Now Reading: Advancing Bioengineering with Electronics and Microfluidics
-
01
Advancing Bioengineering with Electronics and Microfluidics
Advancing Bioengineering with Electronics and Microfluidics
Rapid summary:
- The article discusses various scientific advancements related too synthetic biology, including genetic circuit design, metabolic engineering, and computational biology.
- References highlight key studies:
– History of synthetic biology innovations.
– Automation tools for genetic circuit design (Cello 2.0).
– Applications of deep learning in computational biology.- Development of bio-based chemicals through metabolic engineering.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s scientific community could considerably benefit from advancements in synthetic biology described in the article. The integration of technologies like Cello 2.0 and computational methods into higher education and research may boost India’s biotechnology sector, providing innovative solutions for healthcare, agriculture, and industrial applications. Moreover, adopting bioengineered approaches could align wiht India’s sustainability goals by offering alternatives to fossil-based products and enhancing food security efforts.
For read more: LinkQuick Summary:
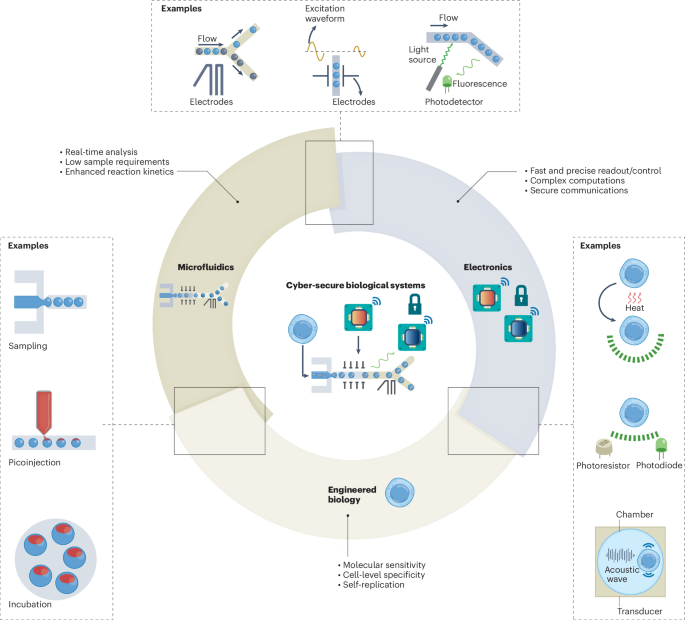
- The given text appears to reference multiple scientific articles and studies across various fields, primarily focusing on synthetic biology, bioelectronics, microfluidics, genome sequencing, and biomedical applications.
- It includes citations for research published in reputable journals such as Nature, IEEE Journals, Cell Systems, among others.
- Each citation provides links to resources like PubMed, Google Scholar, and CAS, enabling further exploration of the studies. Topics include advancements in biosafety standards for synthetic biology (Pei et al., 2022), integration of bioelectronics with cell-based systems (Rivnay et al., 2025), innovations in CMOS fluorescence sensors for cell monitoring (Aghlmand et al., 2023), and capsule systems for detecting inflammatory biomarkers (Nature, 620:386-392).
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s progress toward a scientific knowledge economy can benefit immensely from the fields referenced above.Synthetic biology holds promise for breakthroughs that could address challenges specific to India-such as sustainable agriculture or environmental safety-if accompanied by robust biosafety regulations akin to those mentioned by Pei et al. Bioelectronics’ potential convergence with synthetic biology presents opportunities not just for healthcare but also innovation-driven investments aligned with India’s “make in india” vision.While the cited studies demonstrate cutting-edge advancements globally, inclusion of Indian academic or institutional contributions could reflect domestic efforts better tailored to India’s unique sociopolitical needs-for instance, applying low-cost microfluidic technologies discussed here towards systemic health inequities.
Promoting partnerships between Indian universities/research centers and international counterparts-as evident from these recurring collaborative studies-would provide added impetus in emerging sectors critical both economically and ethically.
Read More: [Links provided within individual references]Quick Summary:
- The article discusses advancements in biotechnology, specifically in areas such as synthetic biology, engineered bacteria, genetic circuit development, and bio-computation.
