Now Reading: Retired Coal Plants Could Be Repowered for Green Energy Transformation
-
01
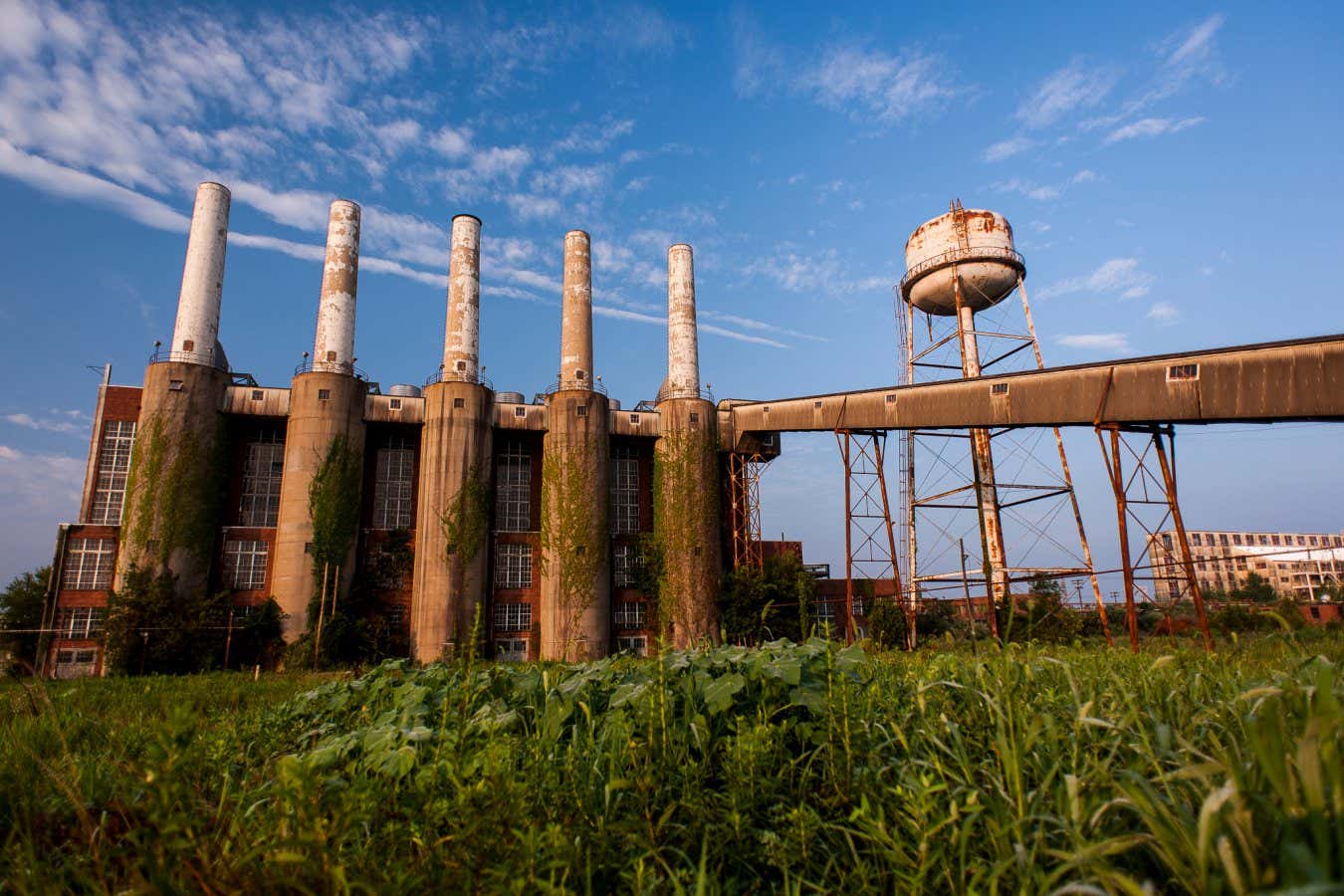
Retired Coal Plants Could Be Repowered for Green Energy Transformation
Retired Coal Plants Could Be Repowered for Green Energy Transformation

Quick summary
- Retired coal-fired power plants can perhaps provide backup or emergency electricity using renewable energy stored as heat in dirt rather of fossil fuels.
- Teh system involves heating large dirt piles using electricity during low-demand periods, storing the heat at about 600°C, and later transferring it through liquid-filled pipes to create steam that generates electricity via turbines.
- This method supplements intermittent wind and solar energy production while being cheaper than lithium batteries or hydrogen fuel for long-term storage.
- Challenges include reducing system costs related to piping and electrical connections.
- Natural materials like silicon dioxide and aluminium oxide found in dirt are resilient to high temperatures, making this approach feasible for implementation.
- Nearly 300 US coal plants retired from 2010-2019; additional closures are expected due to competition with renewables and natural gas.
- Repurposing these facilities could bring economic benefits such as local jobs and tax revenue.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This innovative plan for reviving retired coal power plants offers notable potential for IndiaS transition toward clean energy solutions. India’s grid heavily relies on thermal energy generation but faces challenges due to fluctuating renewable inputs like wind and solar. Introducing “heat battery” technology-which uses abundant materials like dirt-could address gaps in continuous power availability at a lower cost compared to conventional alternatives such as lithium-based storage.
Additionally, repurposing India’s aging coal infrastructure would help reduce environmental waste while sustaining local employment opportunities around those regions-a critical factor given how retiring traditional industries frequently enough disrupt associated communities. though, meticulous cost assessments regarding piping logistics and overall scalability are necessary before widespread adoption becomes viable.
India could observe this model closely as part of its broader clean-energy policy strategy while balancing sustainability goals against economic considerations.