Now Reading: Delhi to Launch Cloud Seeding Trials in September to Tackle Air Pollution
-
01
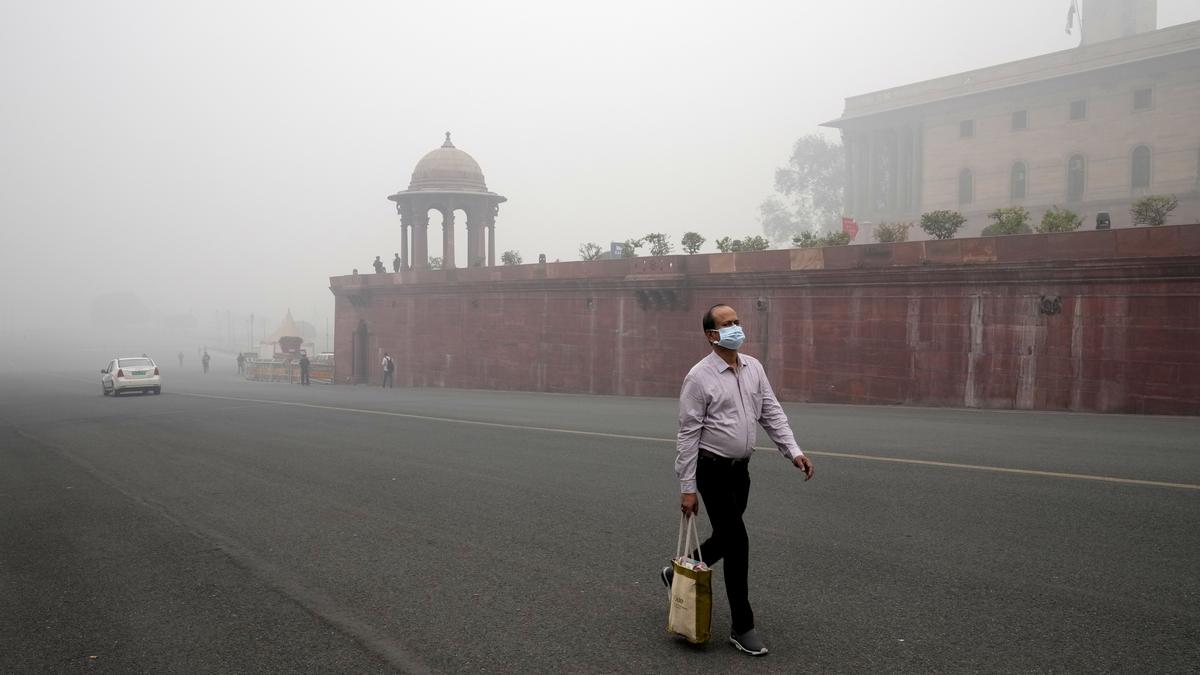
Delhi to Launch Cloud Seeding Trials in September to Tackle Air Pollution
Delhi to Launch Cloud Seeding Trials in September to Tackle Air Pollution

Speedy Summary:
- Delhi’s First Cloud Seeding Trials: Delhi will conduct its first-ever cloud seeding trials in the first two weeks of September 2025 to combat air pollution by inducing artificial rainfall.
- Project Timeline and Preparations: Initially planned for July, trials were postponed due to unsuitable weather conditions. The revised window coincides with retreating monsoon conditions deemed more favorable.
- Budget and leadership: ₹3.21 crore allocated for the project, led by IIT-Kanpur’s Department of Aerospace Engineering.
- Aircraft Details: The trial will use a Cessna 206-H (VT-IIT) aircraft equipped with cloud seeding instruments approved by DGCA. necessary licenses and safety protocols are in place.
- Trial Areas: Five sorties planned over pollution-prone areas in north Delhi (rohini, Bawana, Alipur, Burari) and adjoining regions in Uttar Pradesh (Loni, Baghpat).
- Implementation Approach: Hygroscopic particles like sodium chloride will be released into clouds below the base to stimulate precipitation and potentially reduce airborne pollutants.
- Official Statement: Surroundings Minister Manjinder Singh Sirsa expressed optimism about the initiative as a scientific solution for improving Delhi’s post-monsoon air quality.
Indian opinion Analysis:
Cloud seeding emerges as an innovative scientific intervention against persistent air pollution in delhi-a city grappling with hazardous air quality levels regularly. By targeting localized weather modification through this method during retreating monsoon conditions, authorities aim not only to reduce airborne pollutants but also set a precedent for using advanced technology to address environmental challenges.
IIT-Kanpur’s leadership of this initiative enhances credibility given its technical expertise. However, such projects carry inherent uncertainties-success hinges on favorable meteorological conditions during implementation. If accomplished,this pilot project could propel broader adoption across othre polluted regions in India while inviting scrutiny on cost-effectiveness versus traditional anti-pollution measures like stricter emission standards or urban forestation initiatives.
While Delhi’s experiment is set within clear operational safety guidelines laid down by nodal aviation authorities like DGCA-and avoids prohibited zones-it hints at policy openness toward unconventional solutions at considerable expense (₹3.21 crore). Observers might expect further data transparency post-trial evaluation to gauge both ecological impact and technological efficacy nationwide.
Read More: The Hindu Article