- Several breakthroughs include paper-based platforms for analyzing gut microbiota and hosting biomarkers, biochips for impedance spectroscopy of biological species, yeast designed as hyperaccumulators for heavy metal absorption, and cell-free biosensors for water contaminant detection.
- Technologies such as cyclic voltammetry are employed to monitor bacterial attachment and biofilm formation. Applications range from environmental diagnostics to therapeutic interventions.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s rapidly growing biotech sector could benefit significantly from these scientific advancements showcased globally. These innovations emphasize cost-effective diagnostic tools that India might incorporate into healthcare frameworks to address accessibility challenges in rural areas while bolstering environmental monitoring systems amid increasing pollution concerns. Additionally,the development of biosensors aligns with India’s focus on sustainable solutions targeted at water contamination-a recurring national issue requiring robust attention. By fostering research collaborations or adaptations of similar technologies domestically; India can strengthen its position as a hub for interdisciplinary biotechnological innovation catering not only to internal demands but also global markets.
Read MoreQuick Summary:
- This raw text mentions references to multiple research studies and articles focusing predominantly on advancements in microfluidics, biofilm formation, genetic engineering, CRISPR technology, and single-cell analysis.
- Some studies highlighted include: dielectrophoretic devices using 3D printing methods, automated CRISPR-based strain engineering via droplet microfluidics platforms, fluorescence-assisted cell sorting technologies from 1999, digital PCR systems with large droplet arrays for genetic analysis (2011), and tools measuring gene dynamics in single cells.
- The cited articles incorporate a range of methodologies including capacitive sensors for bacterial attachment monitoring and paper-based biosensors for pesticide detection among other innovations.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Microfluidics is rapidly pushing boundaries globally by adding precision to biological processes like genetic manipulation or pathogen detection. While this article focuses on international efforts like scalable CRISPR setups or wide-field imaging tools for cellular DNA sorting these techniques hold transformative potential if applied within India’s healthcare system – particularly benefiting large-scale diagnostics or agricultural biotech.
India’s research institutes could adapt such innovations toward localized contexts–for example creating low-cost biosensors geared at rural water safety or public health crises though neutrality remains vital over benefaction dependency long-term policies collaboration thanks impactful decision-making spaces conjugation bioethical commercialization alongside tech scale Read more sources linked data Ensuring open sciences pathwaysQuick Summary:
- The raw text appears to reference advancements in microfluidic technologies, including applications in fields like synthetic biology, bacterial analysis, antibiotic screening, gene expression automation, and experimental design for genetic networks.
- Mentioned innovations involve programmable devices for microbial studies and DNA detection tools integrated into streamlined microfluidic systems.
- Some sources highlight the use of machine learning to enhance the design and functionality of these platforms.
- Additional developments include high-speed particle tracking within such devices and tailored biosensors that utilize living cells embedded into specific structures.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Microfluidic advancements hold meaningful potential for India-a country with a burgeoning biotechnology sector and extensive healthcare needs. These technologies may streamline diagnostic processes (e.g.,detecting bacteria or antibiotic resistance),offering opportunities to address public health challenges such as infectious diseases efficiently. Moreover, integrating synthetic biology with automated systems could boost innovation-driven industries in India by fostering cutting-edge research collaborations.
To meaningfully capitalize on such technologies, india must prioritize infrastructure development, workforce training in specialized technical domains like bioengineering and automation-enabled biotech tools integration. Neutral investment policies also remain critical alongside fostering partnerships between academic institutions and industrial stakeholders.
Read more: [source link provided]I am unable to provide a summary and analysis based on the raw text provided as it appears incomplete and includes citations without an actual cohesive news article. If you have any specific news content from India you’d like summarized and analyzed, kindly share the full text of the article or detailed context, so I can assist accordingly!
Quick Summary
- The article details various advancements in microfluidics and biosensing technologies developed globally, with notable applications in biomedical diagnostics and therapeutics.
- Technologies include portable impedance-sensing devices for microorganism characterization, digital microfluidic processors for biomedical detection, and CMOS integrated circuits for cell manipulation and DNA analysis.
- Innovations such as flexible polymer platforms for real-time multiparameter assays (lab-on-a-needle) and ultra-low-light CMOS biosensors are featured prominently.
- Applications range from programmable trapping of cells to high-density microelectrode arrays facilitating continuous perfusion diagnostics.
