Now Reading: Greenland Ice Sheet Sees Unprecedented Melt with 90 Billion Liters of Water
-
01
Greenland Ice Sheet Sees Unprecedented Melt with 90 Billion Liters of Water
Greenland Ice Sheet Sees Unprecedented Melt with 90 Billion Liters of Water

Rapid Summary
- Event: Scientists documented a massive subglacial flood under the Greenland ice sheet in 2014 where 24 billion gallons (90 billion liters) of meltwater burst through nearly 300 feet (91 meters) of solid ice.
- Revelation: A previously unknown subglacial lake was found; this phenomenon challenges prior assumptions about the flow patterns and characteristics of meltwater beneath ice sheets.
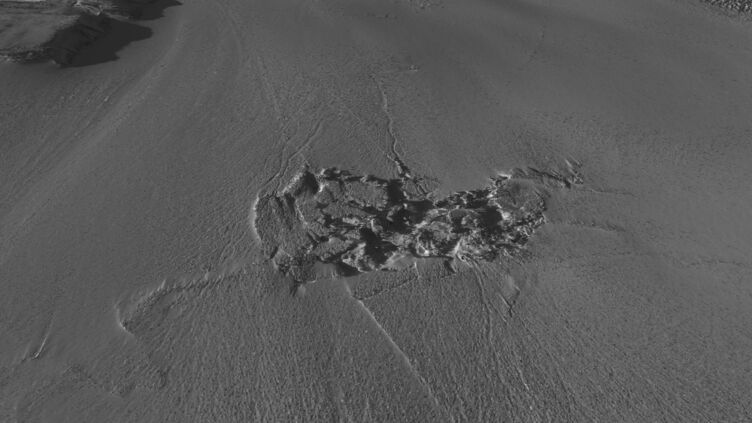
- Impact: The flood created a crater spanning 0.77 square miles (2 square kilometers), fractured surrounding ice, and uprooted blocks as tall as 82 feet (25 meters).
- research Details: Using satellite data from NASA and ESA, researchers modeled the event, revealing unexpected hydrological activity under Greenland’s ice sheet.
- Significance: Findings contradict previous models suggesting the base of Greenland’s ice sheet is frozen solid and raise questions about better understanding its hydrology to grasp future implications.
!A satellite image of the crater
indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery sheds light on previously underestimated dynamics within permanent ice sheets like those in Greenland. For India-a nation already facing significant risks due to climate change-the study emphasizes why global scientific efforts in glaciology are critical. Rising sea levels driven by unpredictable meltwater events could have consequences for vulnerable coastal regions worldwide, including vast stretches along India’s densely populated coastline.
From an analytical perspective, advancements such as these underscore India’s need to proactively invest in climate resilience strategies while supporting international partnerships for research on cryosphere behavior. Safeguarding ecological balance at home may require robust data inputs from studies around remote regions like Greenland impacting global processes. This observation highlights how interconnected local policies are with planetary systems increasingly influenced by melting polar environments.