Now Reading: How Tear Gas Works and the Risks of Its Use in Crowd Control
-
01
How Tear Gas Works and the Risks of Its Use in Crowd Control
How Tear Gas Works and the Risks of Its Use in Crowd Control

Rapid Summary
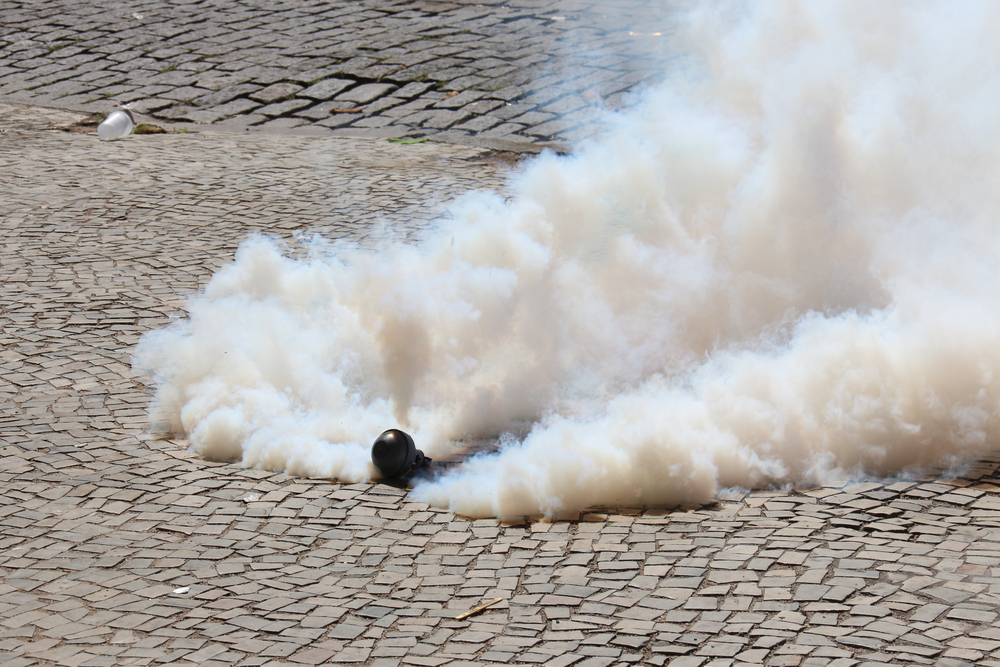
- definition of Tear Gas: A chemical weapon categorized as “demonstration control agents” (DCAs) used to disperse large crowds, primarily in outdoor settings. Commonly contains CS, CN, and CR chemicals.
- Mechanism of Action: Causes burning and itching sensations in eyes,nose,mouth,skin irritation,blurred vision,difficulty swallowing or breathing and other symptoms like rashes or nausea upon exposure.
- Fatal Risks: In enclosed spaces or for individuals with preexisting conditions (e.g., asthma), exposure can result in severe health complications or fatalities.
- Long-term Health Effects: Studies indicate potential menstrual cycle disruptions for women exposed to DCAs as well as pulmonary and ocular issues.
- accountability Concerns: Currently there is minimal oversight on the use of tear gas by authorities; records on its frequency and concentration are often untracked.
- Global Usage Trends: Instances reported globally-recent incidents include use during protests in Georgia and France-with police deploying tear gas against civilians.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Tear gas holds relevance for India amidst a backdrop of growing public demonstrations that may invoke crowd control measures by law enforcement agencies. While tear gas serves its utility to rapidly disperse gatherings deemed disruptive or violent, its application must align with strict ethical boundaries due to documented risks including severe health implications when misused-notably inside enclosed spaces.
The lack of accountability touched upon in the research highlights a critical gap requiring urgent institutional reforms for transparency purposes if public trust is maintained around such actions nationally.Regulatory norms ensuring proper documentation during its deployment may protect human rights while achieving operational goals effectively without disproportionately harming civilians.
In India’s context given higher rural density Often congested villages areas logistics-practical rethinking