Now Reading: New Tarantula Species Discovered with Unusually Long Genitalia
-
01
New Tarantula Species Discovered with Unusually Long Genitalia
New Tarantula Species Discovered with Unusually Long Genitalia

Rapid Summary
- Arachnologists have identified four new tarantula species with elongated palps, setting a record for the longest genitalia among known tarantulas.
- These species belong to a newly established genus named Satyrex, derived from the Greek mythological figure Satyr and the Latin word “rex” (king).
- the spiders are native to regions of the Arabian Peninsula and Horn of africa.
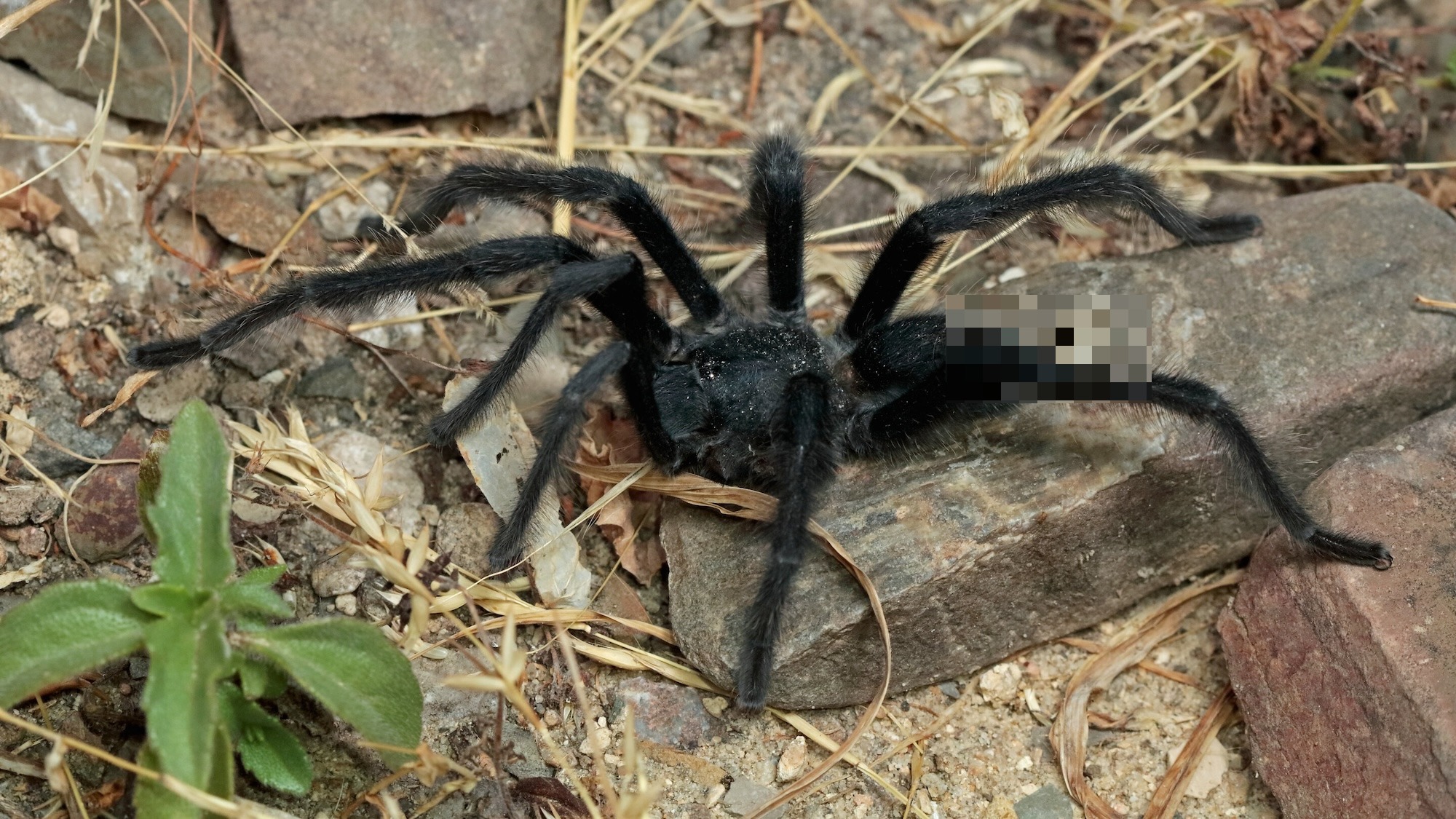
- The largest species, Satyrex ferox, has a leg span of 5.5 inches and hisses loudly when disturbed by rubbing specialized leg hairs together.
- Other species include Satyrex arabicus (Saudi Arabia), Satyrex somalicus (Somalia), and Satyrex speciosus (bright coloration).
- An existing tarantula (monocentropus longimanus) was reclassified under this genus due to similarities in elongated palps.
Images:
- !Black Tarantula – Caption: Satyrex Ferox was named for its particularly aggressive behavior.
- !Brown Tarantula – Caption: Satyrex speciosus is named for its bright coloration.
- !Gray Tarantula – Caption: S. arabicus can be found in Saudi Arabia.
Indian opinion Analysis
The discovery of these distinct spider species is scientifically notable because it advances evolutionary biology and biodiversity research in global ecosystems, including overlapping ecological zones near India like Yemen or Somalia on the Horn of africa’s edge.
For India, such studies may inspire further exploration into its own diverse arachnid population across varied habitats-ranging from deserts to rainforests-noting that India’s spider fauna remains under-researched compared to other regions globally.
Additionally, evolutionary traits like elongated palps to avoid mating aggression shed light on broader reproductive survival strategies across animal groups-a topic that could resonate with Indian researchers working on conservation biology or ethology.Scientific achievements such as this affirm interconnected global learning opportunities crucial in protecting ecosystems amid accelerating climate pressures worldwide-a focus India has increasingly emphasized through policies like Project Tiger’s expansions to marine life CSR wildlife-linked innovation too..