Now Reading: Lunar Meteorite Discovery Sheds Light on Billion-Year Gap in Moon’s Volcanic History
-
01
Lunar Meteorite Discovery Sheds Light on Billion-Year Gap in Moon’s Volcanic History
Lunar Meteorite Discovery Sheds Light on Billion-Year Gap in Moon’s Volcanic History

Speedy Summary
- Finding: The lunar meteorite NWA 16286 was found in Northwest Africa in 2023 and weighs 311 grams.
- Significance: It is only one of 31 officially recognized lunar basalts on Earth, making it a rare geological specimen.
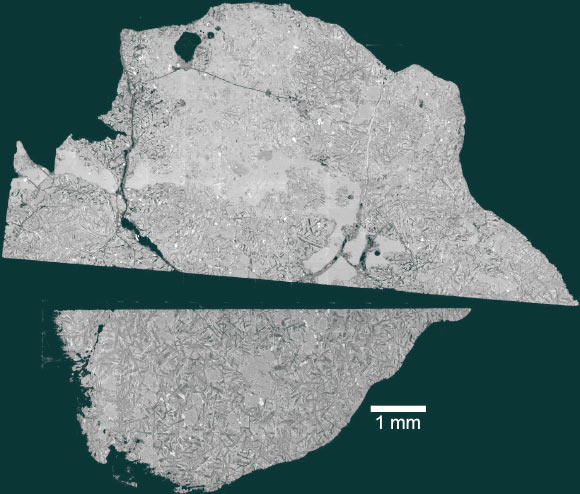
- geochemical Profile: The meteorite contains melted glassy pockets and veins, suggesting it was shocked by asteroid or meteorite impacts.Its unique chemical composition includes olivine crystals and moderate titanium levels.
- Age: Lead isotope analysis dates the rock to approximately 2.35 billion years old, filling a billion-year gap in known lunar volcanic activity records.
- Formation & Source: The rock likely solidified from a lava flow originating deep within the Moon’s interior, with an unusually high uranium-to-lead ratio linked to ongoing heat-generating radiogenic processes within the Moon.
- Insights on lunar Volcanism: Analysis shows that volcanic activity on the Moon persisted much longer than previously assumed.
- Scientific Context: Researchers believe studying such samples could guide future landing sites for sample-return missions aimed at unraveling more about the Moon’s geological evolution.
Image credit: Backscattered electron image of NWA 16286 sample by Joshua Snape/University of Manchester.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery of NWA 16286 offers critical insights into planetary science and extended our understanding of Earth’s closest neighbor-the Moon. Its geochemical profile not only fills a gap in lunar volcanic history but points to prolonged internal heat-generation mechanisms that defy earlier assumptions about moon-wide cooling trends. For India, which has ongoing aspirations in space exploration exemplified by missions like Chandrayaan, findings like thes set an inspiring precedent for deeper engagement with planetary research.
India already contributes significantly to satellite technology and space sciences but may benefit strategically from collaborative efforts focused on extraterrestrial geology.Broadening dialog with institutions globally-such as University of Manchester researchers analyzing this specimen-could help discover new methodologies applicable during India’s future moon missions. Additionally, identifying nuances like those surrounding this particular basalt may guide more targeted exploration strategies for upcoming lunar landers or rover deployments by ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation). While global achievements showcase humanity’s collective strides toward interplanetary understanding, each nation stands to enrich its scientific base through sustained participation both technologically and academically.