Now Reading: Ice Age Fossil Trove Discovered in Remote Norwegian Cave
-
01
Ice Age Fossil Trove Discovered in Remote Norwegian Cave
Ice Age Fossil Trove Discovered in Remote Norwegian Cave

Rapid Summary
- Researchers excavated Norway’s Arne Ovamgrotta cave, unknown for over 75,000 years, uncovering remains of 46 different animal species.
- Excavation efforts began in 2021, led by the University of Oslo and Bournemouth University.
- Confirmed discoveries include polar bears, Atlantic puffins, bowhead whales, extinct collared lemmings (first documented in Scandinavia), codfish bones indicating thawed conditions during the ice age.
- Findings reveal a warmer climate period around 75,000 years ago that later shifted back to intense cold temperatures causing extinction events.
- Study highlights challenges cold-adapted species faced during thes transitional eras as analogous lessons for modern Arctic conservation amid rapid climate warming today.
!Polar bear bone in cave The cave’s remains are linked to 46 different species. Credit: Trond Klungseth Lødøen
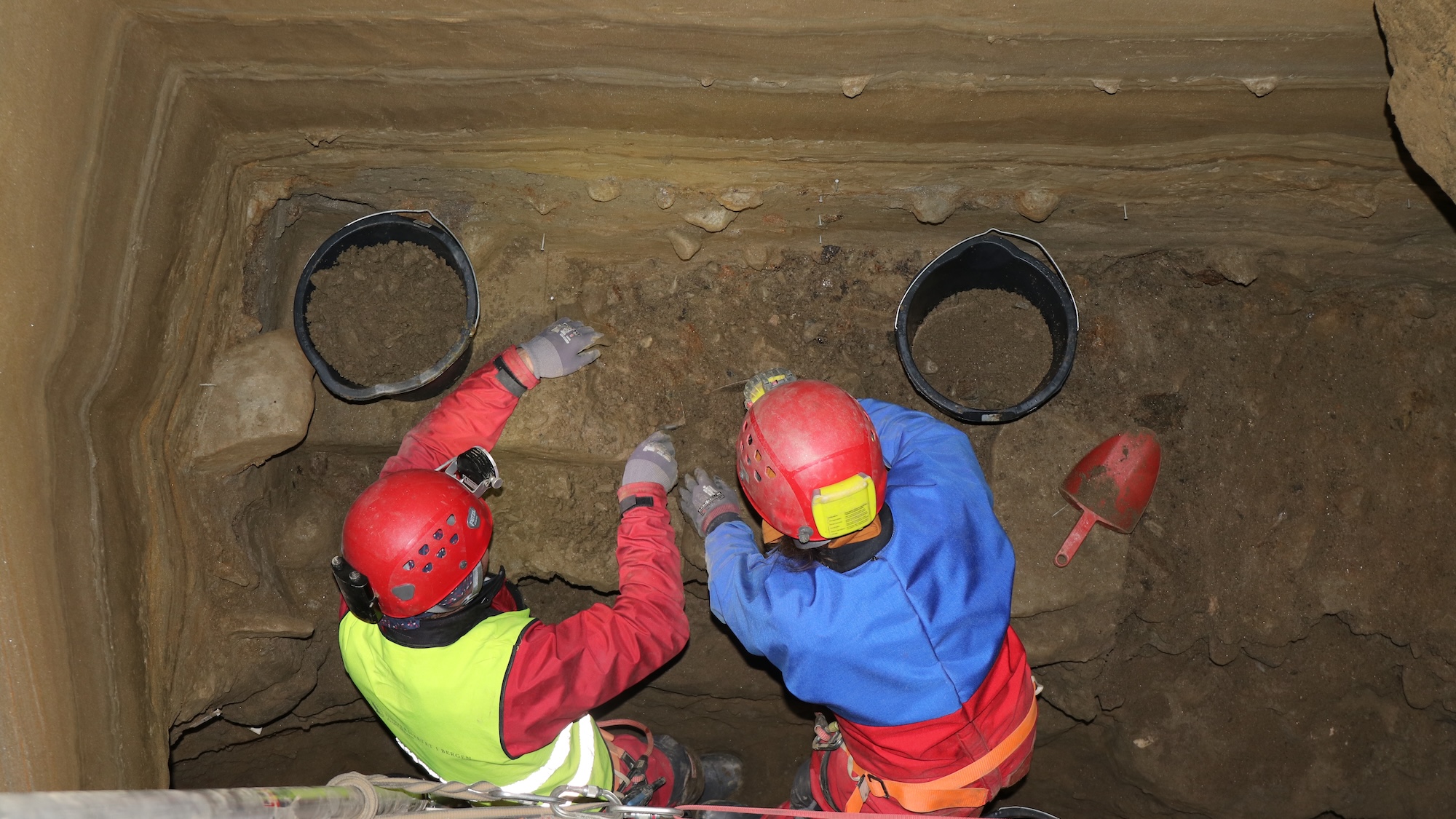
!Cave excavation site The team removed the animal remains from inside 42 feet of sediment. credit: Trond Klungseth Lødøen
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research unveils potential parallels applicable globally-and relevant for India-regarding biodiversity loss amidst climactic changes. The discovery indicates how even cold-adapted creatures struggled with environmental fluctuations during glacial periods-resulting in widespread extinctions-a cautionary detail relevant today with rising global temperatures threatening ecosystems worldwide.India’s diverse habitats ranging from Himalayan glaciers to coastal wetlands already face threats due to human-induced climate changes and habitat fragmentation similar to what Arctic animals endure presently under warming patterns highlighted here.
This study reinforces the importance of long-term scientific approaches supporting adaptive conservation strategies not only abroad but across ecologically sensitive areas like Sundarbans mangroves alongside collective safeguards adapting vulnerable native resources worsening forced-displacement/migration categories increasingly complicated challenges Read more here