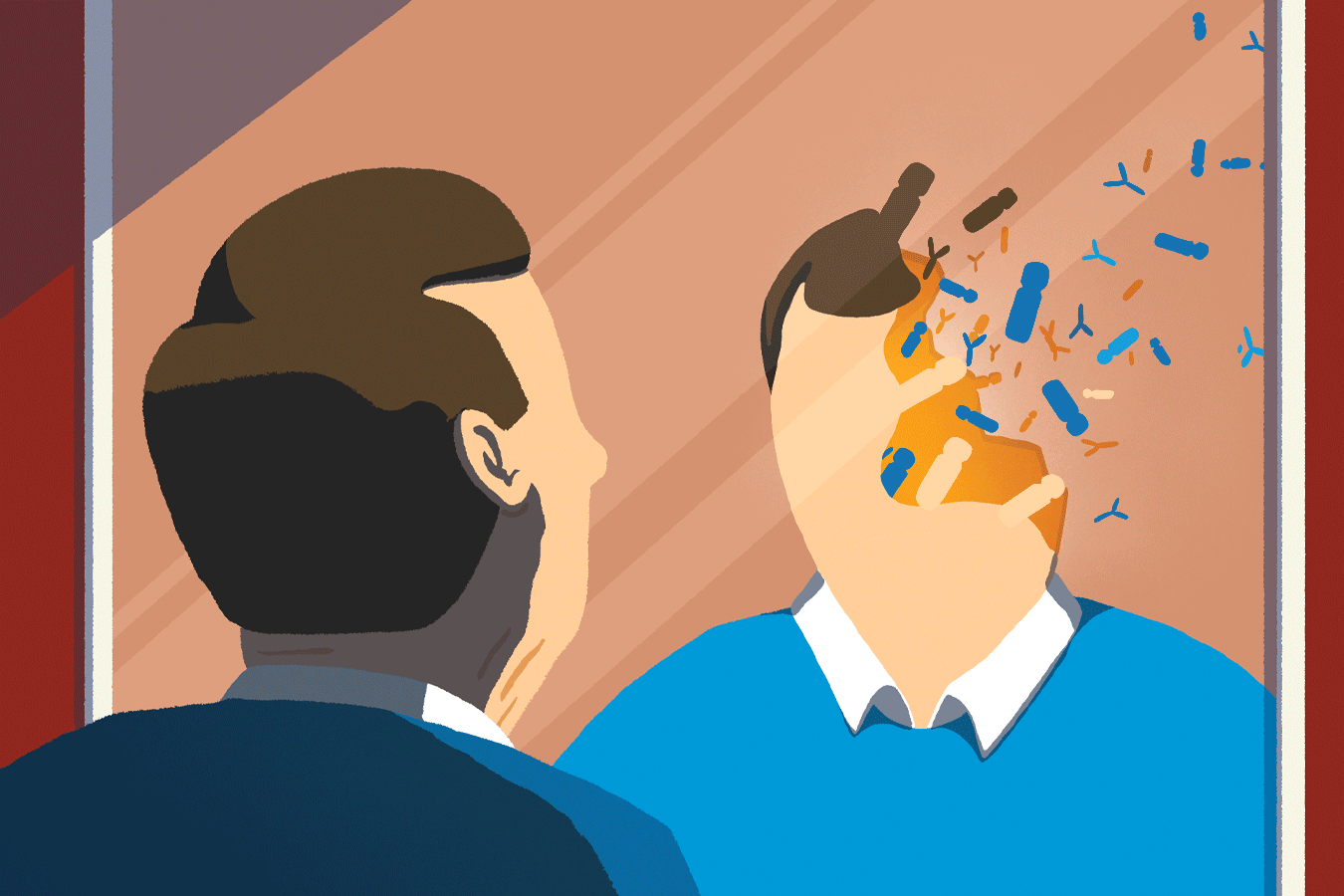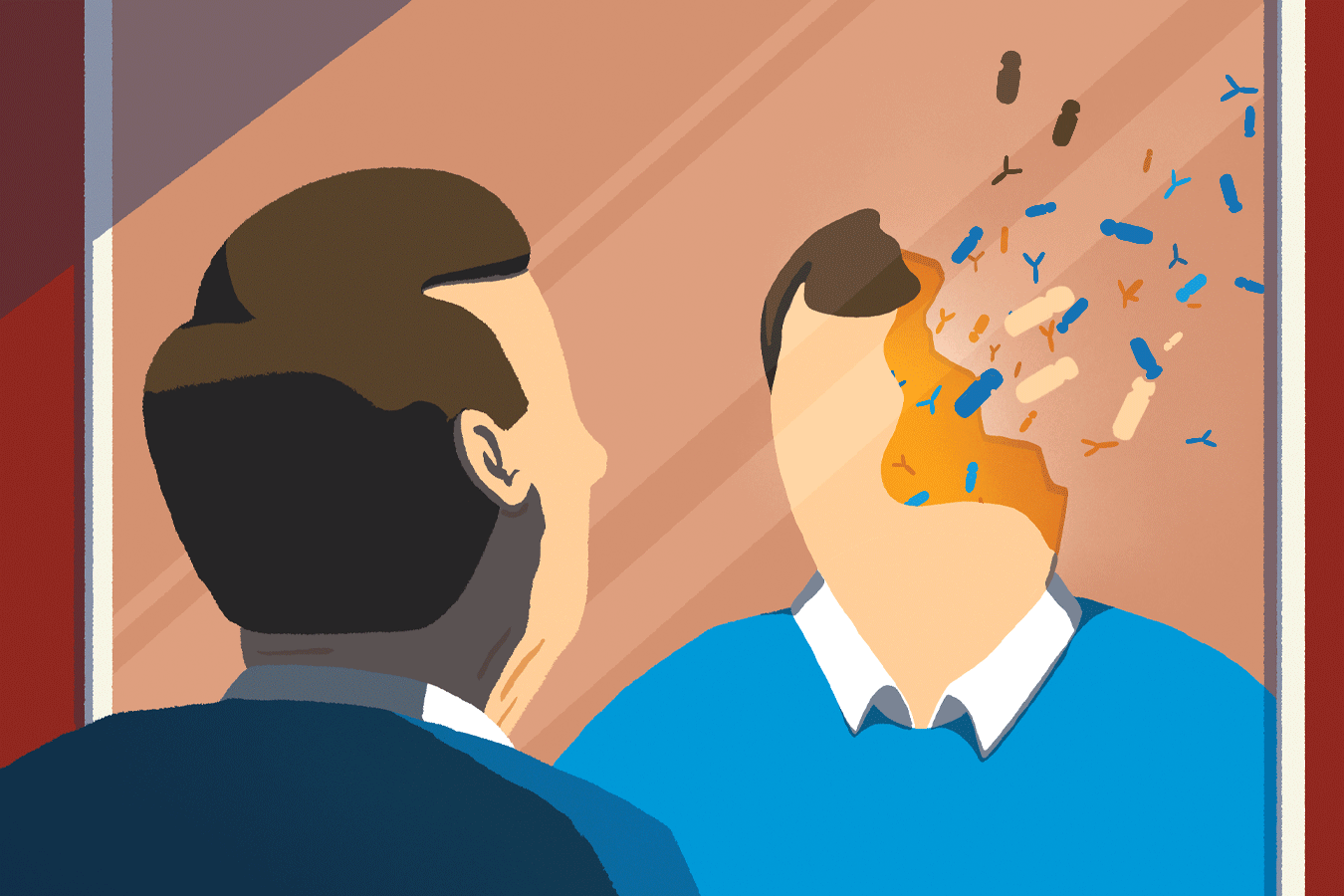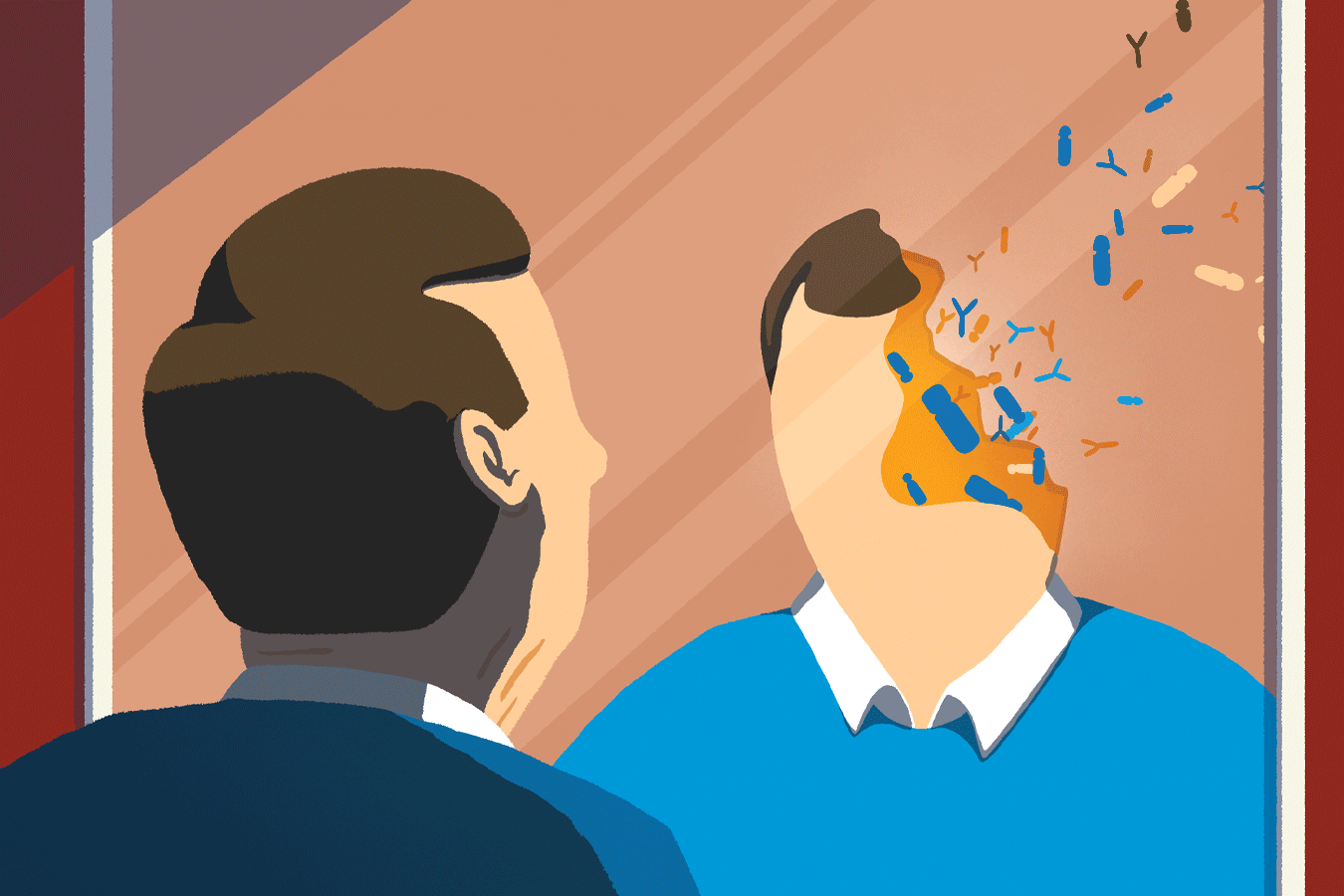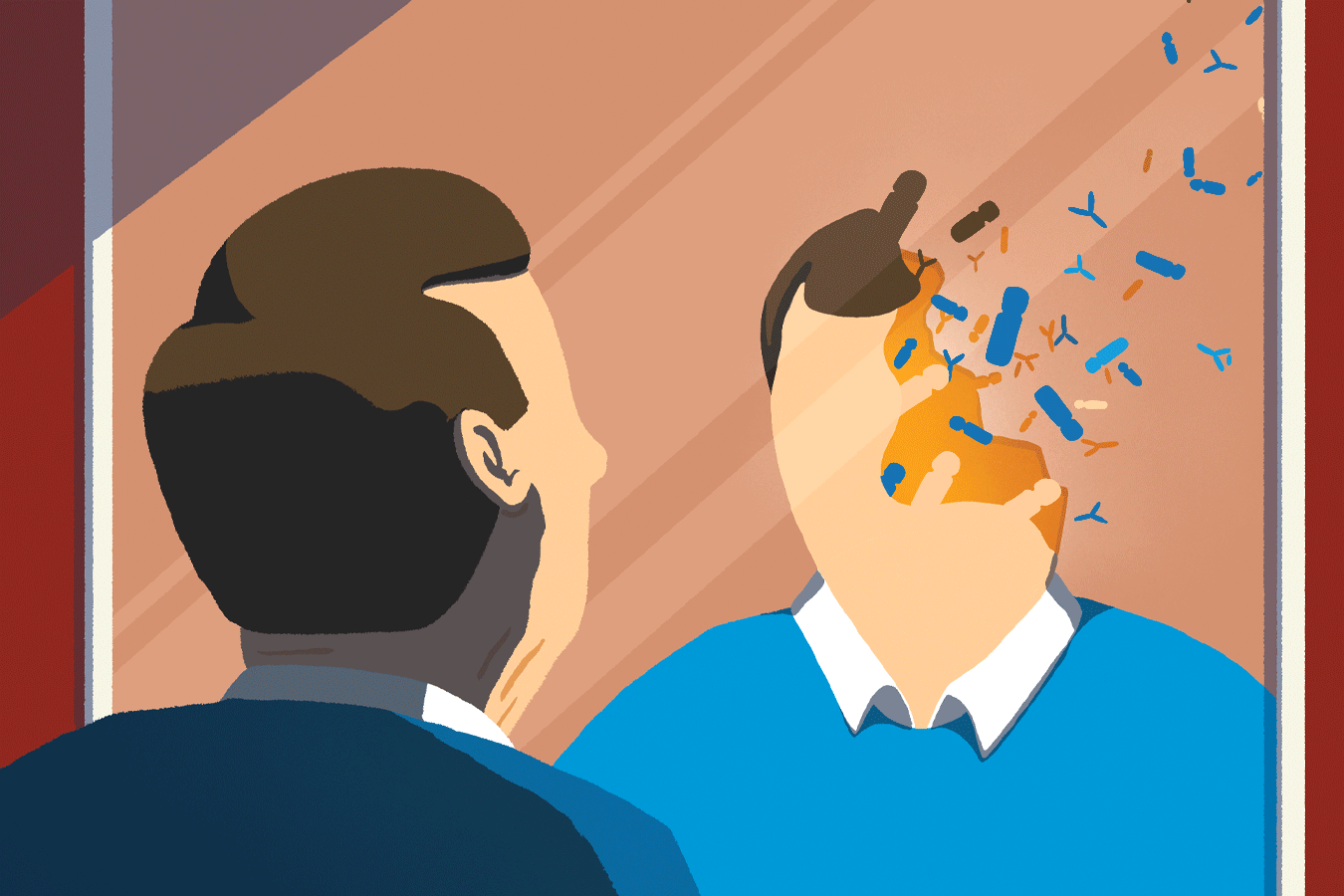
- Recent research suggests the loss of the Y chromosome in men’s cells as they age may be a major factor driving age-related diseases like cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s.
- Researchers indicate this chromosomal loss weakens the immune system alongside overall health impacts.
- Kenneth Walsh from the University of Virginia states that losing Y chromosomes considerably shortens male lifespan.
- Studies are exploring potential pathways to mitigate these effects to improve men’s health outcomes in aging.
!Y Chromosome Loss
Image credit: Andy carter
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...
























