Now Reading: Robot Powers Up by Consuming Smaller Machines
-
01
Robot Powers Up by Consuming Smaller Machines
Robot Powers Up by Consuming Smaller Machines

Swift Summary:
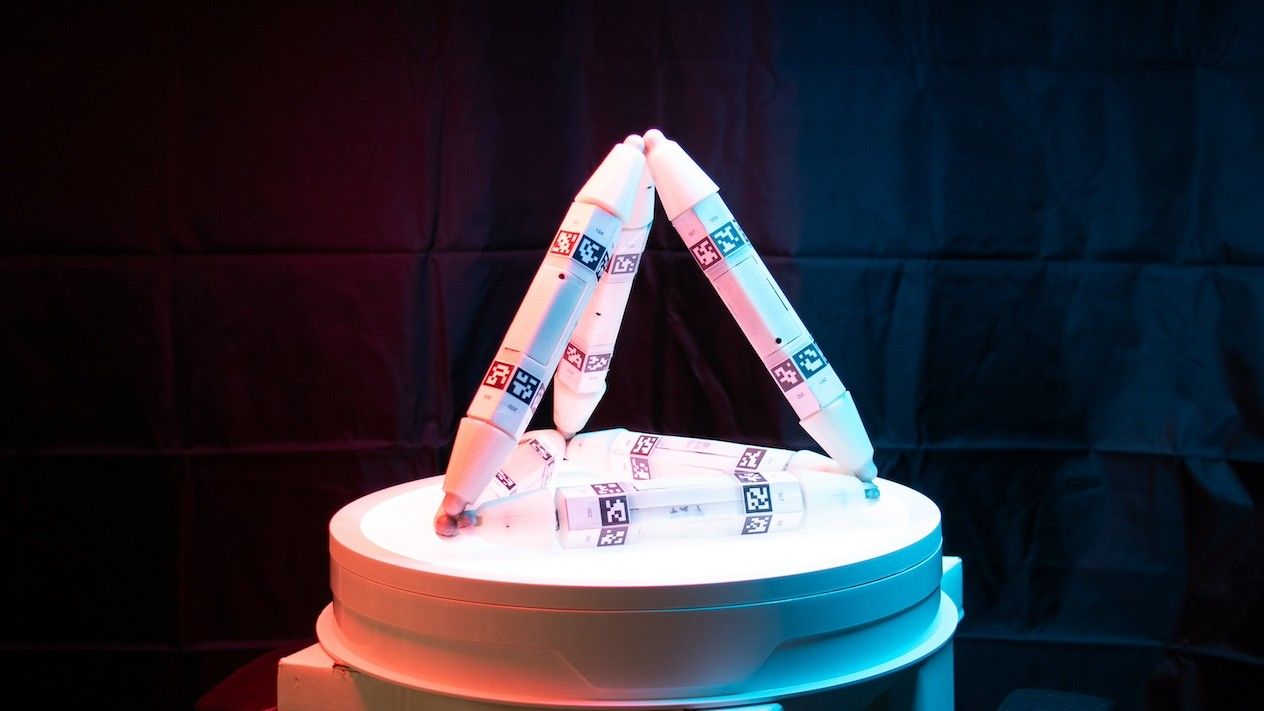
- Scientists have developed a prototype robot capable of growing, healing, and improving itself by consuming materials from its surroundings or even parts of other robots. this advancement is termed “robot metabolism.”
- The research was published in the journal Science Advances on July 16 and lead by Philippe Martin Wyder at Columbia University.
- The robots are made with six-sided “truss links” featuring magnetic connectors that enable modular assembly, repair, and adaptive growth.
- Two key rules exist for robot metabolism: complete self-growth either autonomously or assisted by similar machines, and reliance only on external energy/materials provided to truss links.
- In experiments, these modules assembled themselves into adaptive structures – evolving from 2D shapes into 3D tetrahedrons capable of traversing uneven terrain using additional links as walking aids.
- Co-lead author Hod Lipson highlighted the modularity-inspired design resembling biological systems that reuse components akin to amino acids in lifeforms.He emphasized the importance of robotic self-sustainability as human involvement diminishes over time.
- Potential applications include disaster recovery and space exploration; though, Lipson cautioned against imagining dystopian scenarios surrounding autonomous robots.
!Robots that Grow by Consuming Other Robots – YouTube
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This pioneering progress in robotics holds significant global implications for technology-led industries like disaster management and space exploration. For a country like India striving toward advancements in both areas (e.g., Chandrayaan missions), such innovations could inspire novel approaches to machine autonomy in extreme environments or inaccessible terrains.The concept of robot metabolism presents potential benefits where adaptive technologies can reduce dependence on human intervention while optimizing energy use.
however, ethical considerations become paramount when discussing cannibalizing machines – especially amid IndiaS ongoing discourse surrounding automation’s impact on employment. This technological leap encourages policymakers to deliberate how such systems can coexist harmoniously with societal progress without displacing jobs but instead advancing capabilities strategically. If harnessed responsibly with strict regulations ensuring safety protocols alongside international guidelines around AI ethics frameworks, India will stand well-positioned to integrate developments like these into its future technological landscape.