Now Reading: Scientists Use Sunlight to Extract Water and Oxygen from Moon Dust: Is Lunar Application Feasible?
-
01
Scientists Use Sunlight to Extract Water and Oxygen from Moon Dust: Is Lunar Application Feasible?
Scientists Use Sunlight to Extract Water and Oxygen from Moon Dust: Is Lunar Application Feasible?

Quick Summary:
- Scientists from China developed a one-step method to extract oxygen and methane from lunar soil. This could provide breathing air and rocket fuel for moon settlers.
- Lunar regolith is used as a catalyst to release water when heated to 200°C; combining extracted water wiht astronauts’ exhaled CO2 produces methane.
- Transporting supplies like water from Earth to the moon is costly ($83,000 per gallon),but the moon’s shadowed craters contain trapped minerals with water.
- The technique reduces infrastructure complexity compared to previous methods that required transporting additional catalysts from Earth.
- Challenges persist, including thermal insulation of lunar soil, difficulty in uniformly heating it, and insufficient CO2 production by astronauts for large-scale operations.
- Experts suggest further refinement of the technology before operational request on a moon base.
Images included:
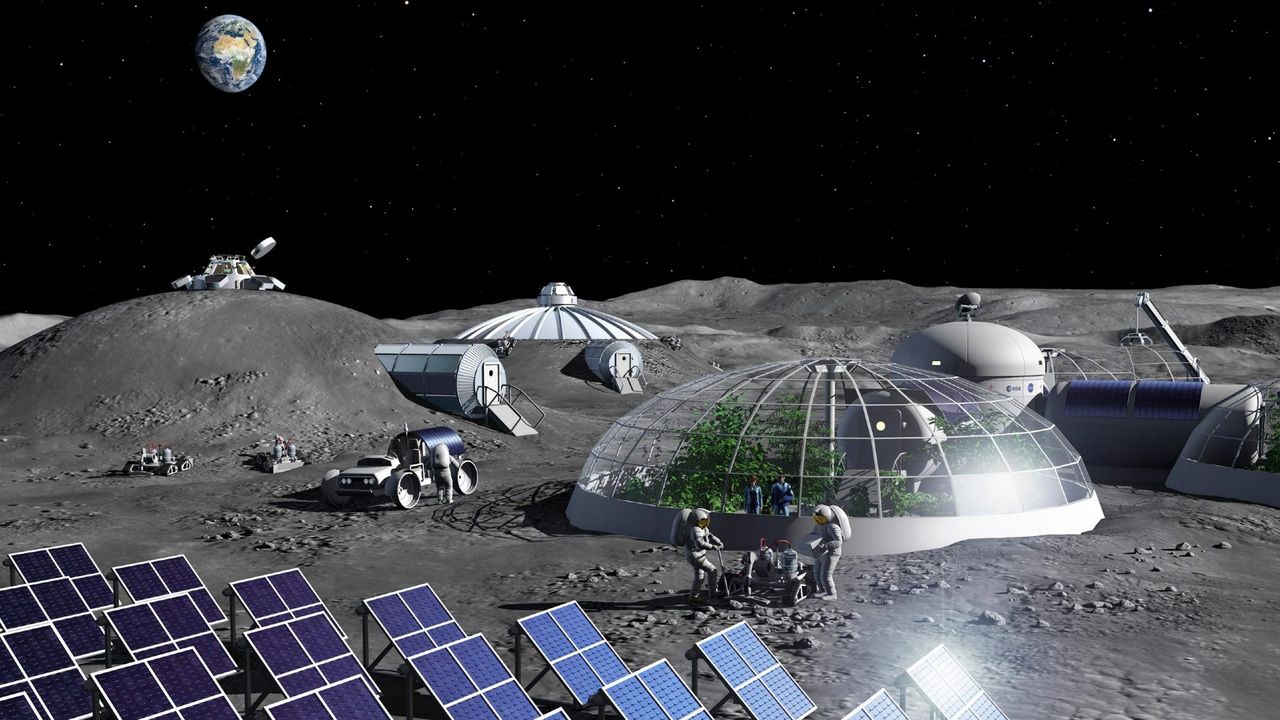
- Moon Base Artist impression: Astronauts walking alongside solar panels and habitats on the moon surface (Image credit: ESA – P. Carril).
- Lunar Soil in Photothermal Reactor: Chang’e 5 lunar soil sample used in experiments (Image credit: Sun et al.).
- Exhibited Lunar Soil Samples: Display of chang’e 5 collected samples at World Expo Exhibition Center (Image credit: VCG/VCG via Getty Images).
indian Opinion Analysis:
The development of this cost-efficient technique to extract essential resources like oxygen and methane from lunar regolith holds great promise for reducing dependency on Earth’s supplies during future space colonization missions or settlements on extraterrestrial bodies such as the Moon or Mars.
for India, which has been actively advancing its space exploration ambitions through missions like Chandrayaan, such innovations align well with enduring strategies for interplanetary exploration amid global competition for resource-efficient technologies. As countries aim towards long-term human presence beyond Earth, methods enabling self-reliant infrastructure can reduce costs while fostering collaborative opportunities in international space ventures.
However, this research highlights key technological uncertainties-such as scaling challenges in weak gravity environments or reliability under extreme lunar conditions-which demand patience before practical deployment during missions like NASA’s upcoming Artemis program or India’s own future aspirations toward building habitats in space.
India’s potential contribution lies both scientifically-exploring alternative catalysis techniques-and strategically-as nations consider partnerships leveraging ISRO’s proven record at cost-effective mission execution alongside its presence-building role across emerging markets globally equivalent technologies critical mix.xt