Now Reading: FMCG Companies Focus on Restoring Product Sizes
-
01
FMCG Companies Focus on Restoring Product Sizes
FMCG Companies Focus on Restoring Product Sizes

Swift Summary
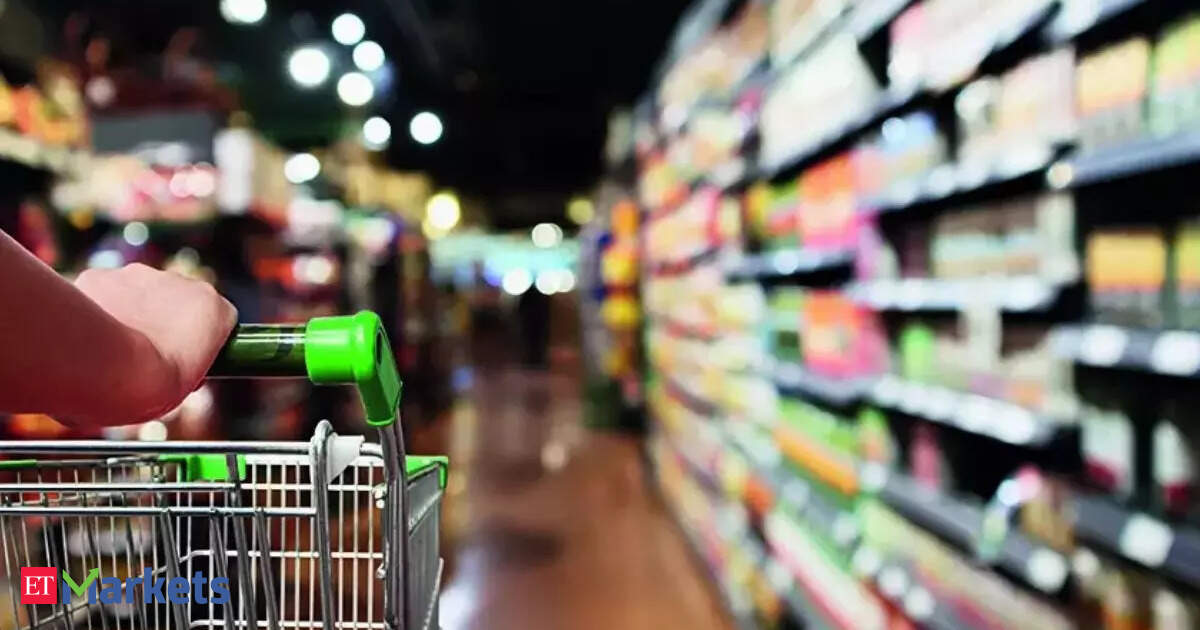
- FMCG companies in India plan to restore grammage (quantity) in smaller packs of Rs 5 and Rs 10, following the expected overhaul of GST tax slabs. Price reduction for these packs is considered impractical.
- Shrinkflation-reducing pack quantities due to high raw material costs-was common over the last two years, driven by inflation in palm oil, coffee, cocoa, and packaging materials.
- prime Minister Narendra Modi announced GST reforms aiming to simplify slabs by scrapping the 12% rate and retaining a revised structure with most daily-use items taxed at the minimum slab (5%).
- Major FMCG executives said adding quantity back into products will expedite demand growth among rural consumers where smaller packs dominate sales; about 62% of Britannia’s sales come from such price points.
- Leading distributors anticipate replenishment and competitive adjustments within days following GST announcements. Industry players like Nestle,Tata Consumer Products,Hindustan Unilever are preparing faster rollouts.Lower rates are predicted to considerably boost consumer demand during moderate growth periods seen recently.
Image Included: !Image
Indian Opinion Analysis
The anticipated GST reform marks a pivotal moment for India’s consumer goods market-it reduces taxation burdens on key daily essentials while simplifying compliance under uniform slabs. This move could ease cost pressures faced by FMCG firms after years of battling raw-material price inflation that lead many brands to practice shrinkflation.
Restoring grammage or pack sizes without altering unit prices aligns practically with transaction norms typical for small-value items catering largely to India’s rural economy where affordability drives consumption habits heavily reliant on fixed pricing models like Rs 5 or Rs 10 packets.
By reverting from shrinkflation alongside tax cuts lowering costs further downstream supply chains via larger margins passed onto consumers quickly affects near-term purchasing sentiment within underprivileged demographics aiding inclusive equitable impacts envisioned consistently modeled systemic product measures tested marginal moderation aggregation slowing indexed revival sektors