Now Reading: NASA-ISRO NISAR Satellite: Why It Matters
1
-
01
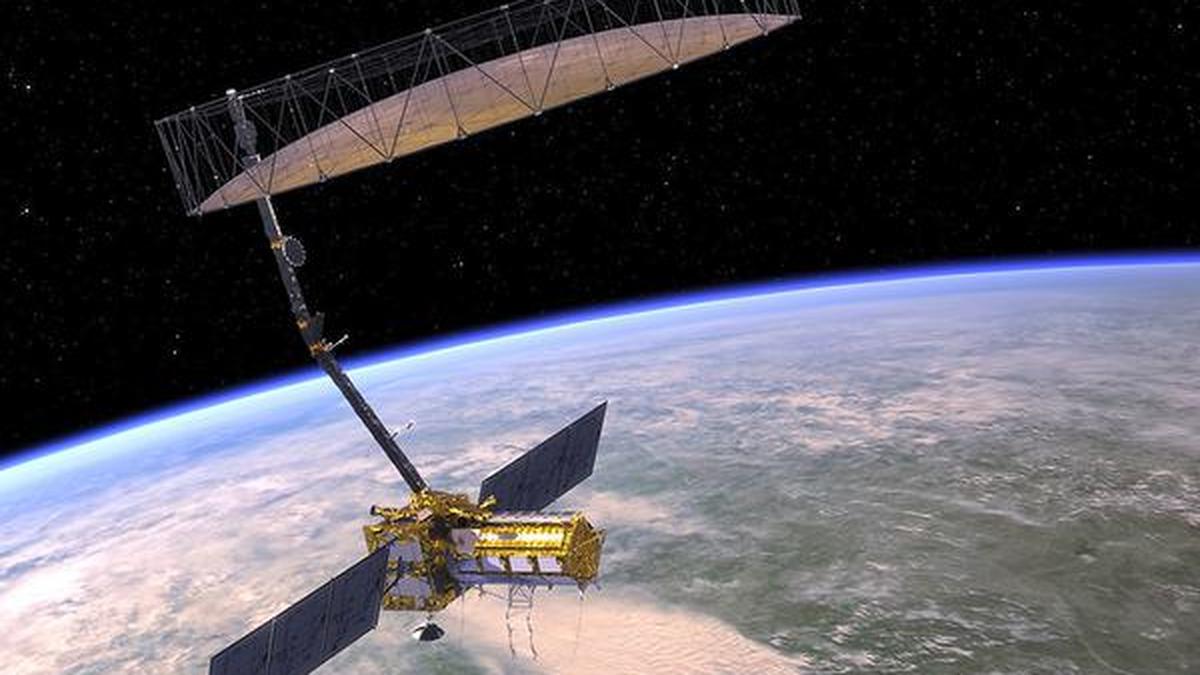
NASA-ISRO NISAR Satellite: Why It Matters
NASA-ISRO NISAR Satellite: Why It Matters

Quick Summary:
- ISRO plans to launch the NISAR satellite on july 30 from Sriharikota using a GSLV Mk-II rocket.
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is an advanced earth-observation satellite aimed at detecting changes in the earth’s surface with dual-band radar capabilities.
- The mission costs over $1.5 billion and has been in development for more than a decade. its planned mission lifetime is three years, with a design life of five years.
- Features include state-of-the-art L-band SAR (for tracking forest and soil changes) and S-band SAR (dedicated to Indian agricultural, forestry, and disaster management needs).
- The radar can operate in all weather conditions,day/night,penetrating clouds and vegetation. It will scan every spot on Earth every 12 days and capture fine-resolution data with swath widths up to 240 km.
- Application areas span disaster response (e.g.,floods/landslides),ecosystem mapping,food security research,land subsidence monitoring,biomass calculation,active cropland study maps (quarterly),accuracy in flood/dry zone mapping during disasters within five hours post-data acquisition.
- Data acquired globally will be freely accessible within hours; some resolution limitations apply above latitudes ~60º or certain regions (<10% of the Earth's surface).
Indian Contributions & Collaborative Work:
– NASA provided major antenna setups/carbon chassis operations but Bengaluru ISAT-NRCC also innovatively key **Chassis Testing Operational too-final spacecraft drive 낮’s including full standardized joint Avionix AI Pipeline end-to=””;
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...