Now Reading: Scientists Discover Potential New Human Ancestor: Homo juluensis
-
01
Scientists Discover Potential New Human Ancestor: Homo juluensis
Scientists Discover Potential New Human Ancestor: Homo juluensis

Rapid Summary
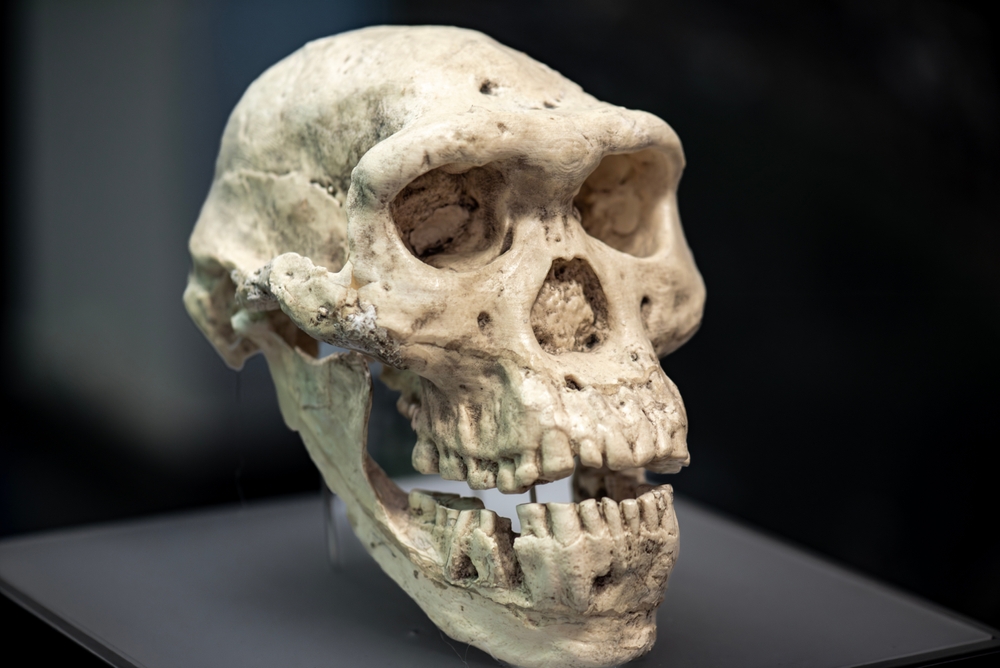
- Paleoanthropologists Christopher Bae adn Xiujie Wu proposed a new species classification, Homo juluensis, to group certain enigmatic hominin fossils found across East and Southeast Asia.
- Fossils included in this classification feature robust anatomical traits, including larger cranial capacities (1,700 cubic centimeters compared to Homo sapiens‘ 1,350 cm³).
- Key specimens include Denisovan fossils found in Siberia’s Denisova Cave,a jawbone from tibet (2019),another from Taiwan (2023),and assorted fossils from Xujiayao and Xuchang in China.
- The classification has sparked debate among experts; some propose alternative categorizations like Homo longi, introduced by Chris Stringer of the Natural History Museum in London.
- Researchers agree on the fluidity of categorizing ancient humans due to overlapping anatomical traits within species but acknowledge that fossil studies are inherently subjective to interpretation.
- Archaeological evidence suggests members of H. juluensis were skilled hunters with remains linked to horses and gazelles alongside crafted tools at Xujiayao excavation sites.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study of hominin classification underscores the complexity of unraveling human evolutionary history. While Bae’s work groups Asian hominins as part of the newly proposed species Homo juluensis, broader implications touch scientific debates about mankind’s interconnected biological heritage across regions-including India. central India’s Narmada Man remains excluded from definitive classifications despite its potential importance alongside Asian counterparts like Maba Man or tibetan discoveries.
For India specifically, these findings highlight how fragmented fossil records can limit understanding but also confirm South Asia’s critical position within human evolutionary discussions-offering fertile ground for further archaeological explorations into prehistoric life amid global frameworks like those shaping concepts such as Homo juluensis. Continued interdisciplinary studies could provide clarity not just for regional context but contribute globally toward refining methodologies used in categorizing ancient species based on shared or divergent physical capabilities in hunting and tool-making development.