Now Reading: Fishing Gear Emerges as Key Source of Microplastic Pollution on Indian Coasts
-
01
Fishing Gear Emerges as Key Source of Microplastic Pollution on Indian Coasts
Fishing Gear Emerges as Key Source of Microplastic Pollution on Indian Coasts

Quick Summary
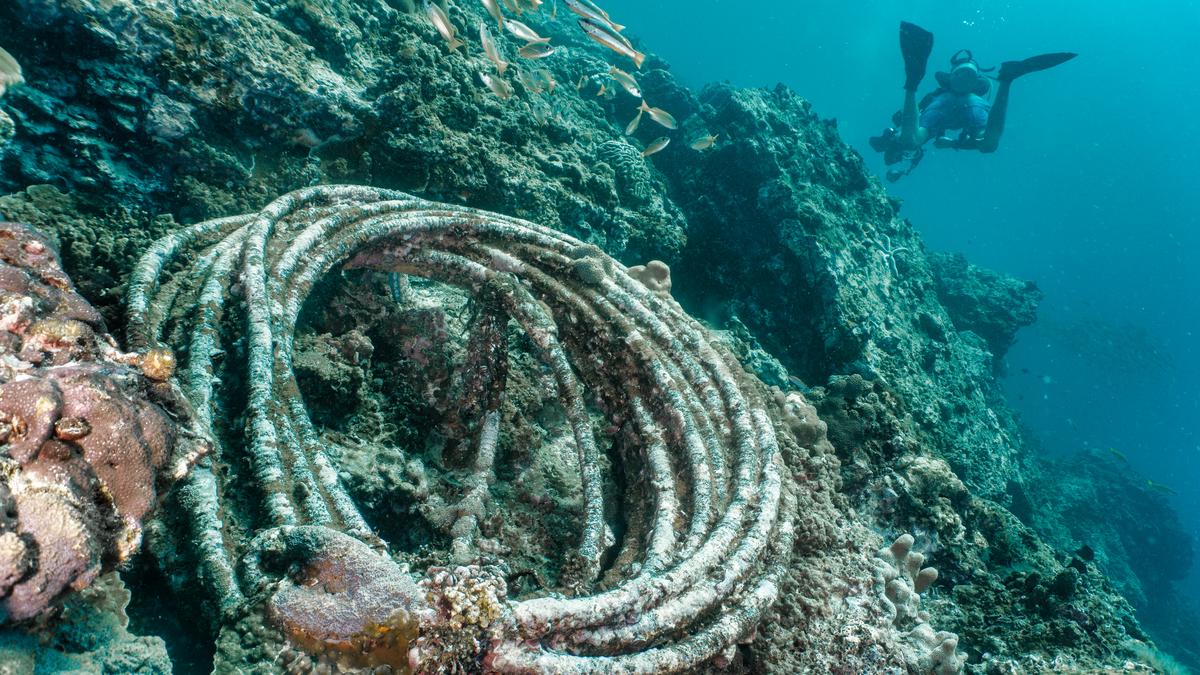
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), through the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR), conducted field surveys from 2022 to 2025 along India’s coastline to measure microplastic and marine debris levels.
- Surveys where conducted on 19 west coast transects (Porbandar,Gujarat to Kanyakumari,Tamil Nadu) and 25 east coast transects (puri,Odisha to Thoothukudi,Tamil Nadu).
- Major sources of microplastic pollution identified: riverine inputs and abandoned/lost/discarded fishing gear (ALDFG).
- Microplastics are particles sized between 1 micrometre (µm) to 5 millimetres (mm). Thay can be primary microplastics or formed as secondary breakdown products.
- Concerns cited: potential links between microplastics and tumours; toxicity impacting marine/aquatic life.
- India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) commissioned research last year on detecting microplastics in food products due to increasing concerns about contamination.
- Tests by environmental group Toxics Link found presence of various forms of microplastics in all samples tested across salt and sugar.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Microplastic pollution presents significant ecological challenges for India’s coastal ecosystems. The findings underscore its major sources-riverine inputs and discarded fishing gear-which reflect gaps in waste management infrastructure and sustainable fishing practices. Surveying such vast stretches along the coasts highlights India’s growing focus on understanding this issue scientifically. Though, health implications linked with microplastic contamination call for significant policy interventions.
The involvement of FSSAI points toward increased institutional recognition but also raises questions about public exposure risks extending beyond marine environments into everyday staples like salt or sugar.While research initiatives signal progress, proactive measures such as reduction strategies at rivers’ origins or stricter fishing equipment handling regulations are essential steps forward. A dual focus combining ecosystem stewardship with human health safeguards will likely define future actions against this widespread issue.
Read more at: The Hindu