Now Reading: Measuring the Vastness of the Cosmos
-
01
Measuring the Vastness of the Cosmos
Measuring the Vastness of the Cosmos

Rapid Summary
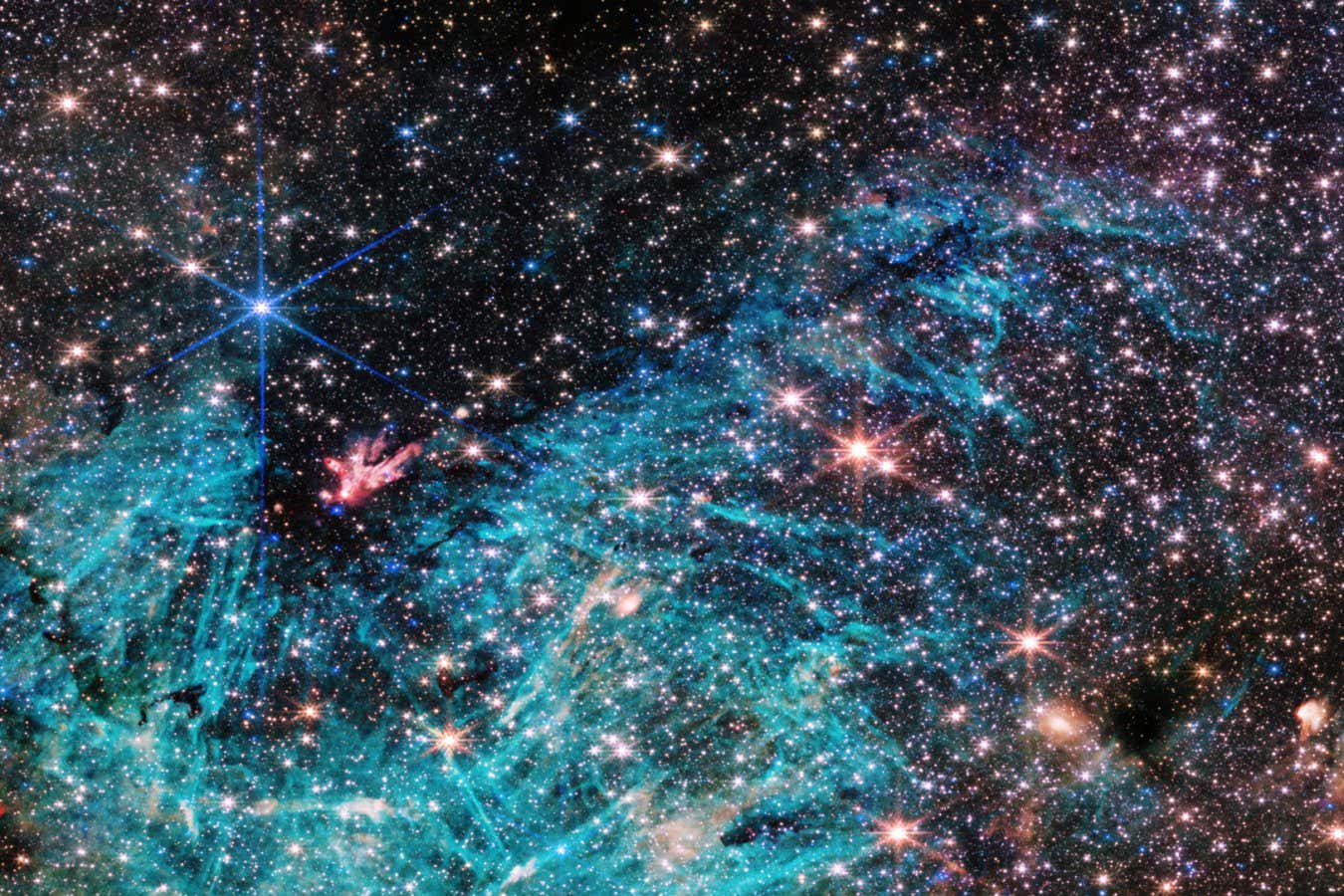
- NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s nircam instrument captured a detailed image of the Sagittarius C (sgr C) region in the Milky Way,showing an estimated 500,000 stars and intriguing structures in ionized hydrogen clouds.
- The scale of the Milky Way and the universe is described to illustrate astronomical distances; light takes 100,000 years to cross the galaxy compared with 5.5 hours from Sun to Pluto.
- Space-time expansion explains larger-scale distances and how galaxies are pulling away due to Hubble expansion. Locally, some galaxies like Andromeda are on a collision course with others.
- Astronomers gauge distance using techniques like cepheid variable stars and supernovae measurements, relying on redshift phenomena caused by space-time stretching light waves.
- Redshift is crucial for understanding cosmic distances but defies Newtonian conservation laws under general relativity principles.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The exploration into measuring vast cosmic scales offers insights into humanity’s ability to understand it’s place in an ever-expanding universe. For India-hosting organizations such as ISRO that are increasingly visible on the global space exploration stage-the methods described underline opportunities for deeper participation in astrophysical research. Advances proposed by NASA’s James webb Telescope demonstrate how collaborative efforts can expand our knowledge base.
The implications for India also extend beyond astronomy: fostering scientific literacy about concepts like redshift and general relativity could inspire more students toward STEM fields. With upcoming missions such as Gaganyaan and lunar explorations planned by ISRO already sparking national interest, leveraging these international advancements might nurture public enthusiasm for space science domestically while enhancing technical expertise globally.