Now Reading: Sharpest Mars Images Unveil Mystery Rock and Ancient Terrain
-
01
Sharpest Mars Images Unveil Mystery Rock and Ancient Terrain
Sharpest Mars Images Unveil Mystery Rock and Ancient Terrain

Quick Summary
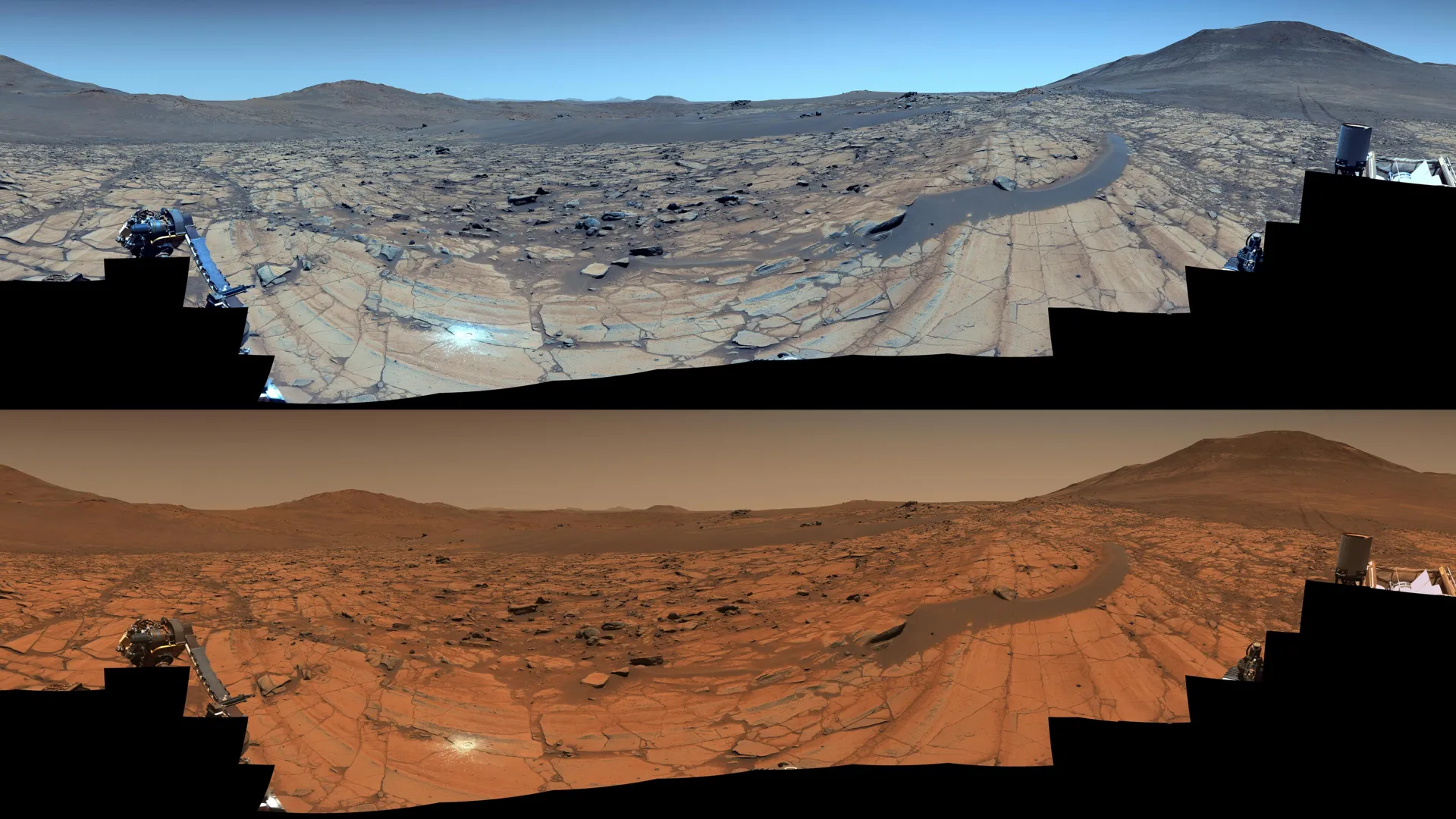
- NASA’s perseverance rover captured a high-resolution panorama of Mars on May 26, 2025, during its 1,516th Martian day (sol).
- Images were taken at “Falbreen,” showing diverse Martian terrain, including float rocks and sand ripples.
- A standout feature is a large “float rock” resting atop a sand ripple, believed too have been transported from another location.
- The shown boundary line separates two geological units: lighter-toned olivine-rich rocks near the rover and darker clay-bearing rocks farther away.
- Clear skies provided an excellent view of hills up to 40 miles (65 kilometers) away. enhanced-color and natural-color versions highlight different aspects of the terrain and sky.
- An abrasion patch created by Perseverance reveals subsurface characteristics for rock sampling. This is its 43rd abraded patch since landing in Jezero Crater in February 2021.
- The science team aims to study Falbreen for insight into perhaps older geological terrains than jezero Crater itself.
Indian Opinion Analysis
NASA’s efforts with the Perseverance rover underline how technological innovation can drive humanity’s exploration ambitions. The discoveries at “Falbreen,” especially the juxtaposition of younger olivine-rich rocks against older clay-bearing formations, serve as evidence that Mars hosts rich geological diversity awaiting further study. For India as an emerging space power with missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan, these milestones inspire deeper engagement with planetary sciences.
The clear takeaway here is how international collaboration or competition might advance such scientific endeavors-India has already demonstrated cost-effective interplanetary mission planning. Cooperation in advanced space research could enhance technological expertise while fostering shared goals such as material analysis technologies or even crewed explorations beyond Earth orbit.