Now Reading: India and NASA Prepare for NISAR Satellite Launch on July 30
-
01
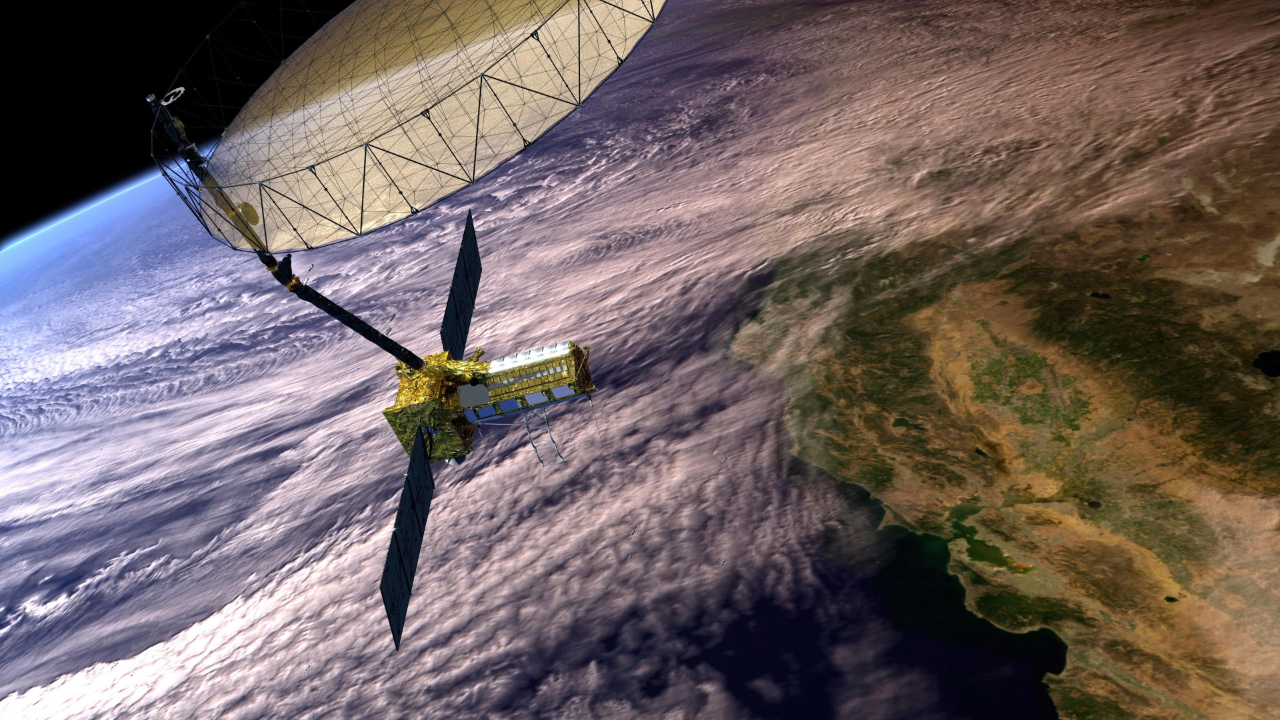
India and NASA Prepare for NISAR Satellite Launch on July 30
India and NASA Prepare for NISAR Satellite Launch on July 30
Quick Summary:
- A collaborative Earth-observing satellite, NISAR, developed by ISRO and NASA, is set to launch on July 30.
- The launch will use India’s GSLV Mk II rocket from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota at 5:40 p.m. IST.
- The GSLV Mk II rocket is a powerful three-stage vehicle with advanced features like solid and liquid-fueled boosters and an Indian-developed Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS).
- NISAR uses cutting-edge radar technology to monitor global changes as small as one centimeter every 12 days over land, ice, oceans, and more.
- Its applications include detecting natural hazards (earthquakes, landslides), human-induced changes (urban development), helping food production systems, and improving disaster preparedness.
- Deployment into a polar orbit is expected approximately 18.5 minutes after liftoff from an altitude of 744 kilometers; the mission’s duration is at least five years.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The upcoming launch of NISAR marks an vital milestone for india’s space science contributions globally while underscoring effective collaboration between ISRO and NASA.Such joint missions enhance technical capabilities – including Earth-monitoring tools critical for understanding climate change impacts or improving disaster response mechanisms globally.
For India specifically, this project elevates its position in space research while offering actionable data about environmental conditions that can guide policymaking around agriculture management or urban planning challenges domestically. As climate-related risks rise worldwide alongside infrastructure demands from rapid urbanization within India itself – datasets like those provided by NISAR could support sustainable development initiatives moving forward.Read More