Now Reading: Hubble Captures Star Formation in Distant Galaxy
-
01
Hubble Captures Star Formation in Distant Galaxy
Hubble Captures Star Formation in Distant Galaxy

Fast Summary
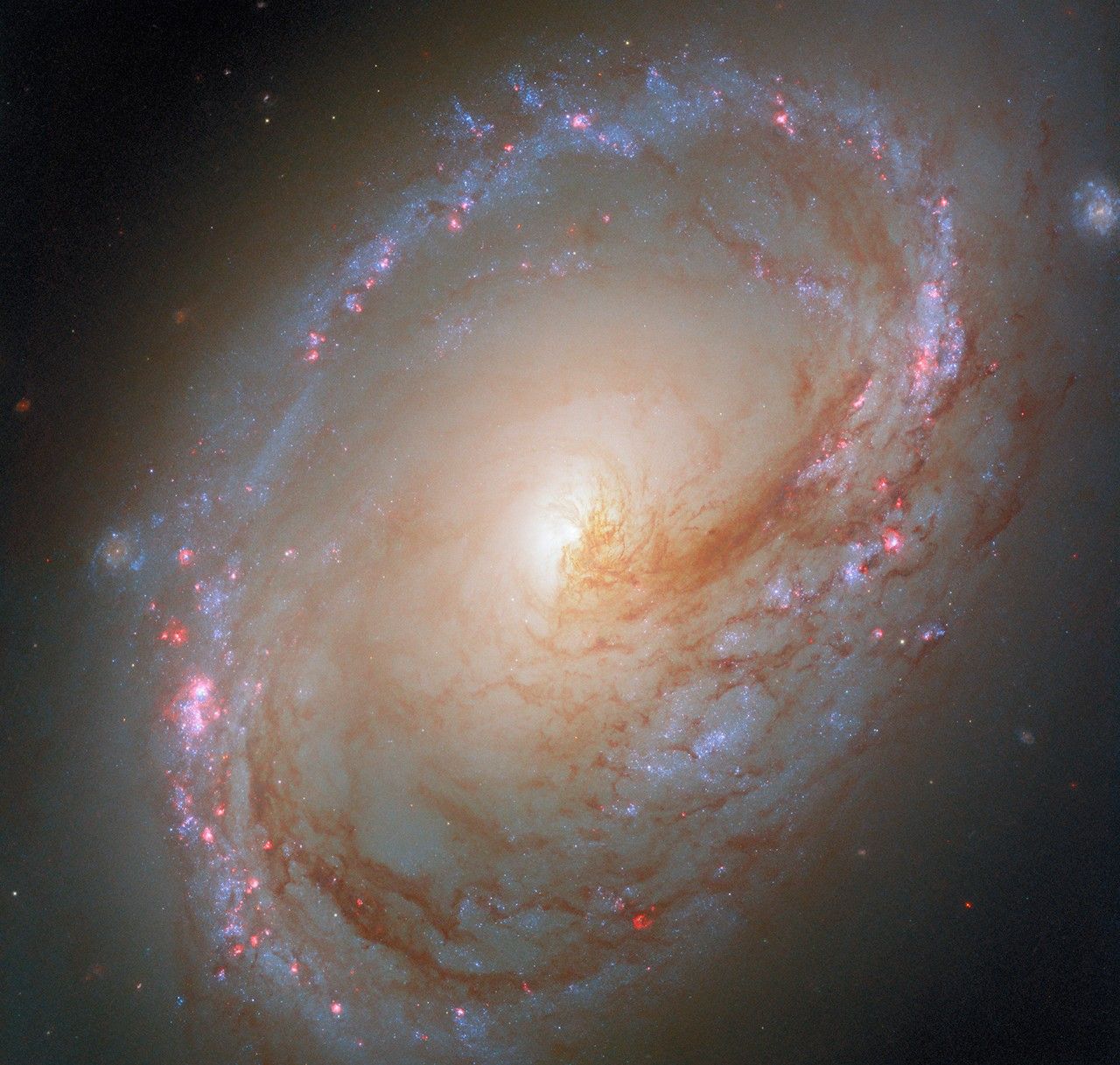
- Galaxy Highlighted: Messier 96, a spiral galaxy located 35 million light-years away in the constellation Leo, is the focus of NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope studies.
- Asymmetry Explained: The uneven distribution of gas, dust, and an off-center core may result from gravitational interactions with neighboring galaxies.
- Latest Observations: The new image incorporates ultraviolet, near infrared, visible/optical light wavelengths and includes data on ionized hydrogen (H-alpha) and nitrogen (NII).
– Ionized hydrogen reveals ongoing star formation regions due to young stars.
– Ionized nitrogen provides insights into star formation rates and interstellar gas properties.
- Scientific Goals: Astronomers aim to study mechanisms of star formation in dusty clouds as well as how stars filter starlight and interact with their local environments.
- Imagery History:
– Earlier images released in 2015 focused on optical and near-infrared detail regarding dust/gas spread within the galaxy’s weak spiral arms.
– Updates in 2018 included ultraviolet wavelengths that pinpointed areas where high-energy young stars were forming.
Indian Opinion analysis
the observations made by the Hubble Space Telescope are advancing the understanding of galaxy dynamics and star formation processes. While this study focuses on Messier 96-a distant celestial entity-its importance transcends astronomical curiosity. Robust understanding can offer broader insights into galactic systems similar to our own Milky Way. This fosters advancements not only for space sciences globally but also bolsters India’s ambitions around integrating advanced astrophysical capabilities such as improved imaging technologies for its missions.
Indian efforts like ISRO’s AstroSat mission demonstrate synergy between global research outputs like those from NASA/ESA. Leveraging such findings could further equip Indian scientists to explore more intricate questions about our universe while strengthening collaborative ventures across international space agencies.