Now Reading: Rare Asteroid Explosion Over France Mimics Bomb-like Impact
-
01
Rare Asteroid Explosion Over France Mimics Bomb-like Impact
Rare Asteroid Explosion Over France Mimics Bomb-like Impact

Quick Summary
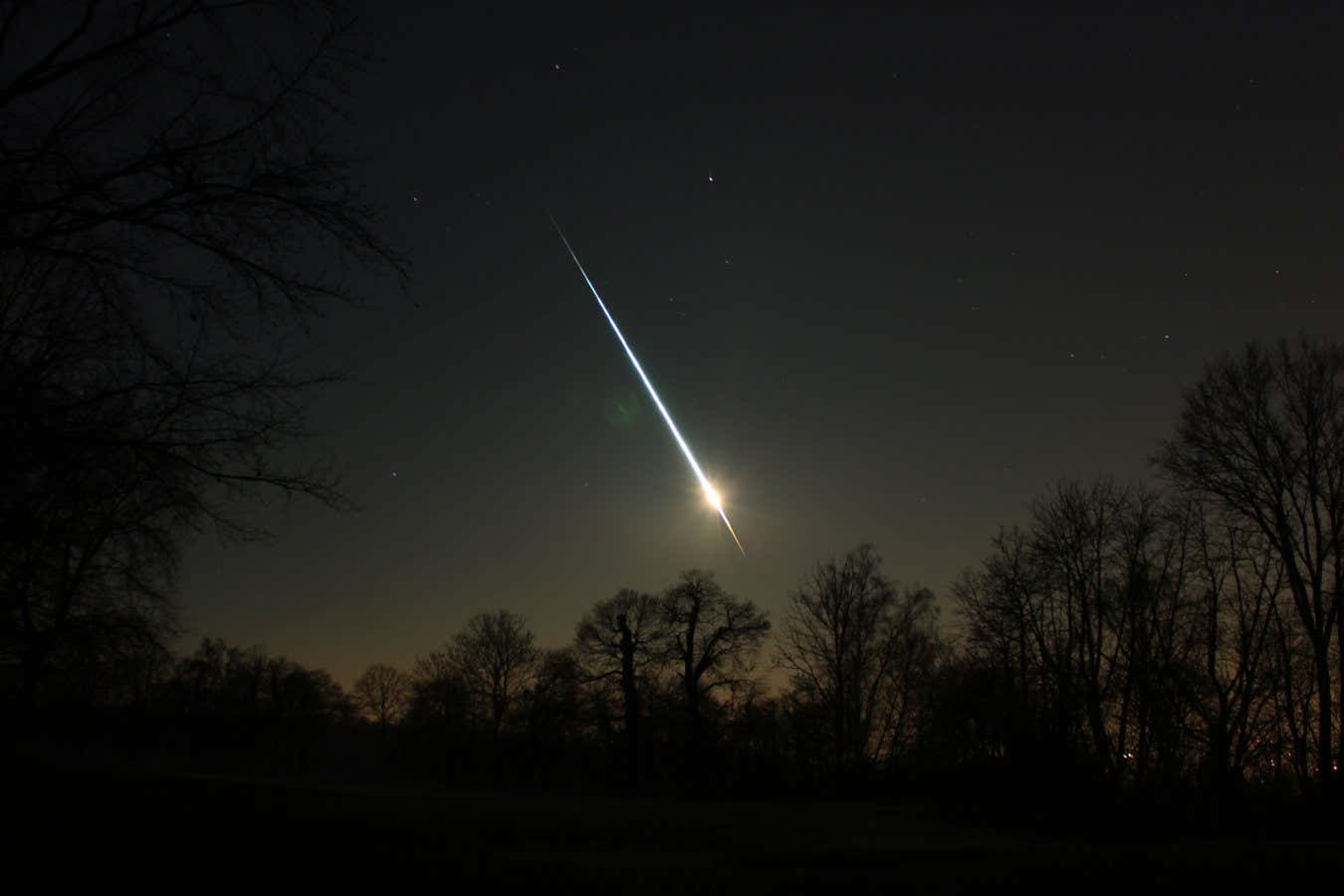
- Event Overview: Asteroid 2023 CX1 entered Earth’s atmosphere on february 13, 2023, over Normandy, France.
- tracking: The asteroid was observed about seven hours before impact and produced a bright fireball with meteorites collected afterward.
- Explosion Characteristics: Unlike typical asteroids that disintegrate gradually, it exploded at 28 km altitude in a single event with an energy equivalent to about 29 tons of TNT, losing 98% of its mass instantly.
- Size and impact Risk: At only 72 cm across (size of a beach ball), it posed no danger to Earth this time. Similar events involving larger asteroids could be potentially hazardous due to amplified effects.
- Previous Observation: A similar explosion occurred over Slovenia in 2020 (Novo Mesto meteor), though less extreme in terms of mass loss.
- Composition Insights: Research revealed asteroid CX1 comprised toughened L-chondrite material likely resulting from past impacts within the Massalia asteroid belt. This toughness may explain its unusual fragmentation behavior.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The rare fragmentation pattern displayed by asteroid CX1 raises significant implications for planetary defense strategies.India’s role as part of global initiatives such as the committee on Space Research (COSPAR) could benefit greatly from understanding fragmentation risks associated with common L-chondrites like this one. While the immediate risk posed by smaller asteroids remains limited, preparedness for larger bodies following similar explosive behaviors is critical. India’s advancements in space research-seen through missions like Chandrayaan-may allow it to contribute actively to developing predictive models and evacuation protocols aligned with global standards. Collaboration between Indian scientists and international experts studying material compositions like L-chondrites might also bolster mitigation efforts.