Now Reading: Curiosity Rover Detects Mysterious Changes in Martian Atmosphere
-
01
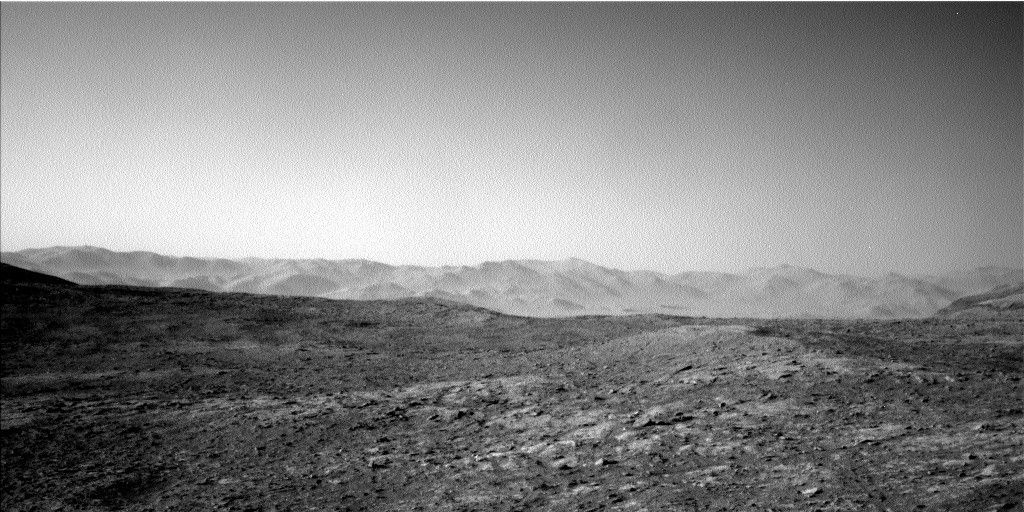
Curiosity Rover Detects Mysterious Changes in Martian Atmosphere
Curiosity Rover Detects Mysterious Changes in Martian Atmosphere

Rapid Summary
- Mission Update: The Mars Curiosity rover resumed operations after enduring southern Mars winter, now benefiting from warmer temperatures which free up power for activities.
- Geological Analysis: Curiosity brushed a rock target named “Hornitos” with potential cross-cutting veins and analyzed it using APXS (Alpha particle X-Ray Spectrometer). Mastcam captured images of other targets including “Volcán Peña Blanca” and “Ayparavi.” ChemCam conducted a 5-point chemical analysis on the “Ayparavi” target.
- Atmospheric Studies: Nighttime APXS measurements were used to study argon levels in Mars’ atmosphere to trace global circulation patterns.chemcam conducted “Passive Sky” observations, collecting data without it’s laser, to understand daily and seasonal atmospheric trends around Gale Crater.
- Mobility: The rover drove about 37 meters (121 feet) during planned operations while recharging for further exploration.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s space research community may find inspiration in Curiosity’s adaptability during extreme seasonal changes on Mars. the detailed methods employed – such as simultaneous use of APXS and ChemCam instruments- highlight innovation in maximizing energy efficiency while collecting diverse scientific data. This approach coudl serve as a reference point for India’s own efforts in planetary exploration, especially with upcoming missions like Chandrayaan or interplanetary plans.
Furthermore, the focus on atmospheric studies has long-term implications for understanding Earth’s past climate trends through comparative analysis with Martian systems. As India expands its scientific contributions globally through ISRO collaborations, reports like these emphasize areas where international partnerships could flourish – namely robotic mobility techniques or advanced environmental instrumentation designs that deepen planetary knowledge.