Now Reading: Brain Study Reveals Unique Patterns in Pessimism and Optimism
-
01
Brain Study Reveals Unique Patterns in Pessimism and Optimism
Brain Study Reveals Unique Patterns in Pessimism and Optimism
Quick Summary
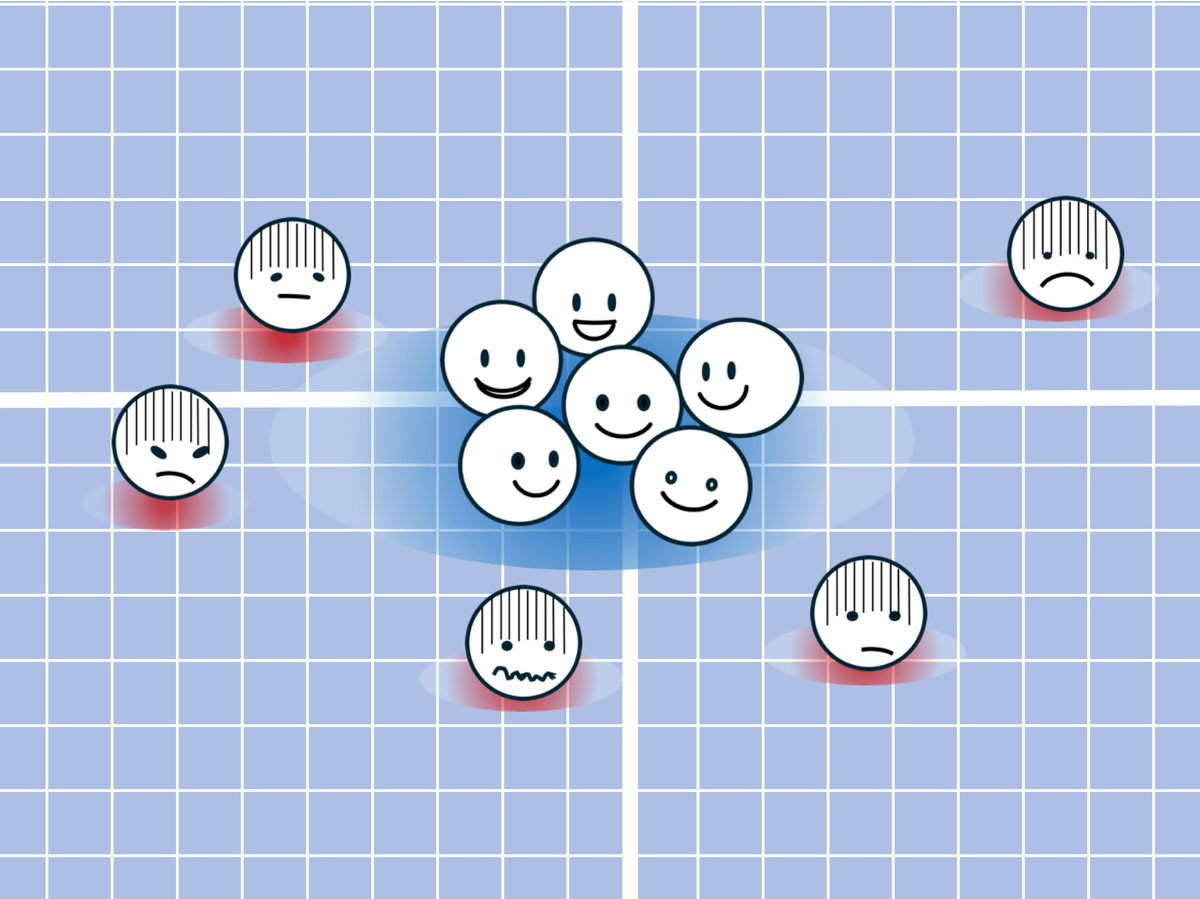
- Research Findings: A study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA shows that optimists have similar brain activation patterns in the medial prefrontal cortex (responsible for imagining future events),while pessimists exhibit more diverse neural activity.
- Study Details: Participants underwent fMRI scans as they imagined specific future events involving themselves or their spouses, followed by questionnaires categorizing them as optimists or pessimists. Conducted on two groups-37 participants initially and 50 participants in follow-up research.
- Key Observation: Optimistic individuals showed greater differentiation between neural responses to positive and negative imagined events compared to pessimistic individuals.
- Social connection Link: optimism is correlated with larger social networks, suggesting a shared cognitive framework may facilitate better interpersonal relationships among optimists. This concept ties into previous studies showing similarities in brain activation among socially central individuals versus more idiosyncratic traits in lonelier individuals.
- Cultural Impact & Traits Overlap: Researchers hypothesize cultural values influence optimism; overlapping constructs like loneliness and social network centrality require further exploration to avoid biases.
!Image Description: Graphic showing emojis depicting optimistic brain activation patterns
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research highlights the neurobiological underpinnings of optimism and its implications for social dynamics-a topic particularly relevant for India’s diverse societal framework where community-building plays a vital role across cultures. The findings emphasize how certain “positive” traits like optimism contribute toward stronger connections within one’s social networks, an essential aspect for India’s collectivist ethos.
However, caution regarding cultural bias underscores the need to contextualize such “universal” principles when applied broadly across societies differing vastly from Japan or Western paradigms studied here-like India’s emphasis on pragmatic resilience over personal idealism due to its socio-economic diversity.
In practical terms, identifying shared mental models within communities could offer insights into mechanisms that improve collaboration and inclusivity among Indians amidst growing urbanization pressures while promoting tolerance for individual differences-a lesson from understanding what makes pessimistic outlooks unique yet adaptable.