Now Reading: Microbiome RNA in Plasma Identifies Colorectal Cancer Cases
-
01
Microbiome RNA in Plasma Identifies Colorectal Cancer Cases
Microbiome RNA in Plasma Identifies Colorectal Cancer Cases
Swift Summary:
- The article discusses the human genome reference (GRCh38.108) as the basis for a new study focused on cancer diagnostics using cell-free DNA tools.
- Raw and processed sequencing data are available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus under accession number GSE264208.
- Source data from this research are provided, linking too detailed references through associated studies published in journals such as genes Chromosomes Cancer and Nat Cancer. These highlight advancements like plasma DNA tissue mapping, circulating biomarkers, and liquid biopsy technologies.
- The discussion involves global opportunities and challenges revolving around noninvasive diagnostic techniques based on genomic methylation or epigenetic profiling.
Images Presented: None included in the source text.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India stands to benefit considerably from innovations revolving around cell-free DNA diagnostic technologies given its growing cancer burden, with nearly 14 lakh cases estimated annually (as per external statistics). These methodologies could perhaps address critical gaps in early detection, especially across rural healthcare settings where access remains limited.
Liquid biopsy techniques mentioned in this study could reduce reliance on invasive procedures while providing accurate prognosis and monitoring options for Indian populations.However, challenges like scalability, affordability of advanced genome-based tools, and training specialized medical professionals must be addressed firmly to ensure successful deployment across public health systems. As India progresses toward genomic medicine adoption via schemes like Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission or partnerships with biotech firms globally-it remains crucial that such innovations are tailored inclusively considering population diversity both genetically & socially.Link for read more about dataset accessibility/info within here.Quick Summary
- The raw text appears to be highly technical in nature and pertains to recent advancements, studies, and methodologies concerning RNA sequencing, transcriptomics, and molecular diagnostics.
- Key topics include cell-free RNA granules formation, transcriptome profiling for biomarkers related to cancer detection, preeclampsia prediction using cell-free RNA techniques, mRNA modifications at single-base resolution using advanced methods like BID-seq and PALM-seq.
- Several references cited are from prestigious journals such as “Nature,” “Science,” “Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA,” among others supporting these innovations.
Indian Opinion analysis
India’s growing biotechnology sector stands to benefit greatly from advancements in molecular diagnostics as outlined in this article. Techniques like PALM-seq or BID-seq could offer life-saving applications for Indian researchers focused solving Cancer /Maternal profiling with cheap alternatives etc but
Quick Summary
- The news article provides references and research studies on advanced RNA sequencing methods and their significance in medical diagnostics.
- Specific studies highlight novel approaches such as BID-seq for mRNA pseudouridine sequencing, PANDORA-seq for identifying regulatory small RNAs, and precision tools like AQRNA-seq for mapping cellular small RNA landscapes.
- Topics resonate with early cancer detection techniques, cell-free RNA innovations, microbiome signals in cancer diagnostics, and modern tRNA analysis methods.
- Research cited spans global contributions across prominent journals like Nature,eLife,and PLoS Genetics,among others.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s emerging biotech sector can benefit immensely from the advancements detailed in the article. With increasing emphasis on precision medicine within India’s healthcare framework, tools like advanced RNA technologies have promising implications. They could help expedite research into oncology diagnostics-a key priority given India’s rising cancer incidence. Moreover, India’s contributions to global scientific collaborations could be strengthened by investing further into cutting-edge genomics infrastructure. Such innovations also align well with initiatives surrounding affordable healthcare access through early disease detection technologies.
Read More: nih.gov PubMed linkCertainly! Below is the requested concise write-up based solely on the data provided.
Quick Summary
- The article delves into studies related to cellular stress responses, focusing primarily on tRNA and its modifications in organisms such as Escherichia coli.
- It references various research methodologies including NAIL-MS (cell-culture modification analysis) to observe human nucleic acid dynamics and machine learning applications for microbiome studies.
- Specific topics included microbial genome characterization, therapeutic biomarker development using tRNA sequencing, gut microbiota roles in diseases like colorectal cancer, and advanced diagnostics leveraging methylation detection (e.g.,SEPT9 plasma marker).
Indian Opinion Analysis
India has recently invested in molecular biology and biotechnology research, which aligns with global trends highlighted here-particularly studies that explore mechanisms of genetic regulation during stress or disease.The insights from these articles show potential applications ranging from biomarker-driven diagnostics to improved antibiotics production strategies. For India, adopting such technologies would enhance healthcare tools tailored for localized health challenges like increasing rates of gastrointestinal cancers. Moreover, fostering collaboration between Indian biotech firms and international academia could accelerate advancements not only for fundamental science but also solutions applicable across diverse populations.
Read More: Article Reference Link
—
Let me know if further adjustments are needed!Quick Summary:
- Plasma SEPT9 DNA and gut microbiota are being studied as biomarkers for colorectal cancer diagnosis.
- Recent research highlights connections between specific bacteria (e.g., Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium) and increased risks or progression of colorectal cancer.
- Biomarkers from fecal microbiomes, such as alterations in bile acids or microbial species like Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, show potential for non-invasive diagnostics.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India faces increasing rates of gastrointestinal cancers, including colorectal cancer, due to shifting lifestyles and dietary patterns. The use of advanced biomarker detection techniques from plasma DNA (SEPT9) or gut microbiomes offers promising strides in early detection and non-invasive diagnostic tools. Though, translating this cutting-edge science into affordable solutions remains a key challenge for india’s vast rural population that lacks access to refined healthcare infrastructure. Initiatives to integrate biomarker screenings into public health systems could significantly influence early cancer intervention efforts nationwide.
