Now Reading: New Study Reveals Direct Communication Between Gut and Brain Cells
-
01
New Study Reveals Direct Communication Between Gut and Brain Cells
New Study Reveals Direct Communication Between Gut and Brain Cells
Fast Summary
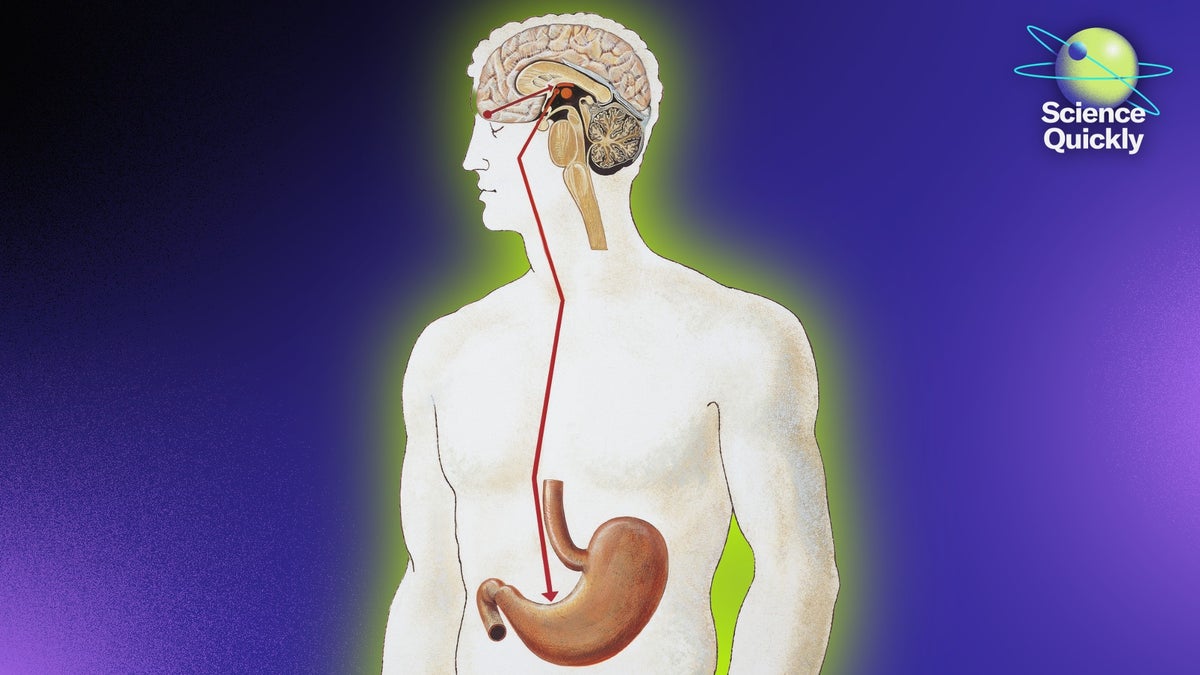
- Recent research highlights that specialized cells in the gut, called “neuropod cells,” communicate directly with the brain to influence appetite and mood.
- These neuropod cells can differentiate between real sugar and artificial sweeteners, releasing distinct signals based on nutrient stimuli.
- The microbiome-microbes living in the gut-interacts with these neuropod cells via specific proteins (e.g.,flagellin),which can regulate feeding behavior.
- Experiments on germ-free mice confirmed that this gut-brain communication circuit exists independently of prior microbial exposure, indicating it is indeed an evolved mechanism.
- Implications of this research include potential future applications for tailoring diets or developing probiotics to optimize health by leveraging these connections.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The revelation of direct communication between the gut and brain through specialized neuropod cells presents a groundbreaking outlook on how human biology responds to diet and microbiota influence.This evidence that our microbiome affects not only physical but also mental well-being offers vital implications for public health strategies worldwide, including India, where both malnutrition and diet-related illnesses are prevalent.
india’s diversity in dietary habits underscores a unique prospect: targeted application of this science may refine conventional cuisines or enable precision nutrition interventions based on individual microbiomes while respecting culinary heritage. Additionally, further exploration into gut-microbe dynamics could illuminate solutions for common lifestyle conditions prevalent in urbanizing populations such as obesity or diabetes.As scientific understanding deepens globally, Indian policymakers might collaborate with researchers to explore the role of local diets and indigenous probiotic sources like curd (“dahi”) in enhancing citizens’ overall health outcomes. However, prudence will be necessary during translational phases into practical therapies due to contextual differences in diet patterns and healthcare accessibility across India’s population spectrum.