Now Reading: Fossil Teeth Uncover Extinct Mammal’s Adaptation to Ancient Global Warming
-
01
Fossil Teeth Uncover Extinct Mammal’s Adaptation to Ancient Global Warming
Fossil Teeth Uncover Extinct Mammal’s Adaptation to Ancient Global Warming
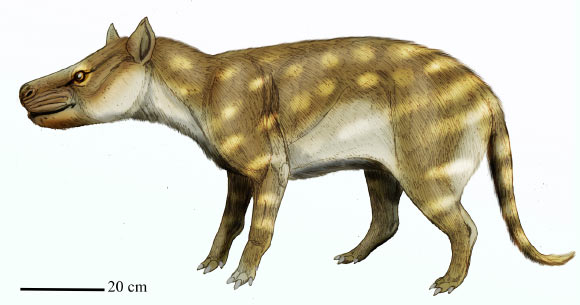
Rapid Summary
- Study Overview: Researchers examined dietary adaptations of the ancient mammal Dissacus praenuntius during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), a period of rapid warming 56 million years ago.
- Key Findings:
– Dissacus praenuntius shifted its diet from eating mostly flesh to consuming harder materials like bones.
– Dental analysis showed microwear textures resembling those of lions and hyenas during this adaptation phase.
– Food scarcity led to dietary flexibility, alongside a reduction in body size.
- Importance:
– the study underscores how environmental stress drives adaptability in animals, favoring generalists over specialists.- Insights could inform modern conservation efforts, highlighting risks for species with narrow diets like pandas while emphasizing survival advantages for generalist species like raccoons or jackals.
- Broader Implications: The PETM parallels modern climate change by showcasing critically important ecosystem upheaval and changes in predator-prey dynamics due to warming temperatures.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research on Dissacus praenuntius, conducted during an ancient climate crisis, provides valuable ecological lessons relevant to India’s contemporary challenges tied to climate change. As India grapples with habitat loss and biodiversity threats exacerbated by rising temperatures, this study reinforces the critical role of adaptability for survival within disrupted ecosystems. It highlights that generalist species are better poised to endure environmental shifts compared with those reliant on narrow diets or specific habitats.
From a policy outlook, such findings underscore the need for habitat preservation strategies focused on promoting ecological diversity and resilience rather than catering solely to niche environments. Efforts like afforestation projects must also accommodate broader food chains while actively conserving vulnerable endemic wildlife struggling against encroaching developmental activity. This logic-driven approach may empower conservation models aiming for long-term stability across India’s varied climates.























