Now Reading: AI-Driven Design Unveils Tailored Peptide Binders Through Masked Language Modeling
-
01
AI-Driven Design Unveils Tailored Peptide Binders Through Masked Language Modeling
AI-Driven Design Unveils Tailored Peptide Binders Through Masked Language Modeling
Quick Summary
- The growth of novel therapeutics involves designing small molecules or protein binders targeting pathogenic proteins.
- Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) methods, such as molecular glues and PROTACs, utilize endogenous enzymes but are limited by accessible binding sites on proteins.
- Advances in deep learning tools like AlphaFold and RFdiffusion have enabled de novo protein binder design based solely on target structures.
- Proteome modeling faces limitations due to the conformational disorder of many disease-related proteins.
- Protein language models (pLMs), such as ESM-2, have revolutionized applications like antibody design and novel peptide generation.
- A new algorithm, PepMLM, builds upon ESM-2 to generate peptides uniquely positioned at the terminus of target sequences for efficient therapeutic binder design targeting challenging-to-drug diseases such as Huntington’s disease.
nature articleQuick Summary:
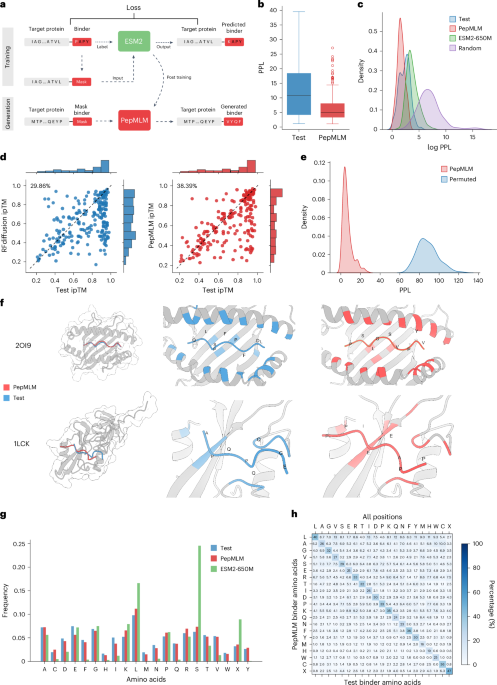
- PepMLM, a peptide-generation model, demonstrates improved ability to design protein binders compared to RFdiffusion. Benchmark analysis revealed PepMLM’s superior performance in modeling binding specificity and structural predictions through metrics like perplexity (PPL) and AlphaFold-Multimer evaluation scores.
- Comparative tests showed higher hit rates for PepMLM relative to RFdiffusion in terms of interface-predicted template modeling (ipTM) and pLDDT scores.Binding design quality was rigorously verified using statistical analysis with distinct observed effects on mismatched pairs.
- Experimental validation included testing peptide binders for two disease-related targets: NCAM1 and AMHR2. PepMLM-designed peptides were found to have stronger binding response in ELISA tests compared to RFdiffusion candidates at low concentrations, suggesting potential therapeutic applications with minimal off-target interactions.
- Using an innovative fusion strategy, PepMLM-generated peptides demonstrated the capability of guiding targeted ubiquitin-mediated degradation of pathogenic proteins like mHTT involved in Huntington’s disease via E3 ubiquitin ligase systems termed uAbs.
- Advanced generation techniques allowed precise amino acid-level incorporation based on biochemical parameters critical for binding affinity improvements across diverse settings.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
PepMLM presents promising advancements within computational drug discovery by significantly improving protein-peptide binder design accuracy and specificity over existing models such as RFdiffusion. These findings could impact India’s healthcare research landscape where AI-assisted molecular therapeutics may reduce reliance on costly experimental screenings while enhancing precision medicine endeavors targeting diseases like acute myeloid leukemia or polycystic ovarian syndrome-conditions relevant domestically due to prevalence rates or biopharmaceutical interests.The study’s demonstration of degrading Huntington’s disease-driving proteins highlights opportunities for applying such systems against neurodegenerative diseases which are gaining epidemiological importance worldwide including India due increasing geriatric demographic proportions Moreover integrating applications opens synergy scope-based Biologics pharma.
