Now Reading: Single Gene Alters Courtship Behavior in Flies
-
01
Single Gene Alters Courtship Behavior in Flies
Single Gene Alters Courtship Behavior in Flies

Speedy Summary
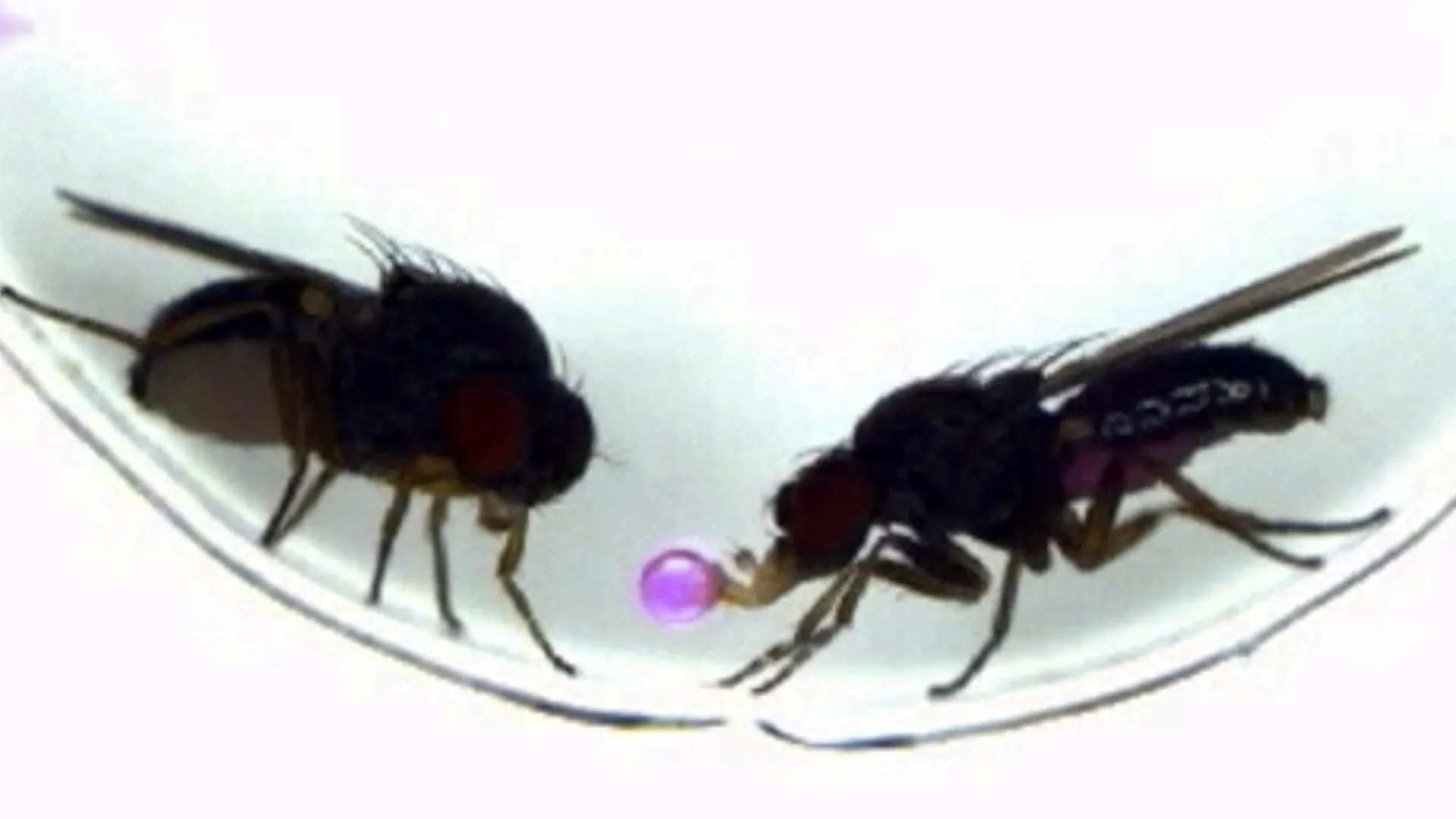
- Researchers in Japan successfully transferred a unique courtship behavior between two fruit fly species by manipulating a single gene.
- Teh experiment enabled Drosophila melanogaster, which usually performs wing vibration “courtship songs,” to mimic the gift-giving ritual of drosophila subobscura involving regurgitated food.
- Both species share the “fruitless” (fru) gene responsible for male courtship behavior but differ in how neurons connect to brain centers regulating this behavior.
- When researchers activated the fru gene in insulin-producing neurons, new neural connections formed, enabling gift-giving behavior in D. melanogaster for the first time.
- Study findings suggest behavioral evolution can occur through minor genetic rewiring rather than requiring entirely new neurons or systems.
- Published on August 14, 2025, in Science, the study involved collaboration between Nagoya University and National institute of Facts and Communications Technology (NICT), led by Drs. Yusuke Hara and Daisuke Yamamoto.
- The project was funded under multiple KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid programs.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This groundbreaking study highlights significant advancements in understanding genetic contributions to complex behaviors across species-a finding that could possibly influence research fields ranging from neuroscience to evolutionary biology. While directly concerning fruit flies, implications arise for broader scientific inquiries into how small-scale genetic modifications might play roles in human neurobiology or help trace evolutionary pathways leading to diversity among organisms.
For India’s scientific community engaged in genetics research or interdisciplinary studies like behavioral science, this can serve as a foundational model emphasizing cross-species insights enabled by precise manipulation at molecular levels. it underscores opportunities not only for extending boundaries of fundamental research but also exploring its applications-such as, conservation strategies targeting endangered species through controlled modification of behaviors critical for survival.
Indian universities and researchers frequently collaborate internationally; utilizing similar frameworks could strengthen India’s contributions toward decoding genetics-driven phenomena globally while fostering partnerships with pioneering institutions abroad like NICT or Nagoya University.