Now Reading: Can a 100W LED Bulb Work in a 60W Socket? Here’s What to Know
-
01
Can a 100W LED Bulb Work in a 60W Socket? Here’s What to Know
Can a 100W LED Bulb Work in a 60W Socket? Here’s What to Know

Rapid Summary
- LED bulbs are energy-efficient, consuming up to 90% less electricity than traditional incandescent bulbs while offering a longer lifespan and compatibility with smart systems like Alexa and dimmer switches.
- Since 2023, incandescent light bulbs have been largely banned in the U.S., driving households to switch to LEDs.
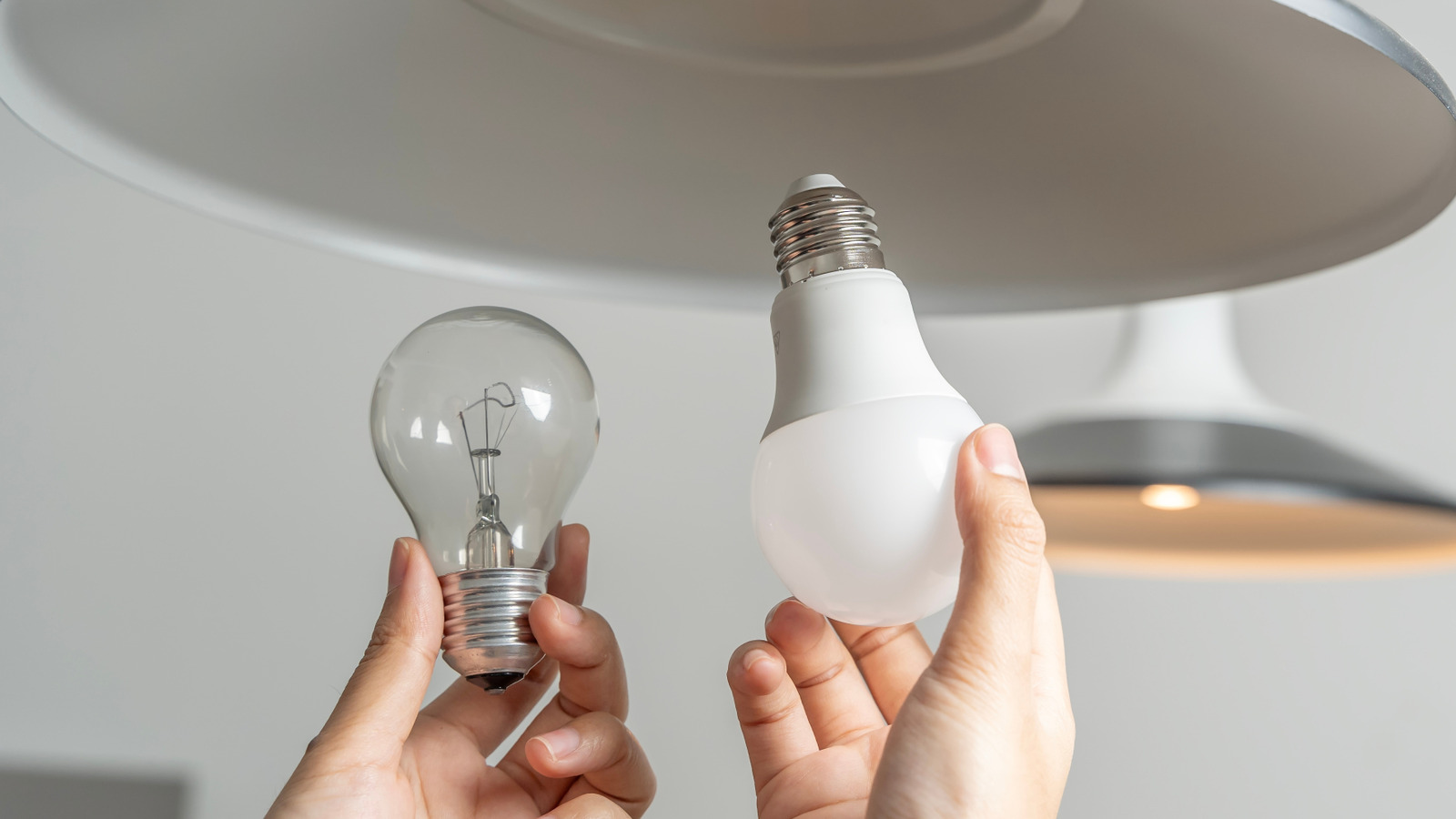
- Modern household LED bulbs labeled “100W equivalent” emit as much light as a 100-watt incandescent bulb but use significantly less power (around 15-19W only).
- light fixtures with a maximum wattage rating of 60W can safely handle “100W equivalent” LED bulbs due to their lower actual power consumption.
- Installing an actual output 100-watt LED bulb (common for industrial uses) into a fixture rated for only 60 watts poses serious safety risks, including overheating and fire hazards.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s ongoing focus on energy efficiency makes information about LED technology highly relevant.The transition from inefficient high-energy incandescent lights to LEDs could provide critically important environmental and economic benefits. Households need clear guidance regarding watt equivalence vs. actual wattage consumption while choosing lighting solutions.Misinterpreting these specifications may lead not just to improper usage but also heightened safety risks in Indian homes where fixtures might lack robust regulatory compliance standards compared to developed countries.
Given India’s push toward sustainable infrastructure alongside urbanization, encouraging consumer awareness of safe practices around the adoption of LEDs aligns with broader goals for resource optimization and climate-resilient urban development.