Now Reading: Australian Man Succumbs to Rare Rabies-Like Disease
-
01
Australian Man Succumbs to Rare Rabies-Like Disease
Australian Man Succumbs to Rare Rabies-Like Disease

Fast Summary:
- A man in his 50s from northern New South Wales, Australia, died from Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV), a rare rabies-like infection.
- NSW Health confirmed he had been bitten by a bat months earlier and received treatment at the time, though no specific details of the treatments were given.
- This is the fourth documented case of human infection with ABLV since it was first identified in 1996.
- ABLV is transmitted through bites or scratches from bats and impacts the central nervous system. once symptoms appear, it becomes untreatable and leads to death within weeks.
- early symptoms include headache,fever,fatigue; advanced stages result in paralysis,delirium,convulsions.
- The public has been strongly advised to avoid contact with bats; only trained individuals vaccinated against rabies should handle them.
- Preventative measures post-exposure include rapid wound care and administration of antibodies and vaccines-effective if symptoms haven’t developed.
Image:
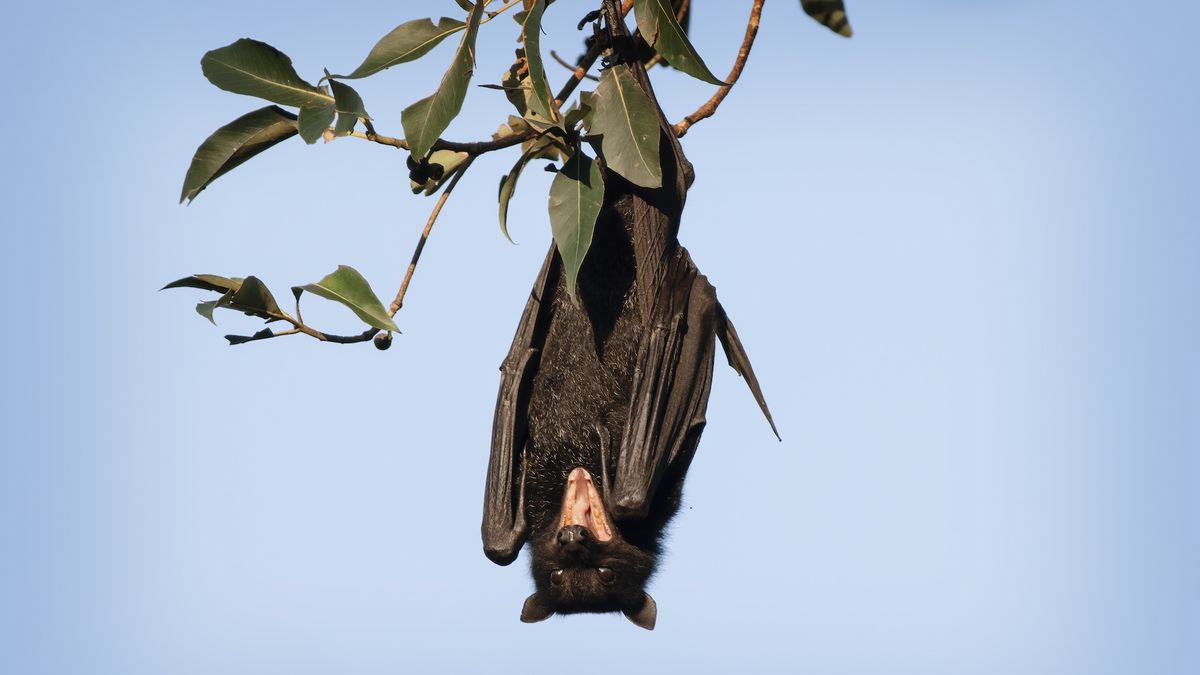
!A bat hanging upside down from a branch
An Australian flying fox. these bats are known carriers of Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV).
(Image credit: Getty Images)
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The tragic death caused by australian bat lyssavirus underscores crucial lessons for India regarding zoonotic diseases. As india shares ecosystems with diverse wildlife-including large populations of bats-awareness about similar viruses is crucial for public health safety.Rabies remains widespread in India due to dog bites, but potential risks of lesser-known Lyssaviruses demand vigilance given our tropical climate’s compatibility with wildlife-related pathogens.For india’s health infrastructure, this case serves as a reminder that rapid public education on handling exposures after animal encounters can save lives. Legislating strict protocols about wildlife interaction alongside nationwide vaccination campaigns for high-risk handlers could be instrumental in reducing future risks related to emerging zoonotic infections.
Read More: Link