Now Reading: Scientists Develop CO₂-Capturing Living Building Material
-
01
Scientists Develop CO₂-Capturing Living Building Material
Scientists Develop CO₂-Capturing Living Building Material

Rapid Summary
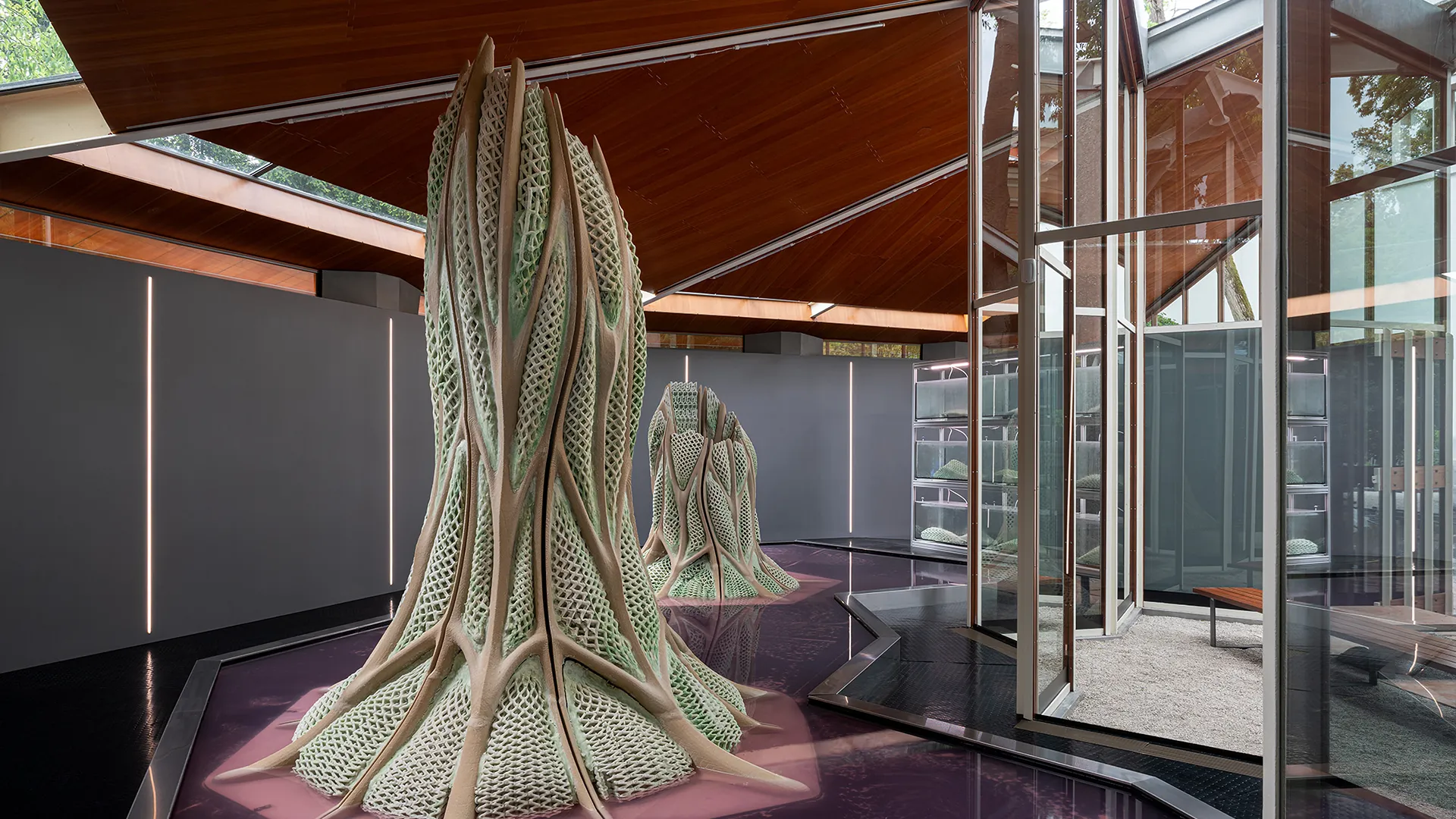
- ETH Zurich researchers developed a “photosynthetic living material” incorporating cyanobacteria into a printable hydrogel, presented in nature Communications.
- The material actively removes CO2 from air through organic biomass growth and mineralization,offering dual carbon sequestration abilities.
- Cyanobacteria efficiently perform photosynthesis even under weak light and enhance the material structurally by precipitating carbonates that bind CO2.
- Laboratory tests confirmed prolonged functionality, with the material binding 26 milligrams of CO2/gram over 400 days-significantly outperforming othre biological approaches.
- Optimized geometry using 3D printing improves light penetration and nutrient distribution for sustained bacterial productivity within hydrogel environments.
- Researchers envision applications such as coatings for building façades to continuously sequester atmospheric CO2.
- Architectural experiments in Venice (Canada Pavilion) and Milan demonstrate scalable uses where living materials were showcased as active infrastructural elements capable of binding up to 18 kg of CO2/year.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research on photosynthetic living materials spearheaded by ETH Zurich highlights promising strides toward addressing global climate challenges through novel interdisciplinary approaches. For India-a nation grappling with urban pollution and escalating construction demands-such innovations could hold transformative potential.The idea of using architectural-scale coatings or structures that actively bind atmospheric carbon aligns well with India’s focus on green infrastructure as part of its climate mitigation policies.
Furthermore, the use of minimal energy inputs like sunlight makes this technology feasible for application across diverse Indian climatic zones. Incorporating these sustainable building materials could not only mitigate emissions but also integrate aesthetics with ecological functionality-a concept notably relevant given india’s push for eco-smart cities.
However, scalability remains a notable challenge ahead; collaborations between scientific research organizations like ETH Zurich and Indian academia or industries may be crucial in refining this technology’s compatibility with local resources. As urbanization continues at a rapid pace in India, forward-looking experiments akin to those exhibited in Venice or Milan could inspire pivotal changes in designing future cities capable of combatting environmental change effectively.