Now Reading: Moon-Grown Rice: A New Frontier for Astronauts’ Diets
-
01
Moon-Grown Rice: A New Frontier for Astronauts’ Diets
Moon-Grown Rice: A New Frontier for Astronauts’ Diets

Fast Summary
- Scientists are developing genetically modified rice for long-term space missions as part of the Moon-Rice project,a collaboration between the Italian Space Agency and three Italian universities.
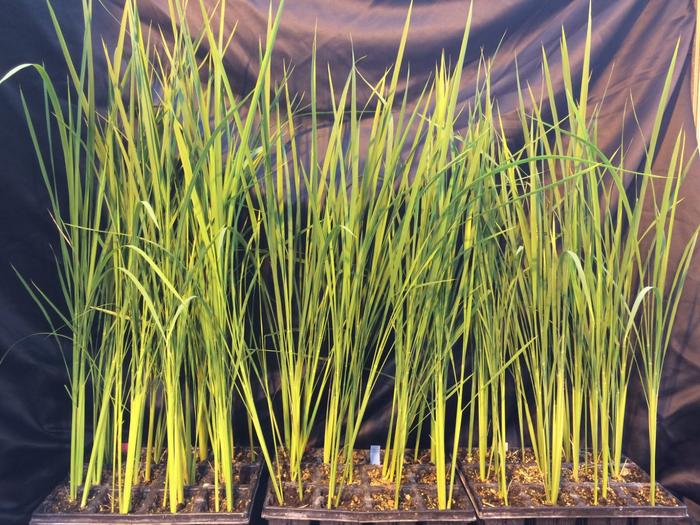
- Goals include producing “super-dwarf” rice that is compact, productive, and nutrient-rich to meet astronauts’ dietary needs during lunar or Mars missions.
- Current advancements:
– University of Milan has isolated mutant rice varieties that grow only up to 10 cm (~4 inches).
– Sapienza University of Rome focuses on optimizing genes for higher growth efficiency.
– Efforts are underway to increase protein content in rice by modifying the embryo-to-starch ratio.
- Testing simulates microgravity conditions using rotational techniques to replicate weightlessness experienced in space stations.
- Nutritional improvements aim at combating common space-related health issues such as bone loss, muscle decline, and cardiovascular problems.
- Other successful attempts include NASA’s Vegetable Production System growing lettuce, cabbage, and kale on the International space Station.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of “super-dwarf” rice tailored for cultivation under extraterrestrial conditions underscores scientists’ growing focus on self-sustaining food systems for future space exploration. India’s promising strides in aerospace technology-including ISRO’s lunar missions-make innovations like these relevant. As human presence beyond Earth becomes viable through international collaborations or indigenous initiatives, creating resilient food sources will be crucial for astronaut health.
Given India’s expertise in agricultural research (like ICAR’s work) and a fast-growing interest in space science through programs like Gaganyaan and Chandrayaan missions, there is potential scope for India’s scientists to contribute toward similar projects leveraging native biodiversity such as local dwarf crop varieties. Such interdisciplinary efforts combining agriculture with aerospace coudl enhance India’s role globally while maintaining nutritional security during aspiring interplanetary ventures.
Read More: Timekeeping Works Differently on the Moon – Here’s How NASA Will regulate Lunar Time