Now Reading: Robots Now Assisting in Operating Room Decisions
-
01
Robots Now Assisting in Operating Room Decisions
Robots Now Assisting in Operating Room Decisions
Quick Summary
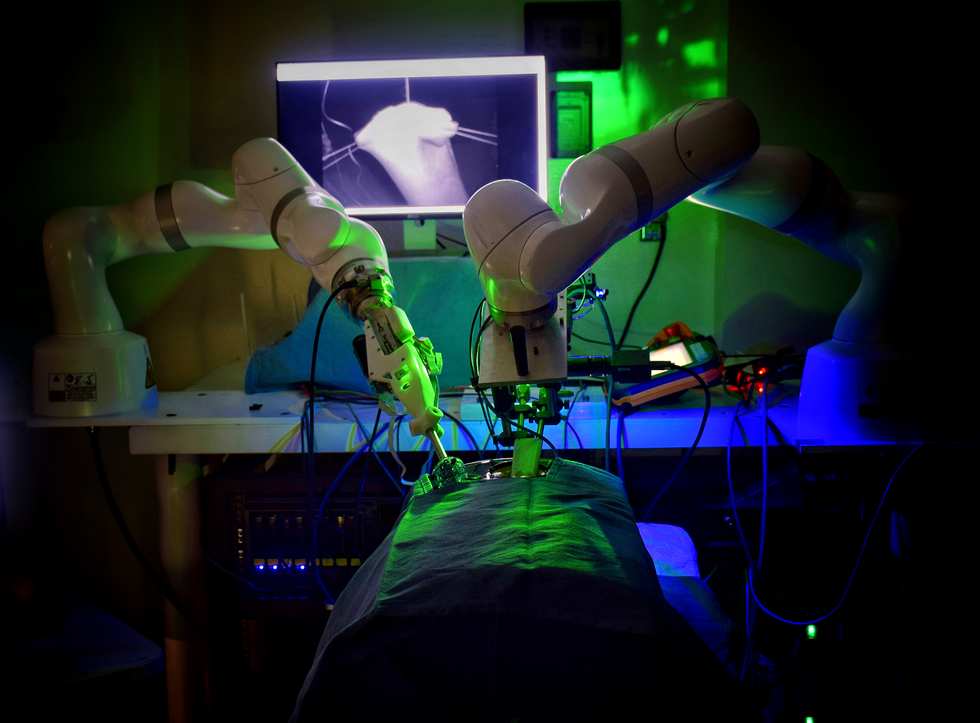
- The Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) autonomously performed laparoscopic surgery on a live animal in 2020, demonstrating advancements in robotic surgical technology.
- Robots like STAR seek to improve precision and patient outcomes by reducing complications such as leaks during gastrointestinal surgeries, where leaks occur in up to 20% of cases.
- Developed at Johns Hopkins University, STAR uses supervised autonomy allowing human surgeons to oversee its actions.
- Innovations include dual camera systems, machine learning for motion compensation, task automation strategies, and advanced needle handling techniques that enhance stitching precision and durability.
- While autonomous robots aren’t yet used widely for human surgeries due to technological complexity and regulatory challenges, autonomous systems are advancing rapidly with AI-driven real-time decision-making capabilities in surgical procedures.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Robotic-assisted surgery has gained traction globally with proven advantages in specific domains like prostate surgery. The progress of autonomous surgical robots such as STAR signals potential shifts toward greater automation within healthcare. For India-a country facing health infrastructure overburdening-the promise of precise automated systems could aid underserved areas with limited expert surgeons. However, notable hurdles include the cost of equipment (which may not be budget-pleasant for public hospitals), specialized training needs that demand high investment upfront alongside ethical considerations around liabilities.
Key implications revolve around addressing India’s looming shortage of medical professionals as innovation develops further. Partnerships between Indian research institutions and global bodies might facilitate affordability or adaptation. Patient safety protocols will need special focus if these technologies integrate into real-world applications locally. Implementation must weigh long-term social impacts while ensuring equitable access nonetheless of region or economic status.