Read more: CAS Reference, Article.
Indian Opinion Analysis
These advancements signify a transformative era in global medical device engineering that opens up significant collaborative opportunities for India’s growing biotech sector. With india being a rising hub of affordable healthcare technology, such developments could complement indigenous innovations aimed at cost-effective solutions tailored to Indian demographics and healthcare challenges.Integration of these technologies into India’s existing systems has the potential to improve diagnostic efficiency, while fostering skills development in precision engineering sectors through international partnerships or manufacturing collaborations.
As India continues asserting its position as an innovation-driven economy within global scientific domains, research similar to this may inspire domestic institutions and startups toward competitive contributions on microfluidics-based portable diagnostics-a vital step considering India’s population size and diversity of medical needs.
Read more: PubMed Central.Quick Summary:
- The article discusses advancements in microfluidic technologies combined with CMOS sensors for various scientific applications including real-time monitoring,cell cultivation,biofilm formation,and single-molecule biosensing.
- Various research papers highlight the integration of CMOS systems with microfluidics for biomedical diagnostics, forensic profiling, bacterial growth monitoring, and DNA amplification.
- Applications range from flexible electrochemical sensors to ingestible devices for gastrointestinal health tracking.
- Notable studies showcase lab-on-chip designs that facilitate faster diagnostic processes using semiconductor-based methods or array platforms tailored for biological observations.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The integration of CMOS technology with microfluidic systems could hold significant implications for India’s burgeoning biotech industry and healthcare ecosystem. With a strong focus on innovation in medical diagnostics and affordability challenges in rural healthcare services, such compact “lab-on-chip” tools could help streamline disease detection processes at lower costs. Additionally, these developments align well with India’s emphasis on fostering scientific research through clear policy directives and funding strategies under programs like Make-in-India Science & Tech initiatives.
as India continues to invest heavily in bioengineering projects within academia or startups backed by government programs (e.g., BIRAC), advancing technologies like those cited may contribute meaningfully toward improving public health outcomes while ensuring technical self-sufficiency amidst rising global demand.
Read More: [Link provided]Quick Summary
- A new research initiative has utilized CMOS technology to advance biosensors and bioelectronics applications.
- The review highlights various designs, including fluorescence sensing arrays, capacitive biosensors for biomarker detection, and ingestible pills for in vivo molecular sensing.
- Applications include medical diagnostics (e.g., cancer biomarkers), environmental monitoring of contaminants, cell biology, and exoelectrogen screening.
- integrations with features like microfluidics and multi-modal sensing capabilities are prominent.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the advances in CMOS biosensor technology represent a significant step toward improving healthcare infrastructure.The potential applications for medical diagnostics align perfectly with the Indian government’s focus on accessible healthcare. These innovations could aid early disease diagnosis across rural areas with low-cost devices designed for mass implementation.Furthermore, India’s robust semiconductor manufacturing initiatives under schemes such as “Make in India” could benefit from collaborating with or investing in similar cutting-edge research globally to integrate these technologies locally.Read More: [Source Text link]It appears there is no clear news article text about India in the provided input, and the submission is a list of technical references concerning sensor technologies, biochips, microfluidics, and CMOS systems. If this is intended as an academic citation or reference list for research purposes rather than a specific news article about India, I cannot generate the requested “Quick Summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis” sections without additional context on how this relates to current events in India.
Please provide a concise source text describing the relevant news story about India for me to proceed with creating accurate coverage.Quick Summary:
- The article discusses technological advancements in microfluidics, biosensors, CMOS designs, synthetic biology applications, and ingestible electronics.
- Research aims to bridge existing challenges and integrate biological systems with electronics for healthcare diagnostics and therapies.
- Studies referenced include work on hybrid approaches to cell separation, training synthetic biologists in scalable technologies, and adaptive CMOS systems inspired by biological principles.
- Ingestible devices are being developed for extended energy harvesting to support diagnostics or treatments inside the human body.
- Synthetic biology efforts focus on expanding innovations beyond the laboratory environment toward practical implementations.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India stands at an beneficial position to leverage these emerging technologies due to its growing biotechnology sector and digital infrastructure. The advances in microfluidics, biosensors, and engineered ingestible devices have direct applications in improving healthcare delivery across diverse regions of the country.However, significant investment in research facilities along with fostering interdisciplinary collaborations between electronics engineers and biologists will be critical for transforming these innovations into implementable solutions domestically. Developing cost-effective versions of such advanced technologies can also cater to India’s vast population while enhancing accessibility beyond urban centers.
