Now Reading: Could Human Hibernation Become Reality? Scientists Explore the Possibilities
1
-
01
Could Human Hibernation Become Reality? Scientists Explore the Possibilities
Could Human Hibernation Become Reality? Scientists Explore the Possibilities
Quick Summary
- scientists are exploring hibernation-like states for humans, inspired by the metabolic properties of animals like bears and squirrels.
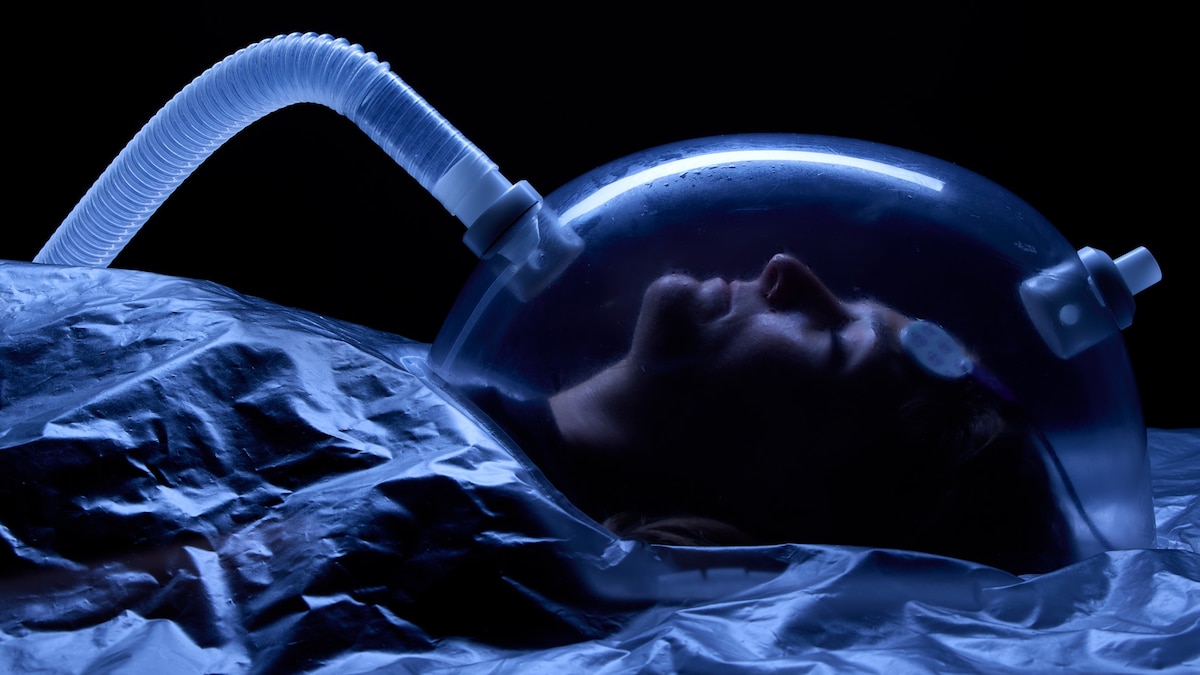
- NASA-supported trials show that inducing “twilight sleep” with specific sedatives lowers metabolism by 20% without immobilizing participants or requiring ventilators.
- Hibernation research aims to reduce payload in long-duration space travel by decreasing astronauts’ need for food, oxygen, and protection from radiation-critical for Mars missions slated for the 2030s.
- Beyond space exploration, mimicking hibernation offers medical benefits on Earth, including larger treatment windows for strokes/heart attacks, combating ICU muscle loss, obesity management, and diabetes therapies.
- Bears show unique biological adaptations during hibernation: resistance to insulin without health consequences; ability to maintain muscles; slowed heart rates with reduced blood clotting risk. Researchers aim to decode these mechanisms using advanced genetic analysis tools.
- Experiments on non-hibernating species like rats have identified hypothalamic neurons linked to body temperature regulation-a possible breakthrough in artificially inducing hibernation in humans safely thru drugs.
Images:
- A test subject monitored after induced sleep 25032906853.jpg”>Image
- Monitoring bears during late hibernation stages Image
- Sleeping squirrel under lab testing conditions Image
Indian Opinion Analysis
Human hibernation research presents promising applications beyond interplanetary travel-it could revolutionize medical treatments and extend operational limits of emergency care in India’s rural areas facing limited healthcare infrastructure. For social implications within India specifically- conversations about economic efficiency environmental adjacencies as auxiliary yet impactful possibilities .
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...