Now Reading: Covid-19 and Flu Linked to Reactivation of Dormant Lung Cancer Cells
1
-
01
Covid-19 and Flu Linked to Reactivation of Dormant Lung Cancer Cells
Covid-19 and Flu Linked to Reactivation of Dormant Lung Cancer Cells
Quick Summary
- A new study indicates that respiratory viruses, such as flu and COVID-19, may trigger the growth of dormant cancer cells in the lungs through inflammation.
- Dormant cancer cells can lie inactive at secondary sites for years before proliferating into detectable tumors.
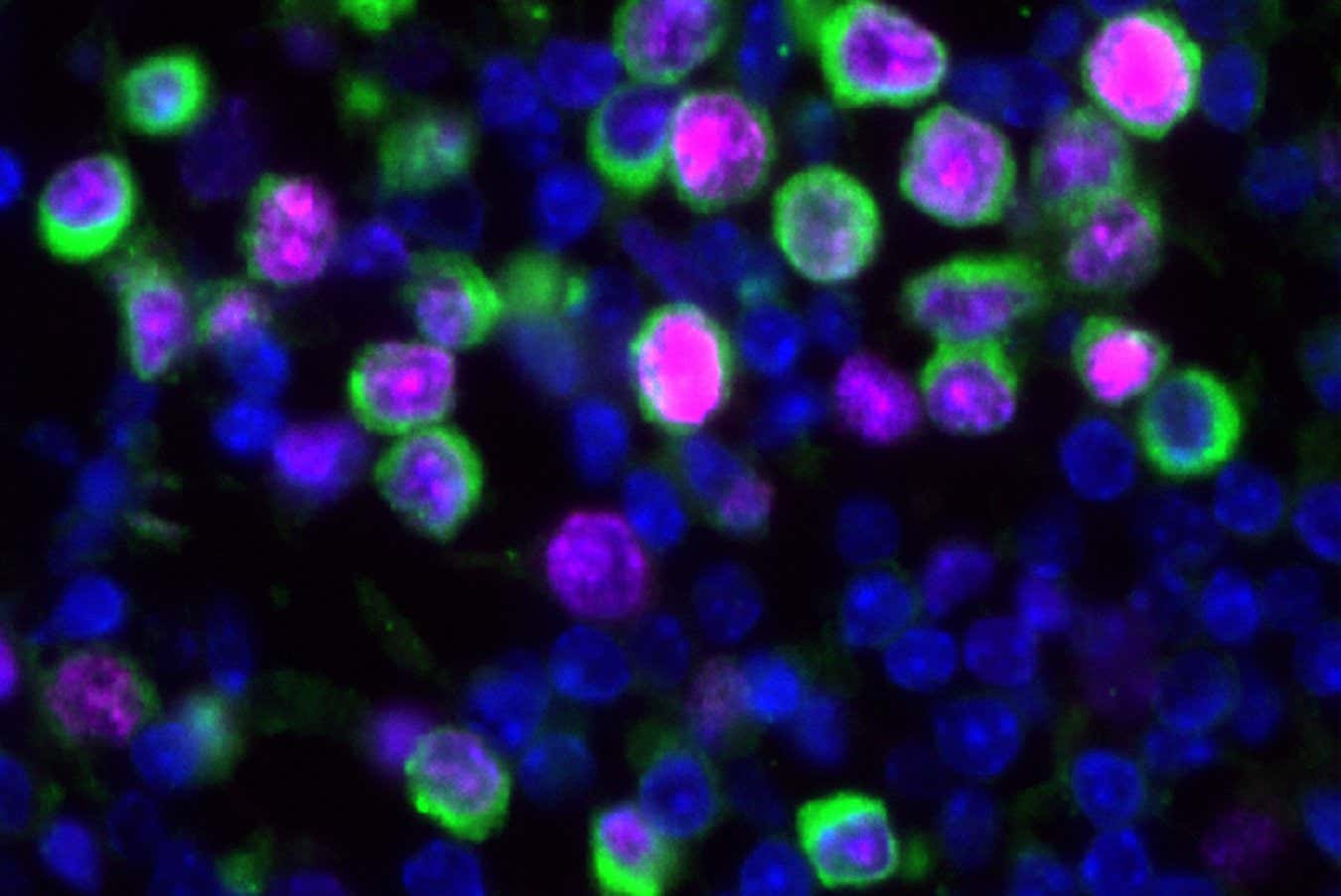
- Experiments on mice showed a 100-fold increase in lung cancer cells after infection with H1N1 (swine flu) and a 10-fold increase after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Uninfected mice showed no such changes.
- Elevated levels of an inflammatory molecule called IL-6 appear to drive this proliferation by reawakening dormant cancer cells without increasing their migration to the lungs.
- Infections caused transient tumor cell growth, but induced genetic changes linked to tumor metastasis even after the immune response subsided.
- Health records from 36,800 U.S.-based women diagnosed with breast cancer prior to the pandemic suggest higher rates of secondary lung cancers among those infected by COVID-19 during its initial years; more research is needed due to testing limitations during that period.
- Researchers propose vaccination against common respiratory viruses as an crucial preventive measure for cancer survivors.
!campaign=RSS%7CNSNS&utmsource=NSNS&utmmedium=RSS&utm_content=home”>Read More
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...