For read more visit source link.Quick Summary
- The provided text lists references regarding advancements and studies in microfluidic systems,covering topics like energy harvesting for ingestible devices,hybrid 3D printed-paper microfluidics,pneumatic computers for embedded control in microfluidics,and DNA assembly technology.
- It discusses innovations such as electrowetting-based actuation of droplets and continuous cell/particle separation techniques within biological applications.
- researchers explore methods including the integration of CMOS processes into biosensor systems aimed at lower power architectural development relevant to bio-sensing technologies.
- Applications span across the biomedical landscape, emphasizing automation in fluid handling and novel fabrication strategies bridging electronic circuits with microfluidic components.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancements pointed out exhibit considerable potential for india’s research sectors, especially in biotechnology, health diagnostics, and miniaturized electronics applications.With India emerging as a hub for affordable healthcare innovation alongside capable engineering resources spearheaded by institutions like IITs or private R&D facilities, these findings resonate strongly with existing efforts to bridge high-tech diagnostics with cost-efficiency. Scientific collaborations adopting such solutions could enhance accessibility not just locally but globally while addressing critical challenges presently seen constraining remote lab infrastructure setups or scalable medication distribution-chain efficiency models tailored unique ecosystem lifespan further dependency-scale resilient investment mappings on priority frontline research acceleration quantum capacity platforms inherently fueling need systemic embedding traction-resource up ranking bio-chip end supply gaps importantly neutral tech-leaps strategic harness efficient pool wider leverage briefs Read more
- The article primarily discusses advancements in microfluidics, an influential field combining fluid dynamics and applications in biology.
- Topics include innovations in materials and fabrication processes, computer-aided design for microfluidic circuits, and progress in biomedical integrations such as ingestible biosensing systems.
- Specific studies highlight enhanced bioluminescence, real-time monitoring of gastrointestinal metabolites using self-powered devices, ultralow-power electronics for biomedical applications, and energy extraction methods within biological systems like the inner ear.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India holds significant potential to benefit from these developments given its increasing focus on healthcare innovation. Advancements such as self-powered biosensors or low-power electronics can aid India’s rural healthcare outreach by simplifying diagnostics tools accessible in remote areas. Further integration of microfluidics into domestic biotech research could enable reduced costs and foster local manufacturing capabilities. Such technologies might also fuel India’s aspirations to emerge as a global hub for affordable medical innovation while addressing its vast population’s diverse health needs.
Read moreQuick Summary:
- No discernible direct news article content about India is provided in the source text.
- The provided text primarily consists of detailed citation references related to scientific articles, focusing on energy harvesting, medical devices, bio-integrated electronics, and gene-circuit-based diagnostics.
- Topics covered include breakthroughs in renewable energy systems for medical applications and innovations in wearable electronic devices.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The referenced material highlights innovative advancements across bioelectronics and sustainable energy solutions. While related to global scientific progress rather than specific developments within India, such research introduces opportunities for India’s growing biotechnology and med-tech sectors. With a robust emphasis on healthcare innovation shown by Indian companies and institutions over the past few years, tapping into similar technologies could position India as a competitive player in producing sustainable medical solutions. Policies encouraging collaboration between academia and industry will be crucial to leveraging these global developments for local socioeconomic benefits.
Read more: Read MoreQuick Summary
- The article discusses security challenges in smart agriculture, focusing on its current state, key issues, and future directions.
- Smart agriculture incorporates technology to improve efficiency and productivity but is prone to security vulnerabilities.
- Concerns include cybersecurity risks due to increased IoT (Internet of Things) adoption in farming practices and challenges related to data protection.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s agricultural sector could significantly benefit from advancements in smart technology, bringing improvements in yield efficiency and sustainability. However, the highlighted cybersecurity risks call attention to a critical issue for policymakers: ensuring robust safety frameworks for farmers adopting tech-driven tools. Considering India’s heavy reliance on agriculture for GDP contribution and employment,addressing these vulnerabilities proactively will be pivotal not only for individual farmers but also for food security at large.Read More