Now Reading: Chile’s Patagonia Glacier Faces Rapid Retreat Crisis
-
01
Chile’s Patagonia Glacier Faces Rapid Retreat Crisis
Chile’s Patagonia Glacier Faces Rapid Retreat Crisis
Fast Summary:
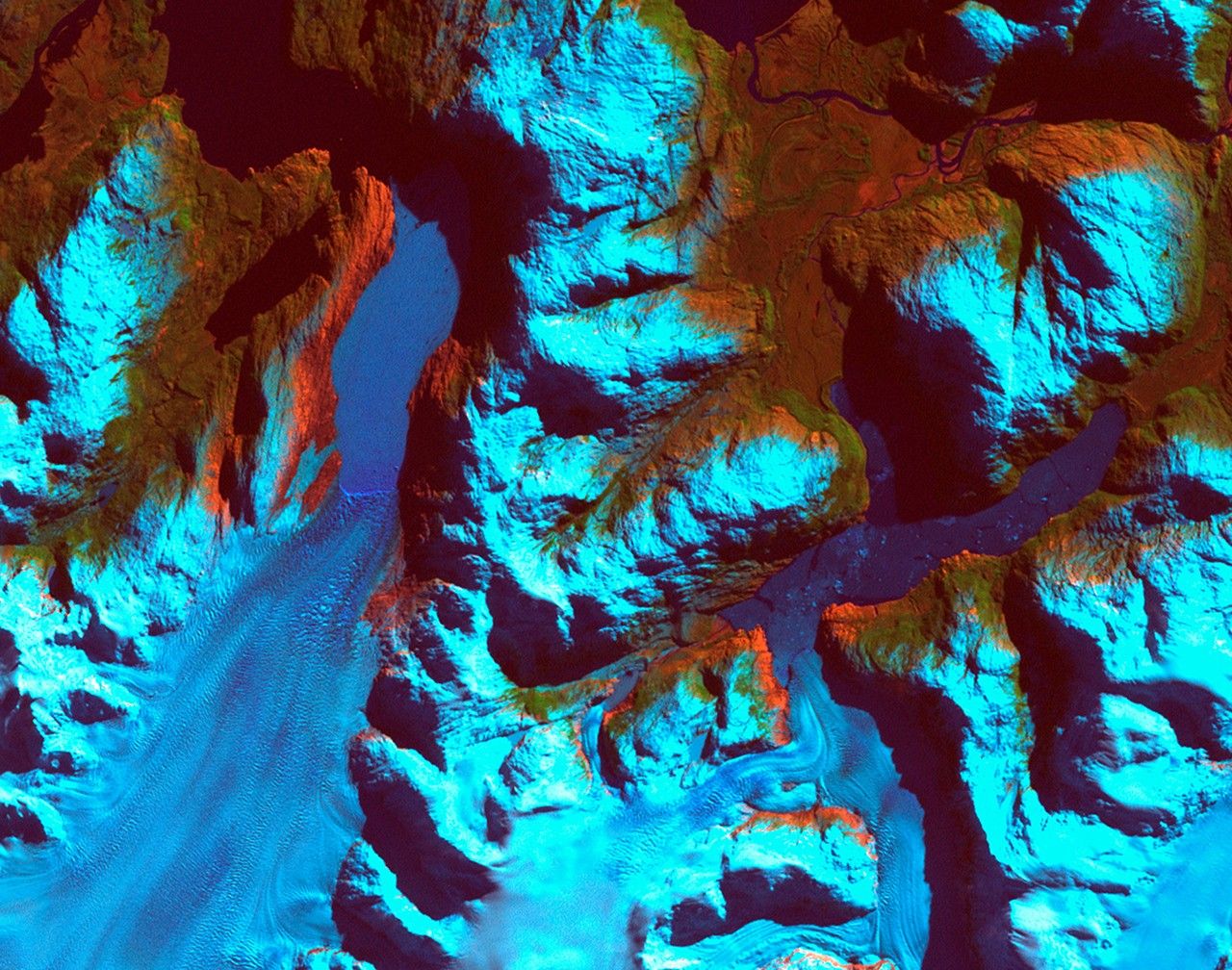
- Event: Retreat of Patagonia glaciers in Chile observed between September 18, 1986, and August 5, 2002.
- Details:
– The glacier on the left retreated nearly 10 kilometers (6.2 miles).
– The smaller glacier on the right receded over 2 kilometers (1.2 miles).
- Impact:
– Formation of two ribbon lakes behind debris left by glacier advances.
- Methodology: Satellite imagery served as a tool for monitoring changes in glacier size and direction, impacting water bodies.
- Data Sources:
– Left image captured by Landsat 5’s Thematic Mapper sensor (1986).
– Right image captured by Landsat 7’s Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus sensor (2002).
Images accompanying text can be viewed below:
Before & After comparative visual:
!RetreatComb2.jpg”>Patagonia Glaciers After
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The retreat of glaciers in regions like Patagonia highlights global concerns over climate change and its cascading effects on ecosystems worldwide. While this event directly pertains to South America, glacial retreats also pose implications for Indian science and policy. India’s Himalayan glaciers are vital for freshwater resources across northern states-any similar trends could have significant ecological impacts domestically.
India’s space program has already been instrumental in advancements related to satellite imagery through missions like ISRO’s Cartosat or RISAT series. This provides India an opportunity to further improve long-term monitoring capabilities using space-based tools akin to those employed by NASA and USGS here.
the case underscores the importance of sustained investment in environmental studies alongside international collaborations given shared challenges like water resource management influenced by glacial dynamics.