For more details on the studies mentioned: Link
Quick summary:
- Study Focus: recent research highlights the role of specific bacteria-peptostreptococcus anaerobius, Parvimonas micra, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Akkermansia muciniphila-as biomarkers in colorectal cancer progression. The paper developed LIME-seq technology for identifying RNA modifications.
- Research Sites: Collaboration involved multiple globally recognized institutions including the University of Chicago and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
- Technology Spotlight: LIME-seq enables quantitative identification of RNA methylations across varied sample sizes, supporting robust biomarker analysis.
- Medical Application: Findings emphasize potential utility in early diagnosis through cfRNA (cell-free RNA) extracted from plasma samples.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancement demonstrated by technologies such as LIME-seq marks meaningful progress in molecular diagnostics, particularly for complex diseases like cancer. For India-a nation with rising incidences of colorectal cancer-studies targeting improved biomarker detection can serve pivotal roles in early screening practices.Integrating such tools into India’s healthcare infrastructure may necessitate investment in genomic facilities and cross-disciplinary collaborations.
Moreover, leveraging discoveries about microbial influence on tumor biology could align well with India’s strong tradition of microbiome research. This study also exemplifies how innovation fosters global scientific partnerships, which could guide Indian researchers to contribute further to cancer diagnostics advancements while addressing public health needs domestically.
Quick Summary
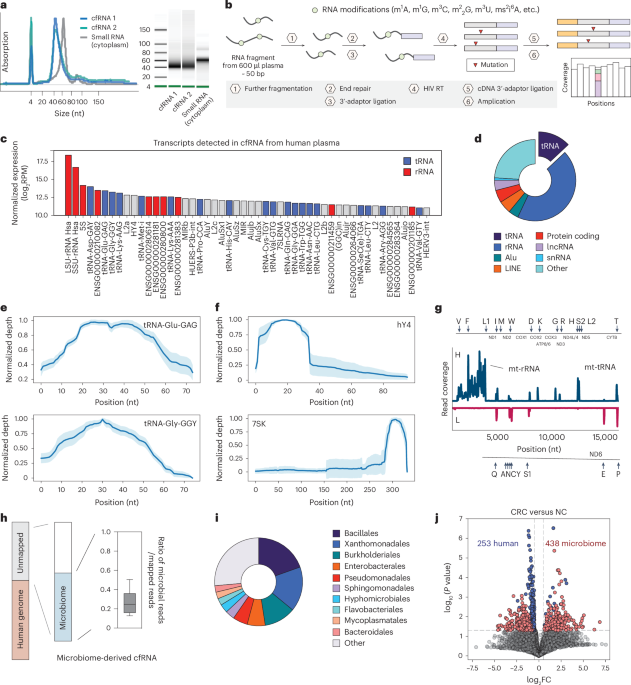
- A study published in nature Biotechnology details the use of LIME-seq technology to analyze microbiome-derived cell-free RNA (cfRNA) as biomarkers for colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnosis.
- The research identifies differential RNA methylation profiles and transcript abundances between CRC patients and non-cancer controls using plasma samples.
- Key findings include distinct mutational signatures in microbial cfRNA, which correlate with CRC stages and can serve as biomarkers for early detection.
- Diagnostic models validated through methods such as leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV), bootstrapping, and external cohorts achieved high predictive accuracy using these cfRNA markers.
- The stability of cfRNA under various storage conditions was examined to ensure reliability during clinical sample handling.
Indian opinion Analysis
The findings reported highlight a pioneering development that could have significant implications for healthcare, including early detection protocols. India’s medical landscape presents immense opportunities for integrating advanced diagnostic technologies like LIME-seq into public health programs aimed at reducing mortality from colorectal cancer-a growing concern in urban populations due to lifestyle changes.
Challenges remain, particularly with scalable deployment across rural areas where infrastructure hinders adoption of precision diagnostics.Nevertheless, India’s extensive network of healthcare providers could benefit from partnering with global research efforts involving cutting-edge solutions such as those targeting microbiome-derived biomarkers. For policymakers and healthcare stakeholders, ensuring accessibility while promoting R&D into local variants of CRC risk factors would be critical in translating this innovation effectively within an Indian context.
Read more: Nature BiotechnologyQuick Summary
- Researchers, including CW ju, R Lyu, and H Li, published findings in Nature biotechnology regarding modifications of microbiome-derived cell-free RNA in plasma for colorectal cancer detection.
- The study demonstrated a novel method to differentiate colorectal cancer samples using changes in microbiome-derived RNA molecules.
- Accepted on June 5, 2025, the article was officially published on July 8, 2025.
- DOI for the publication: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02731-8.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This groundbreaking research highlights significant advancements in non-invasive diagnostics for colorectal cancer through microbiome-related RNA analysis-potentially reshaping diagnostic modalities globally. India’s healthcare sector could leverage such technologies to enhance early cancer detection and treatment outcomes among its population where cancer diagnostics remain limited by accessibility and affordability issues. Adoption of this method might prove beneficial against a background of increasing incidence rates of gastrointestinal cancers in India while creating avenues for collaboration between Indian researchers and global institutions pivotal to medical innovation.