Read moreQuick Summary
- Researchers developed a novel peptide-guided technology, PepMLM, designed to degrade proteins critical in diseases and viruses.
- PepMLM successfully targeted disease-related proteins, including mutant Huntington protein (mHTT) and MSH3 across multiple constructs, showing visible reductions upon induction.
- for emerging viruses like Nipah (NiV), Hendra (HeV), and human metapneumovirus (HMPV), the technology achieved up to 49% reduction of viral phosphoproteins. Four specific antibodies showed near-complete degradation of HMPV levels after infection in experimental settings.
- Results validate high hit rates (>60%) for peptide design using this platform and demonstrate applications ranging from antiviral solutions to therapeutic interventions targeting sensitive cellular mechanisms like ferroptosis-linked pathways.
Link for detailed reading: Nature Article Full Text
Indian Opinion Analysis
PepMLM’s triumphant submission represents promising advancements in computational drug development with potential global benefits but also carries significant implications for India.Diseases caused by viruses like Nipah and hendra have regional relevance; outbreaks recorded predominantly impact South Asia-including India-and underscore the need for innovative therapeutic strategies provided by technologies like PepMLM.
For India, where healthcare systems frequently enough grapple with limited vaccine avenues or antivirals against uncommon yet deadly pathogens, such tools may accelerate preparedness-especially during public health emergencies rooted in zoonotic transmission risks.Additionally, extending these capabilities against broader targets within endemic diseases prevalent across Indian subregions could help combat unaddressed challenges efficiently.
Overall adoption might depend on accessible frameworks without overly resource-demanding setups; significant scalability through partnerships involving indian medical research infrastructure holds promise as a cooperative model spanning preventive medicine innovations locally globally tackling pandemics edge research breakthroughs adaptation long-term deployment feasibility evaluation scientific climate policies necessity shaping vital direction-already-needed transitional areasאשכול anticipatory_strengthenedQuick Summary
- PepMLM leverages ESM-2, a transformer-based protein language model, for designing peptide binders.
- The methodology involves masking binder sequences and reconstructing them based on contextual clues from the target protein sequence using conditional modeling frameworks.
- Training was conducted using ESM-2 versions (650M and 3B) with high computational infrastructure including NVIDIA GPUs.
- Evaluation included metrics like pseudo-perplexity (PPL), test set benchmarking, and structure comparisons to determine alignment accuracy.
- Competing approaches like RFdiffusion were employed as parallel validations to test the design quality of binders generated by PepMLM.
- Experimental validation involved expression, purification processes in bacterial systems, structural visualization through software tools like ChimeraX, and performance assays via techniques such as immunofluorescence staining and ELISA tests.
Indian Opinion Analysis
PepMLM’s implementation represents notable advancements in therapeutic peptide binder development through computational modeling-a field of growing importance globally due to its implications for precision medicine and biotechnology innovation. India’s robust academic ecosystem in bioinformatics can leverage such AI-driven tools to further research applications focused on human diseases or even agricultural challenges involving plant proteins.
Investments into computational biology are critical as models like PepMLM demonstrate their ability to reduce experimentation costs significantly while enhancing predictive accuracy-making them promising candidates for drug discovery platforms within Indian biopharma sectors.
For more details: Read moreQuick Summary:
- The research introduces PepMLM, a model for peptide generation conditioned on target sequences, leveraging masked language modeling (MLM).
- PepMLM is trained on a curated dataset and facilitates functional peptide binder design.
- The code and datasets are accessible on GitHub and Hugging Face platforms with user-friendly demos for practical applications.
- The study highlights advancements in peptide therapeutic designs using machine learning techniques.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The development of programmable models like PepMLM marks significant technological progress in biomedical engineering. India’s vast population faces healthcare challenges that can benefit immensely from innovations such as these. enhancing access to cutting-edge biotech tools will be crucial for Indian pharmaceutical research to stay competitive globally. Moreover, the open availability of resources could democratize scientific exploration, allowing Indian institutions and startups to engage at low costs. Integrating artificial intelligence into such domains aligns well with India’s ambitions in AI-focused growth strategies.
