Now Reading: James Webb Telescope Captures Rare Celestial Pattern Around Dying Star
-
01
James Webb Telescope Captures Rare Celestial Pattern Around Dying Star
James Webb Telescope Captures Rare Celestial Pattern Around Dying Star

Swift Summary
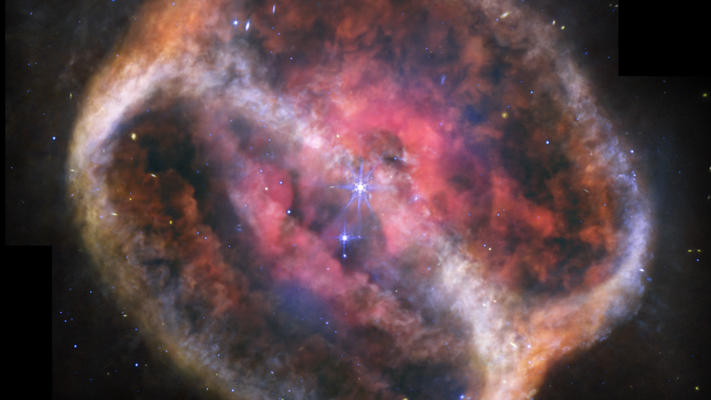
- Astronomical discovery: The james Webb Space Telescope (JWST) captured a detailed image of NGC 1514, a planetary nebula located 1,500 light-years away in the Taurus constellation.
- Central feature: NGC 1514 consists of two stars forming a binary system encased by an intricate structure resembling overlapping rings shaped by gravitational influence and stellar interactions.
- Scientific findings:
– Observed faint filamentary rings formed by faster stellar winds interacting with slower-moving material ejected from the aging star.
– Oxygen was detected in the nebula’s pink center, but more complex molecules were notably absent due to stirring effects caused by long orbital periods.
– Small dust grains slightly heated by ultraviolet light were revealed via infrared observations.
- Past context: Scientists have tracked one of the longest known orbits for a planetary nebula’s binary system (nine years).
- Budget concerns for JWST: The highly-demanded telescope faces potential budget cuts up to 20%, which could impact operations despite its remarkable discoveries.
Image descriptions:
- JWST reveals faint Venn-diagram-like arcs within NGC 1514 (Image credit NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI).
- Full image view of nebula showcasing its grandeur and texture.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the recent study using JWST highlights how cutting-edge technology can enhance our understanding of cosmic phenomena while providing insights into stellar evolution processes relevant on global scales. Discoveries like these not only deepen scientific knowledge but also remind us how interconnected global investments in science can drive human progress across borders-including collaborations involving Indian astronomers contributing to space exploration efforts.
The looming prospect of budget cuts signals an important lesson on balancing priorities between scientific advancements and operational costs-an issue not unfamiliar to india where space research programs like ISRO face similar challenges navigating funding restrictions while achieving world-class outcomes. These updates emphasize both the cost and value inherent in supporting ambitious research programs that push technological limits further-a conversation India must continue fostering as it develops indigenous space capabilities parallel to participating globally.