Now Reading: Canada’s Wildfire Smoke: Rising Concerns Over Increased Toxicity
-
01
Canada’s Wildfire Smoke: Rising Concerns Over Increased Toxicity
Canada’s Wildfire Smoke: Rising Concerns Over Increased Toxicity

Quick Summary
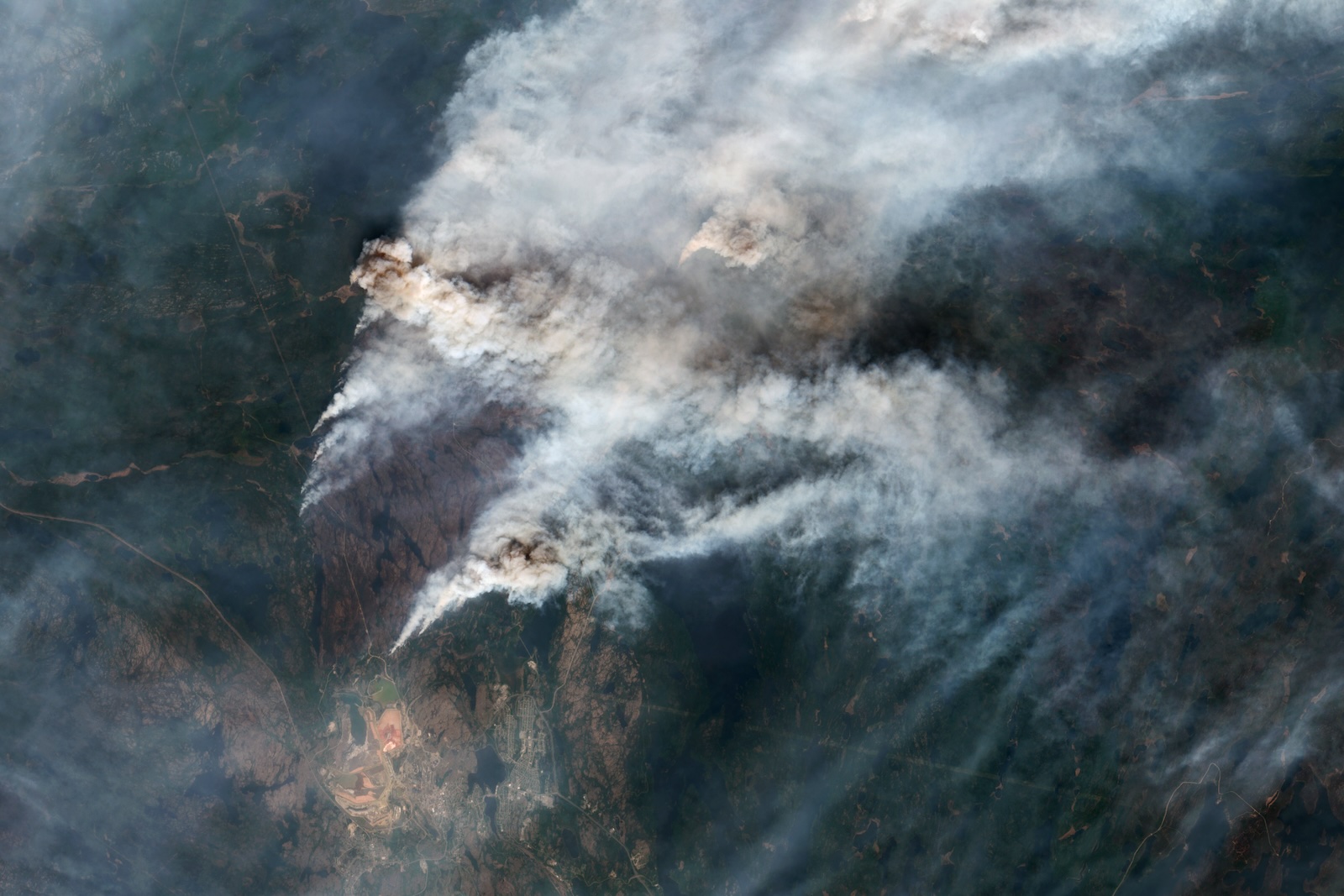
- Over 200 wildfires are burning across central and western Canada, with many being out of control due to inaccessible areas.
- 27,000 people have been evacuated, including the mining city of Flin Flon in Manitoba. No structures have been destroyed there yet.
- smoke from these fires has lead to hazardous air quality across parts of Canada and the U.S., even reaching Europe.
- Wildfire smoke contains PM 2.5 particulate matter linked to health issues such as respiratory problems and increased risk of cardiac arrest.
- Scientists suspect these fires may mobilize toxic metals like arsenic and lead from polluted soils caused by historical mining operations in Canada.
- Peatlands, known for storing carbon and pollutants like metals, burn slowly in fires (called peat or zombie fires) that release dangerous toxins over extended periods.
- Indigenous communities disproportionately face wildfire-related evacuations despite having customary fire management practices that reduce wildfire severity.
Image Included:
!Black smoke fills the sky over a neighborhood burning in Los Angeles
Indian Opinion Analysis
Wildfires raging across Canada underscore critical global concerns about climate change-driven natural disasters. For India-a nation grappling with air pollution crises-the long-range impacts of wildfire smoke offer relevant lessons about transboundary environmental hazards. The presence of toxicants like arsenic further amplifies dangers associated with unchecked industrial legacies.
Equally notable is Canada’s experience with prescribed burns rooted in Indigenous practices. India can learn from this approach as it seeks scalable solutions for managing its own forested regions prone to fire risks during hotter months. Focusing on mitigation strategies while addressing environmental justice issues affecting vulnerable communities could serve India’s dual goals: protecting ecosystems and supporting marginalized groups possibly affected by disasters.
The broader implications tie into accelerating global efforts for climate adaptation while rethinking industrial safeguards-both echo urgent priorities shared by India given its population density near polluting industries combined with evolving environmental stressors.