Now Reading: Pulichintala Project Discharge Adds to Andhra Pradesh Flood Concerns
-
01
Pulichintala Project Discharge Adds to Andhra Pradesh Flood Concerns
Pulichintala Project Discharge Adds to Andhra Pradesh Flood Concerns

Quick Summary:
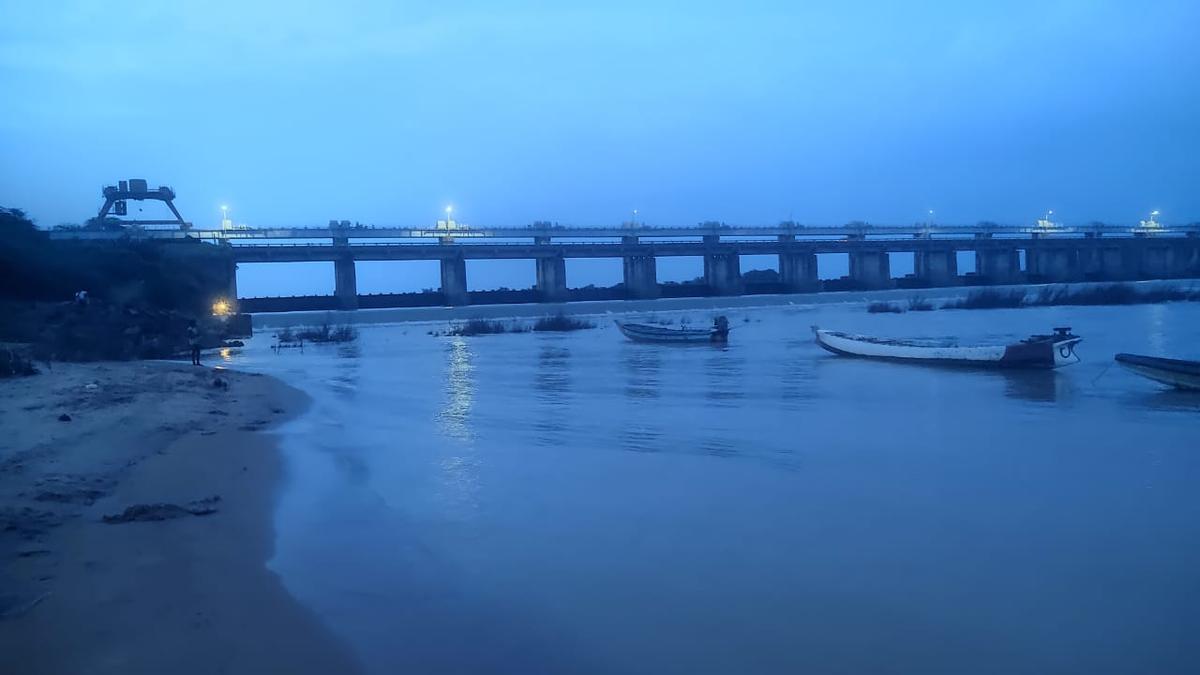
- Pulichintala Project: Received inflows of 2,51,259 cusecs on July 31, 2025; the entire inflow is being released downstream. Water level: 52.13 meters (171.03 feet), slightly below Full Reservoir Level (FRL) of 53.34 meters.
- Krishna River low-Lying Areas Alert: High alert declared in five districts-Guntur, Palnadu, Bapatla, NTR, and krishna-due too rising floodwater levels.
- Nagarjuna Sagar Dam: Water level stands at 585.40 ft out of a full capacity of 590 ft (96% full). Inflows are at 256453 cusecs; Outflows at 296522 cusecs.
- Yeleru reservoir: Current water level is at 253.54 ft with storage capacity utilization of about 43%. Inflows: 1734 cusecs; Outflows:1500 cusecs.
- Dowlaiswaram barrage on Godavari River: Nearly full (98%), current water level is at approximately 42.67 ft amidst flooding concerns. Floodwater exceeding six lakh cusecs directed toward Godavari delta from Polavaram project downstream areas.
- Prakasam Barrage Flood Management: sustained flood conditions with inflows reaching over two lakh cusecs prompting the opening of seventy gates for safe discharge to Bay of Bengal and irrigation canals.
For more updates: Read more
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The ongoing floods in Andhra Pradesh highlight several critical issues tied to climate resilience and infrastructure management in India’s riverine systems. Coordinated water discharge mechanisms across key barrages like Pulichintala and prakasam Barrage demonstrate efforts to mitigate risks while ensuring safety during peak inflow periods.
Though, the high reservoir levels across major dams such as Nagarjuna Sagar underscore vulnerability during monsoon surges due to upstream rainfall intensity-a pattern that may require enhanced predictive monitoring technologies moving forward.
The alerts issued for low-set districts adjacent to rivers indicate proactive disaster management responses by state authorities but also expose recurring challenges in protecting vulnerable populations from seasonal floods that disrupt livelihoods annually.
This situation could prompt further investments into adaptive strategies like improved drainage systems around urban centers while bolstering agricultural resilience projects outside delta regions frequently impacted by such natural calamities.