Read more: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15122756Quick Summary:
- Article highlights advancements in deep learning models focused on protein design and interaction studies.
- Models like ProtGPT2, MMseqs2, AlphaFold-Multimer, and others utilize language models to predict protein structures and binding effects with atomic-level precision.
- Applications discussed include computational optimization of peptides for SARS-CoV-2 degradation, peptide-guided degraders for targeted treatment designs, antibody evolution using general protein language models, and prediction tools like PepNN.
- Collaborative AI systems are being employed to address challenges in structural biology and healthcare innovation.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The article underscores how advanced computational tools like AI-driven protein modelers could provide significant breakthroughs in global biomedical research. For India, embracing such technologies offers a dual advantage: facilitating indigenous innovations in biotech while ensuring the country’s healthcare sector remains competitive internationally. Developing expertise in these applications can open doors for India’s pharmaceutical industry to explore cutting-edge treatment solutions tailored to regional diseases or pandemics such as COVID-19-related conditions.Additionally, investments into research infrastructure tied to machine learning-based biotechnological modeling could drive collaborations between Indian academic institutions and global research initiatives-furthering long-term benefits not just economically but also scientifically.
For further details: PubMed central reference 15Quick Summary:
- The provided text appears to be reference materials that include sponsored links, publication details, academic journal entries, preprints, and digital identifiers related to biomedical research.
- It mentions various studies on topics such as Huntington’s disease, viral infections (Nipah and Hendra), therapeutic peptides, protein language models for biological design, and the applications of artificial intelligence in drug discovery.
- Several references highlight advancements in genome editing mechanisms (e.g., siRNA-mediated silencing) or AI-designed solutions for protein functionality enhancements.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
While the raw text does not directly focus on India-specific issues or developments,it indirectly ties into global scientific progress that India stands to benefit from. India’s growing pharmaceutical and biotech sectors could draw insights from these groundbreaking studies in AI-driven models for developing novel therapeutics or addressing diseases like huntington’s-with potential implications for its domestic healthcare industry. Additionally, India’s emphasis on research collaborations could enhance contributions to solving global health crises involving zoonotic viruses like Nipah-which have previously affected parts of India-through international partnerships on advanced diagnostic tools and vaccines.
Quick Summary
- A research team from Duke University, Cornell University, and other institutions has published findings on PepMLM, a novel technology for designing therapeutic peptide binders using span masked language modeling.
- The study focuses on creating protein-stabilizing peptides to target and degrade harmful proteins, which could benefit treatment approaches in diseases like Huntington’s disease and viral infections.
- Funding sources include NIH grants, startup funds from Duke University and Cornell University, as well as contributions from multiple foundations like CHDI Foundation and Wallace H. Coulter Foundation.
- The researchers disclosed affiliations with biotechnology firms UbiquiTx,Inc., but declared no broader competing interests apart from patents related to the studied technologies.
Read More: CAS | Zenodo DOI
Indian Opinion Analysis
PepMLM represents a noteworthy stride in blending artificial intelligence with biomedical research. While its immediate global implications are evident in addressing protein-driven diseases such as Huntington’s disease or difficult-to-treat viral infections, the system holds significant potential for Indian healthcare innovations. AI-driven methods like PepMLM could open avenues for localized peptides targeting region-specific diseases or genetic conditions prevalent in India.
The ability to computationally design targeted therapeutics may reduce cost barriers associated with traditional drug development-a critical advantage given India’s large population base and healthcare disparities. close collaboration among academic institutions and startups will be pivotal for fostering such advanced technologies locally without outsourcing intellectual capital excessively.
Maintaining transparency around patent claims is crucial when commercializing these breakthroughs globally while ensuring accessibility remains viable across developing nations like India.
Read More: PubMed central | Read More