Now Reading: Astronomers Capture First Moments of Planet Formation in Distant Solar System
-
01
Astronomers Capture First Moments of Planet Formation in Distant Solar System
Astronomers Capture First Moments of Planet Formation in Distant Solar System

Rapid Summary
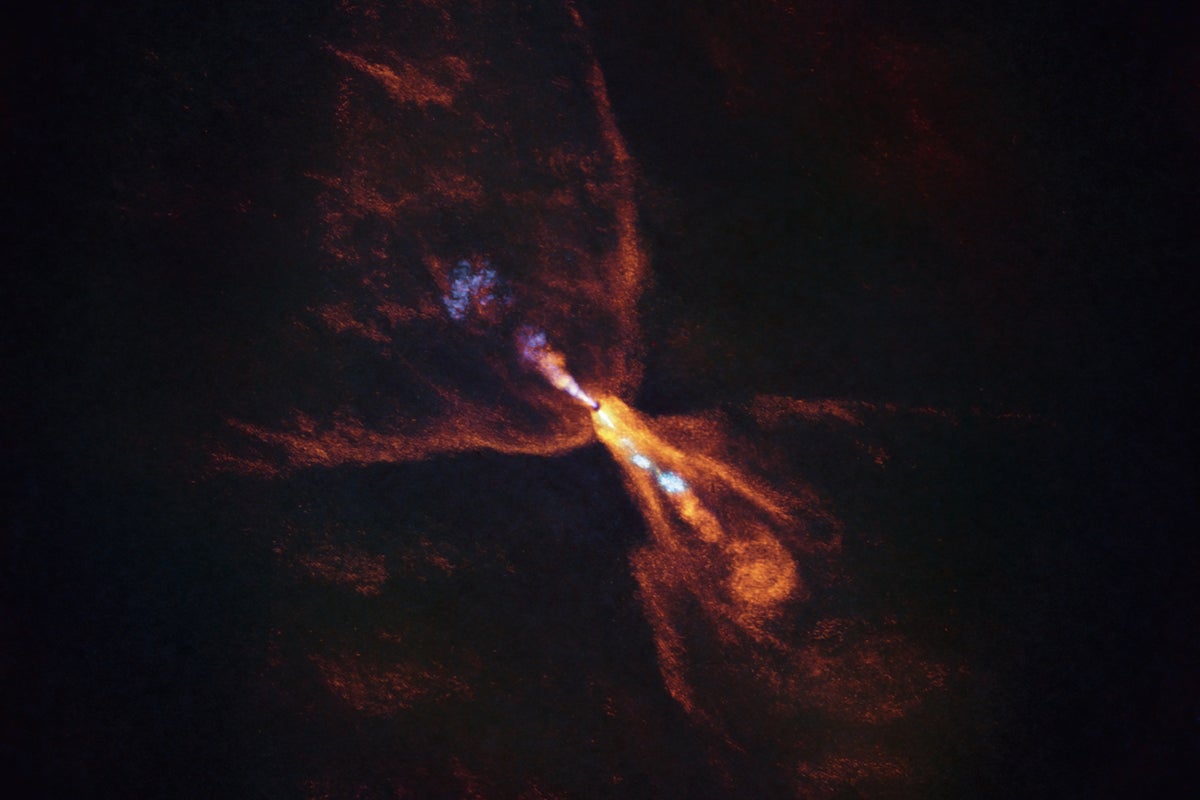
- Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter array (ALMA) to observe HOPS-315, a protostar 1,400 light-years away in Orion.
- The protostar weighs 0.6 solar masses and resembles an early-stage analog of our own sun.
- Observations revealed a protoplanetary disk around HOPS-315 containing crystalline mineral grains formed as hot gas cooled.
- These grains are essential precursors for planetesimals-the building blocks of planets-and mirror conditions thought to have existed during our solar system’s formation.
- Signals detected from silicon monoxide and crystalline silicates suggest early conditions for calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions (CAIs), which are pivotal to understanding “time zero” in planetary creation history.
- The findings confirm that certain regions within the disk align wiht models predicting CAI formation but did not directly detect actual cais.
- Challenges remain due to complex dynamics in star systems involving disks, jets, winds, and molecular clouds; there is potential for further observations of similar stars like HOPS-68.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s involvement in global astronomy research is steadily advancing, exemplified by projects like India’s contributions to space telescopes or astrophysics studies conducted at IITs. Findings about HOPS-315 provide fresh insight into planet formation processes that could help Indian scientists refine theories on planetary evolution or inform studies on asteroid mining prospects relevant to national space ambitions. Such research underscores the importance of India developing domestic infrastructure comparable to JWST or ALMA over time.This discovery also holds long-term importance for India’s growing stature as an emerging player in space exploration. Collaboration with international collaborators remains indispensable; however, cultivating foundational expertise thru deeper investments at ISRO and Indian universities can strengthen independence and global competitiveness as astronomic knowledge expands globally.