Now Reading: Revolutionary Contact Lenses Enable Infrared Vision in the Dark
1
-
01
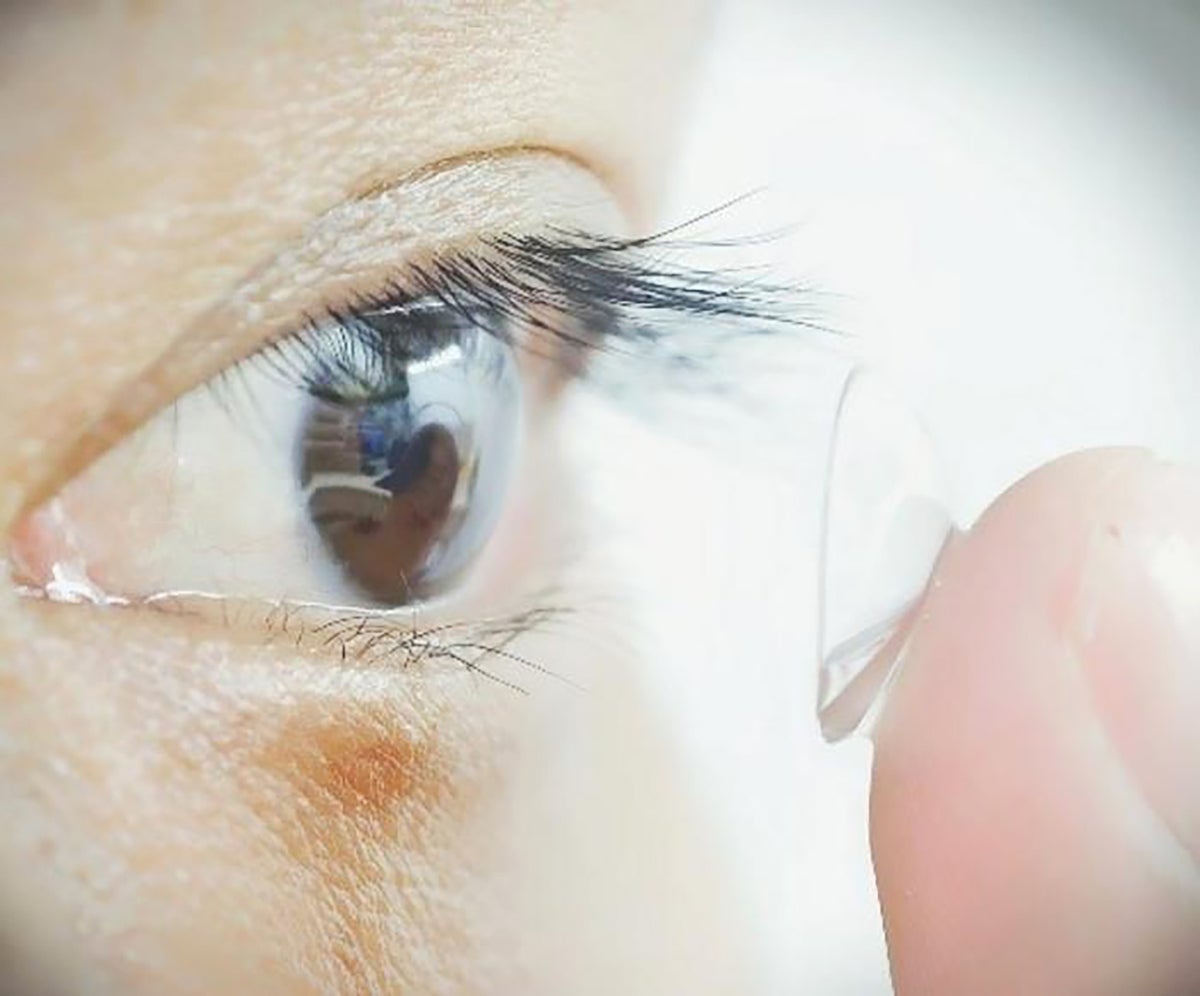
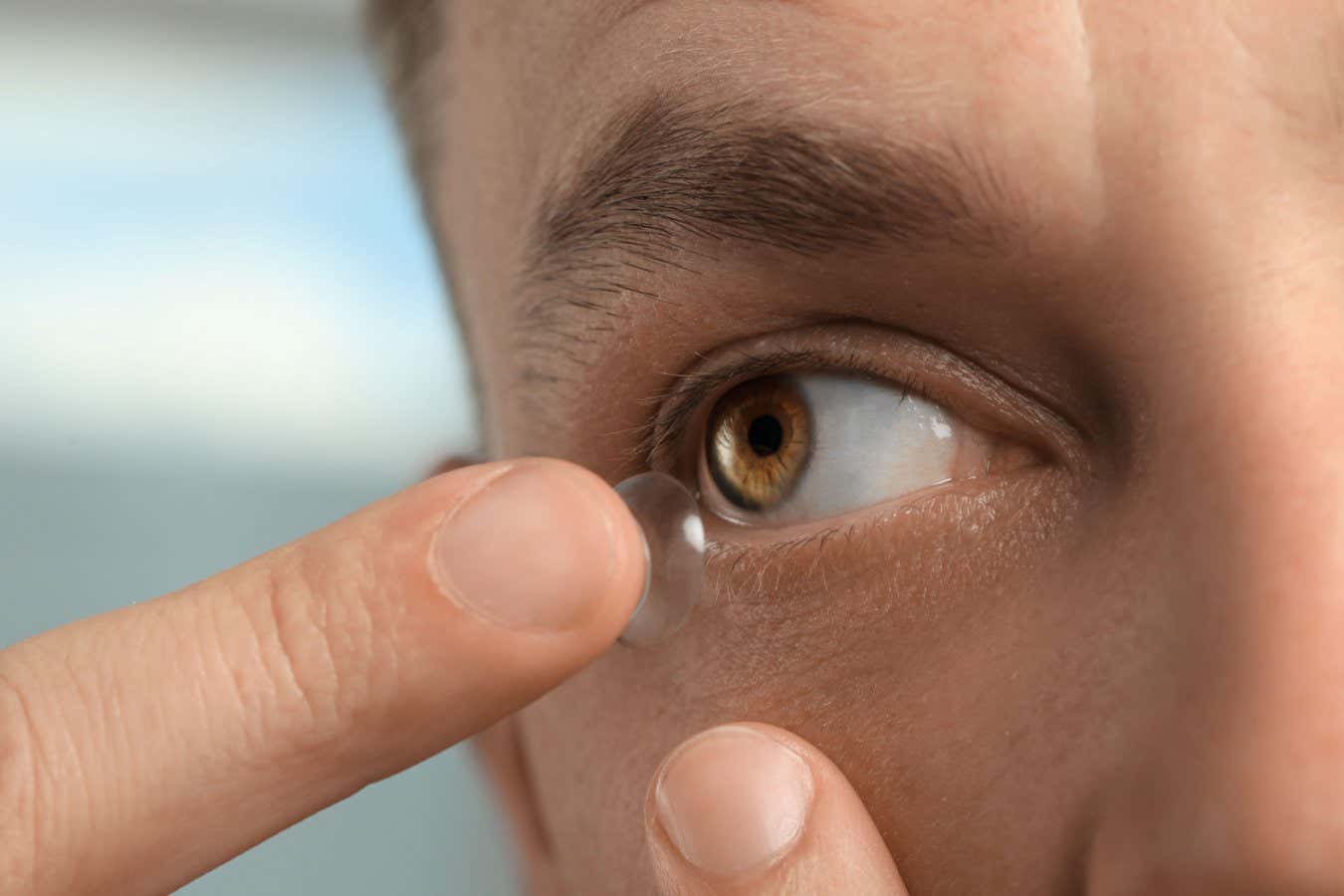
Revolutionary Contact Lenses Enable Infrared Vision in the Dark
Revolutionary Contact Lenses Enable Infrared Vision in the Dark

Quick Summary
- Technology Innovation: Researchers have developed nanoparticle-infused contact lenses that can convert infrared radiation into visible light, enabling potential night-vision capabilities without the need for bulky goggles or batteries.
- Materials Used: These lenses leverage nanoparticles such as sodium gadolinium fluoride, ytterbium, and erbium to absorb and transform infrared wavelengths (800 to 1600 nanometres) into visible colors like blue, green, and red.
- Potential Applications:
– Practical use in military operations for discreet night vision.- Experimental uses include encoding and transmitting data via flashes of light.
- Limitations: The lenses can only detect high-intensity LED infrared sources rather than ambient low-level infrared light; thus detailed vision in complete darkness is currently not possible.
- Health Concerns:
– Risks include heat exposure during light conversion and potential nanoparticle leakage into eye tissue.
– Previous studies involved injecting nanoparticles directly into mice’s eyes; wearable contact lenses are considered a safer alternative.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...