Now Reading: Scientists Uncover Mystery Behind Annual Cloud Formation on Mars
-
01
Scientists Uncover Mystery Behind Annual Cloud Formation on Mars
Scientists Uncover Mystery Behind Annual Cloud Formation on Mars

Swift Summary
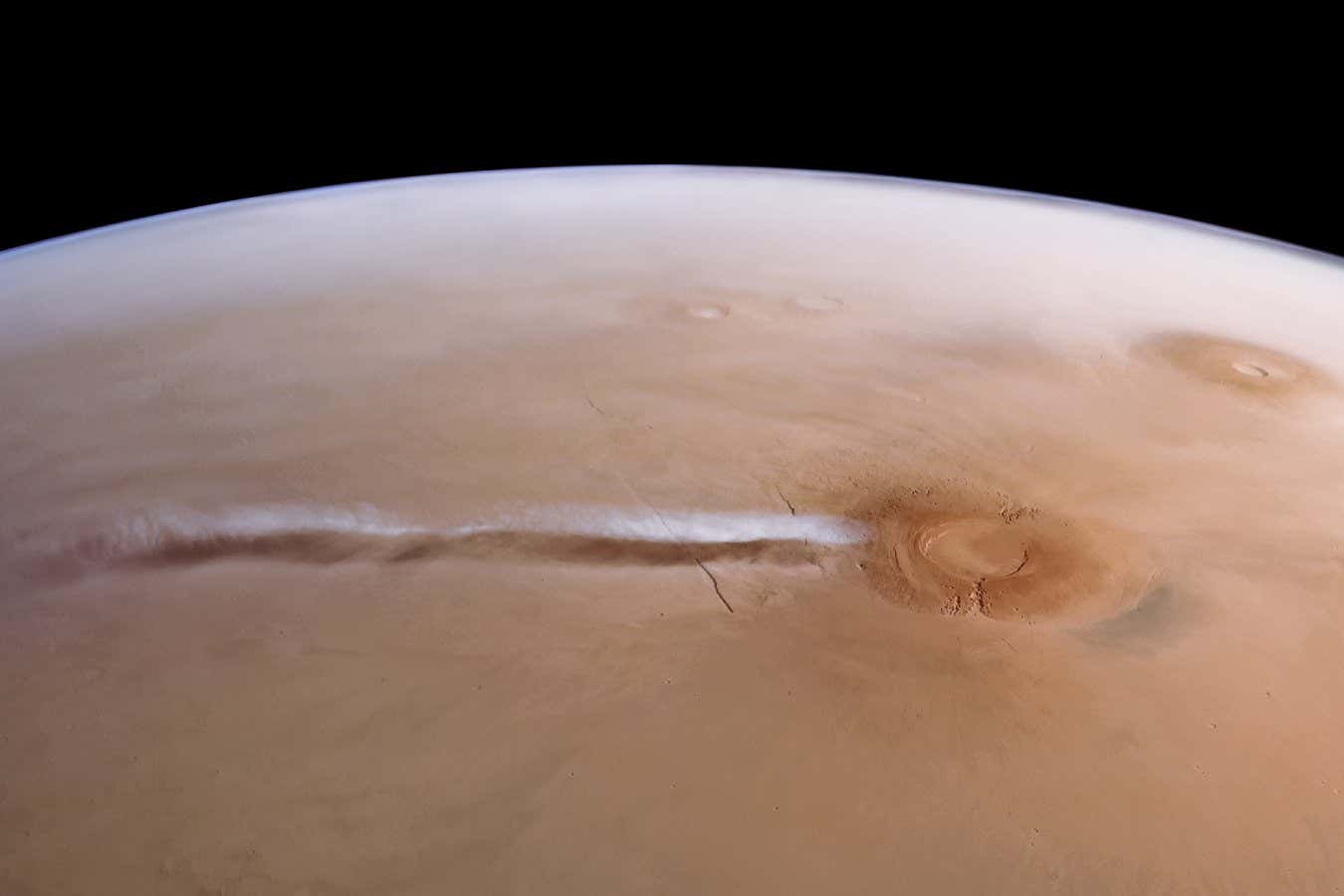
- A cloud forms annually near Mars’s Arsia Mons volcano,spanning up to 1800 km and reappearing daily for about three months during Mars’s winter season.
- This phenomenon puzzled astronomers as prevailing atmospheric conditions on Mars, wiht high dust levels, seemed incompatible with such cloud formations.
- Researchers led by Jorge Hernández-Bernal at Sorbonne University have identified that extremely high water vapour levels in the Martian atmosphere enable these clouds to form through homogeneous nucleation – a dust-free process.
- simulations replicating higher water vapour concentrations successfully reproduced the distinctive elongated tail of the Arsia Mons cloud and its outburst feature.
- These findings challenge prior assumptions that supersaturation (leading to homogeneous nucleation) was virtually unfeasible under Martian atmospheric conditions.
!campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utmsource=NSNS&utmmedium=RSS&utm_content=home”>read More
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study of recurring clouds around Mars’s Arsia Mons holds notable implications for planetary science. By revealing how high levels of water vapour can interact differently in unique atmospheres like those on Mars, researchers expand our understanding of extraterrestrial weather patterns and microphysical processes. These findings may also influence future exploration strategies aimed at detecting moisture-rich regions or studying seasonal variations critical for habitability assessments.
From India’s outlook, this highlights opportunities for collaboration in space research given its burgeoning efforts via missions like mangalyaan. Expanding scientific investigations into atmospheric phenomena could contribute considerably to global knowledge while boosting India’s presence in deep-space studies tied to planetary environments.