Now Reading: Grid-Scale Battery Boosts Scotland’s Power Stability
-
01
Grid-Scale Battery Boosts Scotland’s Power Stability
Grid-Scale Battery Boosts Scotland’s Power Stability

Fast Summary
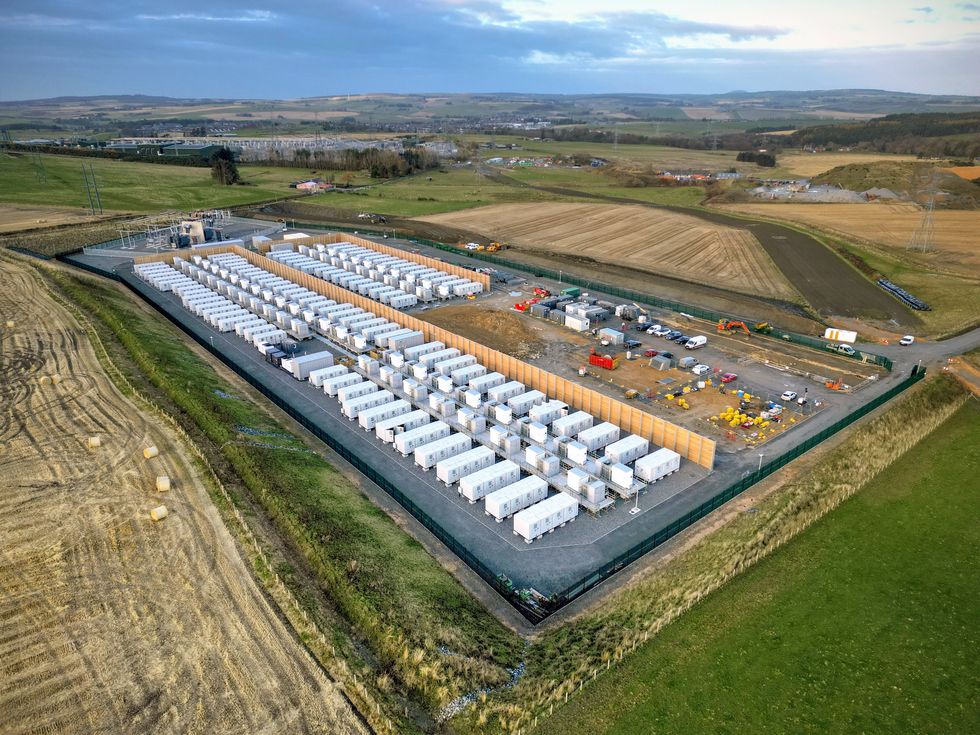
- A 200 MW lithium battery storage site in Blackhillock, Scotland-Europe’s largest-stabilized the grid after an unexpected generator shutdown in march.
- The battery, equipped with advanced grid-forming inverters, simulates inertia and contributes to grid stability without moving parts.
- Scotland is constructing four more of these innovative battery sites as part of it’s energy transition away from coal, gas, and eventually nuclear power by 2030.
- This technology could play a key role in helping the UK achieve its goal of fossil-free grid operation by 2025. The National Energy System Operator (NESO) plans to demonstrate zero-carbon operation for hours by year’s end.
- Grid-scale batteries provide short-circuit current like conventional generators-a notable innovation-but doubts about their reliability during real faults still persist among experts.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Scotland’s prosperous deployment of a large-scale lithium battery highlights the growing global shift toward cleaner energy systems using advanced power electronics over conventional fossil-fuel-based infrastructure. As India pursues ambitious renewable energy targets under frameworks like COP26 commitments, such innovations offer critical lessons-not just on transitioning to renewables but ensuring robust grid stability through emerging technologies such as grid-forming batteries and synchronous condensers.
The dual-use nature of these batteries-providing both operational services like arbitrage while improving stability-is a compelling model for India’s expanding solar and wind capacity across diverse regions with variable demand fluctuations. However, challenges remain: concerns about technical reliability during high-stress events merit careful scrutiny before scaling similar deployments domestically.
India can observe how Scotland balances cost-efficiency with strategic caution by maintaining synchronous condensers alongside newer solutions-a balanced approach that could inform similar experiments within India’s increasingly strained electricity grids while supporting its clean energy transition goals effectively.